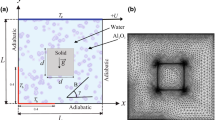
Abstract
In this paper, steady thermocapillary-buoyancy convection of a volatile liquid layer in the case of a two-dimensional enclosed cavity subjected to horizontal temperature gradient is numerically investigated by using the finite difference method. A two-phase model with convective diffusion of vapor in consideration is fully developed. Kinetic theory of gases and vapor-diffusion-limited phase change are used to describe mass flux on the liquid-gas interface, and the latter is validated to play a dominating role in phase change. Numerical results reveal that transition from unicellular flow to multicellular flow in liquid layer is due to the increasing thermocapillary effect, while increasing buoyancy effect has a major impact on gas flow, which can separate the convection in gas phase into a two-layer flow. Evaporation and condensation occur at the interface and the mass flux distribution is bound up with the convective patterns in liquid layer. For a large imposed temperature gradient, the interfacial mass flux fluctuates in the core region with its amplitudes gradually amplifying from the cold to hot side. Thermal boundary effect on temperature and mass flux distribution close to the end walls is discussed. We also simulate a corresponding model ignoring phase change and vapor transport, and find the phase change tends to stabilize the thermocapillary-buoyancy flows due to the reduction of interfacial temperature gradient caused by the latent heat absorbed and released along the interface.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, Y., Iwaski, A., Tanaka, K.: Thermal management with self-rewetting fluids. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 16, 148–152 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02945966
Bekezhanova, V.B., Goncharova, O.N.: Thermocapillary convection with phase transition in the 3D channel in a weak gravity field. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31, 1–20 (2019)
Bénard, H.: Les tourbillions cellulaires dans une nappe liquide. Rev. Gen. Sci. Pures Appl. 11, 1261–1271 (1900)
Brutin, D., Zhu, Z.Q., Rahli, O., et al.: Evaporation of ethanol drops on a heated substrate under microgravity conditions. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 22(3), 387–395 (2010)
Burelbach, J.P., Bankoff, S.G., Davis, S.H.: Nonlinear stability of evaporating/condensing liquid films. J. Fluid Mech. 195, 463–494 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112088002484
Burguete, J., Mukolobwiez, N., Daviaud, F., Garnier, N., Chiffaudel, A.: Buoyant-thermocapillary instabilities in extended liquid layers subjected to a horizontal temperature gradient. Phys. Fluids. 13, 2773–2787 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1398536
Cecere, A., Di Martino, G.D., Mungiguerra, S.: Experimental investigation of capillary-driven two-phase flow in water/Butanol under reduced gravity conditions. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31(4), 425–434 (2019)
Chai, A.T., Zhang, N.: Experimental study of Marangoni-Bénard convection in a liquid layer induced by evaporation. Exp. Heat Transf. 11, 187–205 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1080/08916159808946561
Chan, C.L., Chen, C.F.: Effect of gravity on the stability of thermocapillary convection in a horizontal fluid layer. J. Fluid Mech. 647, 91–103 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112009994046
Chen, P.C., Lin, W.K.: The application of capillary pumped loop for cooling of electronic components. Appl. Therm. Eng. 21, 1739–1754 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-4311(01)00045-X
Chen, X., Zhu, Z.Q., Liu, Q.S., et al.: Thermodynamic behaviors of macroscopic liquid droplets evaporation from heated substrates. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 27(5), 353–360 (2015)
Chen, X., Wang, X., Chen, P.G., et al.: Thermal effects of substrate on Marangoni flow in droplet evaporation: response surface and sensitivity analysis. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 113, 354–365 (2017)
Chen, X., Wang, X., Chen, P.G., et al.: Determination of diffusion coefficient in droplet evaporation experiment using response surface method. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30(5), 675–682 (2018)
Derby, J.J.: Fluid dynamics in crystal growth: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 62, 286–301 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2016.04.015
Haut, B., Colinet, P.: Surface-tension-driven instabilities of a pure liquid layer evaporating into an inert gas. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 285, 296–305 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2004.07.041
Ji, Y., Liu, Q.S., Liu, R.: Coupling of evaporation and thermocapillary convection in a liquid layer with mass and heat exchanging interface. Chin. Phys. Lett. 25, 608–611 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/25/2/069
Li, Y., Grigoriev, R., Yoda, M.: Experimental study of the effect of noncondensables on buoyancy-thermocapillary convection in a volatile low-viscosity silicone oil. Phys. Fluids. 26, 122112 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4904870
Liu, R., Liu, Q.S.: Linear stability analysis of convection in two-layer system with an evaporating vapor-liquid interface. Acta Mech. Sinica. 22, 109–119 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-006-0106-6
Liu, Q.S., Chen, G., Roux, B.: Thermogravitational and thermocapillary convection in a cavity containing two superposed immiscible liquid layers. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 36, 101–117 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0017-9310(93)80070-B
Liu, M., Ren, Y.X., Zhang, H.: A class of fully second order accurate projection methods for solving the incompressible Navier-stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 200, 325–346 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcp.2004.04.006
Liu, R., Liu, Q.S., Hu, W.R.: Marangoni–Bénard instability with the exchange of evaporation at liquid-vapour interface. Chin. Phys. Lett. 22, 402–404 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/22/2/037
Margerit, J., Dondlinger, M., Dauby, P.C.: Improved 1.5-sided model for the weakly nonlinear study of Bénard–Marangoni instabilities in an evaporating liquid layer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 290, 220–230 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2005.04.031
Mo, D.M., Ruan, D.F.: Linear-stability analysis of Thermocapillary-buoyancy convection in an annular two-layer system with upper rigid wall subjected to a radial temperature gradient. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31(3), 293–304 (2019)
Nield, D.A.: Surface tension and buoyancy effects in cellular convection. J. Fluid Mech. 19, 341–352 (1964). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112064000763
Palmer, H.J.: The hydrodynamic stability of rapidly evaporating liquids at reduced pressure. J. Fluid Mech. 75, 487–511 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112076000347
Pearson, J.R.A.: On convection cells induced by surface tension. J. Fluid Mech. 4, 489–500 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112058000616
Peltier, L.J., Biringen, S.: Time-dependent thermocapillary convection in a rectangular cavity: numerical results for a moderate Prandtl number fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 257, 339–357 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112093003106
Qin, T., Tuković, Ž., Grigoriev, R.O.: Buoyancy-thermocapillary convection of volatile fluids under atmospheric conditions. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 75C, 284–301 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.03.027
Riley, R.J., Neitzel, G.P.: Instability of thermocapillary-buoyancy convection in shallow layers. Part 1. Characterization of steady and oscillatory instabilities. J. Fluid Mech. 359, 143–164 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112097008343
Sáenz, P.J., Valluri, P., Sefiane, K., Karapetsas, G., Matar, O.K.: Linear and nonlinear stability of hydrothermal waves in planar liquid layers driven by thermocapillarity. Phys. Fluids. 25, 094101 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4819884
Sáenz, P.J., Valluri, P., Sefiane, K., Karapetsas, G., Matar, O.K.: On phase change in Marangoni-driven flows and its effects on the hydrothermal-wave instabilities. Phys. Fluids. 26, 024114 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4866770
Schmidt, G.R., Chung, T.J., Nadarajah, A.: Thermocapillary flow with evaporation and condensation at low gravity. Part 1. Non-deforming surface. J. Fluid Mech. 294, 323–347 (1995)
Schrage, R.W.: A theoretical study of interface mass transfer. Columbia University Press, New York (1953)
Shevtsova, V.M., Nepomnyashchy, A.A., Legros, J.C.: Thermocapillary-buoyancy convection in a shallow cavity heated from the side. Phys. Rev. E. 67, 066308 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.67.066308
Simanovskii, I., Viviani, A., Dubois, F., et al.: Nonlinear convective flows in a laterally heated two-layer system with a temperature-dependent heat release/consumption at the interface. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 30(3), 243–256 (2018)
Smith, M.K., Davis, S.H.: Instabilities of dynamic thermocapillary liquid layers. Part 1. Convective instabilities. J. Fluid Mech. 132, 119–144 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112083001512
Swarztrauber, P.N.: The methods of cyclic reduction, Fourier analysis and the FACR algorithm for the discrete solution of Poisson’s equation on a rectangle. SIAM Rev. 19, 490–501 (1977)
Villers, D., Platten, J.K.: Coupled buoyancy and Marangoni convection in acetone experiments and comparison with numerical simulations. J. Fluid Mech. 234, 487–510 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112092000880
Wang, X., Liu, Q., Zhu, Z., et al.: Experiments of transient condensation heat transfer on the heat flux senor. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 27(5), 369–376 (2015)
Zhang, L., Li, Y.R.: Three-dimensional numerical simulation on Thermocapillary convection of moderate Prandtl number fluid in an annular shallow Pool with surface heat dissipation. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 1–15 (2019), 31(6):733–747. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-9704-3
Zhang, L., Li, Y.R., Wu, C.M.: Effect of surface evaporation on steady thermocapillary convection in an annular pool. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 499–509 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-016-9510-0
Zhang, Y., Li, Y.R., Yu, J.J., et al.: Three-dimensional numerical simulation on Marangoni convection in a sessile water droplet evaporating in its vapor at low pressure. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 31(2), 231–240 (2019)
Zhu, Z.Q., Liu, Q.S.: Coupling of thermocapillary convection and evaporation effect in a liquid layer when the evaporating interface is open to air. Chin. Sci. Bull. 55, 233–238 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-009-0693-2
Zhu, Z.Q., Brutin, D., Liu, Q.S., et al.: Experimental investigation of pendant and sessile drops in microgravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 22(3), 339–345 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants Nos.11532015, U1738119), the China’s Manned Space Program (TZ-1) and the Joint Project of CMSA-ESA Cooperation on Utilization in Space.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, G., Liu, Q., Qin, J. et al. Numerical Study of Thermocapillary-Buoyancy Convection of Volatile Liquid Layer in an Enclosed Cavity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 32, 305–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09763-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12217-019-09763-1