Abstract
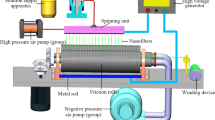
Electrospinning is a simple and cost-effective method to prepare fiber with nanometer scale. More importantly, 3D flexible nanofiber yarns that fabricated by electrospinning have shown excellent application prospects in smart textiles, wearable sensors, energy storage devices, tissue engineering, and so on. However, current methods for preparing electrospinning nanofiber yarns had some limitations, including low yarn yield and poor yarn structure. In this paper, a stepped airflow-assisted electrospinning method was designed to prepare continuously twisted nanofiber yarn through introducing stepped airflow into traditional electrospinning system. The stepped airflow could not only help to improve nanofiber yield, but also good for controlling the formed nanofibers to be deposited in a small area. In addition, the experimental methods of single factor variables were used to study the effects of stepped airflow pressure, applied voltage, spinning distance, solution flow rate, air pumping volume and friction roller speed on nanofiber yarn yield, nanofiber diameter, yarn twist and mechanical property. The results showed that prepared nanofiber yarns exhibited perfect morphologies and the yield of nanofiber yarn could reach to a maximum of 4.207 g/h. The breaking strength and elongation at break of the prepared yarn could reach to 23.52 MPa and 30.61 %, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Veleirnho, M. F. Rei, and J. A. Lopes-DA-Silva, J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 46, 460 (2008).
K. H. Lee, H. Y. Kim, Y. J. Ryu, K. W. Kim, and S. W. Choi, J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 41, 1256 (2003).
Y. Dong, F. Li, X. Zhao, B. Cheng, W. Kang, and G. Cui, J. Ind. Text., doi.org/10.1177/1528083717725115 (2017).
F. Ko, Y. Gogotsi, A. Ali, N. Naguib, H. Ye, G. L. Yang, C. Li, and P. Willis, Adv. Mater., 15, 1161 (2003).
A. F. Lotus, E. T. Bender, E. A. Evans, R. D. Ramsier, D. H. Reneker, and G. G. Chase, J. Appl. Phys., 103, 024910 (2008).
X. P. Zhuang, K. F. Jia, B. W. Cheng, X. Feng, S. J. Shi, and B. Zhang, Chem. Eng. J., 237, 308 (2014).
Y. M. Zhou, J. X. He, H. B. Wang, N. Nan, K. Qi, and S. Z. Cui, e-Polymers, 17, 249 (2017).
T. Yan, Z. Wang, Y. Q. Wang, and Z. J. Pan, Mater. Des., 143, 214 (2018).
M. Tebyetekerwa, Z. Xu, W. L. Li, X. P. Wang, I. Marriam, S. J. Peng, S. Ramkrishna, S. Y. Yang, and M. F. Zhu, ACS Appl. Energy. Mater., 1, 377 (2018).
Y. B. Wu, L. Wang, B. L. Guo, and P. X. Ma, ACS Nano, 11, 5646 (2017).
Y. M. Zhou, J. X. He, H. B. Wang, K. Qi, N. Nan, X. L. You, W. L. Shao, L. D. Wang, B. Ding, and S. Z. Cui, Sci. Rep., 7, 12949 (2017).
E. Smit, U. Buttner, and R. D. Sanderson, Polymer, 46, 2419 (2005).
J. X. He, Y. M. Zhou, K. Qi, L. D. Wang, P. P. Li, and S. Z. Cui, Fiber. Polym., 14, 1857 (2013).
N. Li, Q. Hui, H. Xue, and J. Xiong, Mater. Lett., 79, 245 (2012).
J. X. He, K. Qi, L. D. Wang, Y. M. Zhou, R. T. Liu, and S. Z. Cui, Fiber. Polym., 16, 1319 (2015).
F. Dabirian and S. A. Hosseini, Fibers Text. East. Eur., 17, 74 (2009).
W. E. Teo, R. Gopal, R. Ramaseshan, K. Fujihara, and S. Ramakrishna, Polymer, 48, 3400 (2007).
U. Ali, Y. Zhou, X. Wang, and T. Lin, J. Text. I., 103, 80 (2012).
L. Tian, T. Yan, and Z. J. Pan, J. Mater. Sci., 50, 7137 (2015).
M. N. Shuakat and T. Lin, Rsc Adv., 5, 33930 (2015).
F. Zuo, D. H. Tan, Z. F. Wang, S. Jeung, C. W. Macosko, and F. S. Bates, ACS Macro. Lett., 2, 301 (2013).
N. Hiremath and G. Bhat, Nanosci. Technol., 2, 1 (2015).
X. L. Ma, L. Y. Zhang, J. Tan, Y. X. Qin, H. B. Chen, W. L. He, W. M. Yang, and H. Y. Li, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 134, 44820 (2017).
J. X. He, L. D. Wang, R. T. Liu, M. J. Zhang, W. L. Tan, and Y. C. Wu, Fiber. Polym., 15, 2283 (2014).
J. X. He, Y. P. Lian, X. L. Zhang, Y. C. Wu, and R. T. Liu, J. Polym. Sci. Part B: Polym. Phys., 52, 993 (2014).
P. R. Lord, C. W. Joo, and T. Ashizaki, J. Text. I., 78, 234 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Wang, H., He, J. et al. Investigation of Parameters for Preparing Nanofiber Yarn via a Stepped Airflow-assisted Electrospinning. Fibers Polym 19, 2169–2177 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-8387-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-8387-5