Abstract
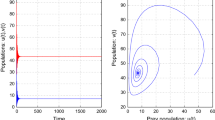
The dynamics of prey–predator system, when one or both the species are harvested non-linearly, has become a topic of intense study because of its wide applications in biological control and species conservation. In this paper we have discuss different bifurcation analysis of a two dimensional prey–predator model with Beddington–DeAngelis type functional response in the presence of prey refuge and non-linear harvesting of both species. We have studied the positivity and boundedness of the model system. All the biologically feasible equilibrium points are investigated and their local stability is analyzed in terms of model parameters. The global stability of coexistence equilibrium point has been discussed. Depending on the prey harvesting effort (\(E_1\)) and degree of competition among the boats, fishermen and other technology (\(l_1\)) used for prey harvesting, the number of axial and interior equilibrium points may change. The system experiences different type of co-dimension one bifurcations such as transcritical, Hopf, saddle-node bifurcation and co-dimension two Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation. The parameter values at the Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation point are highly sensitive in the sense that the nature of coexistence equilibrium point changes dramatically in the neighbourhood of this point. The feasible region of the bifurcation diagram in the \(l_1-E_1\) parametric plane divides into nine distinct sub-regions depending on the number and nature of equilibrium points. We carried out some numerical simulations using the Maple and MATLAB software to justify our theoretical findings and finally some conclusions are given.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malthus, T.R.: An Essay on the Principle of Population (1978)
Verhulst, P.H.: Notice sur la loi que la population poursuit dans son accroissement. Carrespondance mathematique et physique, vol. 10, pp. 113–121 (1838)
Lotka, A.J.: Elements of Physical Biology. Williams and wilkins, Baltimore (1925)
Volterra, V.: Variations and fluctuations of a number of individuals in animal species living together [translation by Chapman R.N., 1931], Animal Ecology, pp. 409-448. Mcgraw Hill (1926)
Chen, B.: The influence of commensalism on a Lotka-Volterra commensal symbiosis model with Michaelis-Menten type harvesting. Adv. Differ. Equ. 43 (2019)
Gupta, R.P., Chandra, P., Banerjee, M.: Dynamical complexity of a prey-predator model with non-linear predator harvesting. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. 20, 423–443 (2015)
Sen, M., Srinivasu, P.D.N., Banerjee, M.: Global dynamics of an additional food provided predator-prey system with constant harvest in predators. Appl. Math. Comput. 250, 193–211 (2015)
Aguirre, P., González-Olivares, E., Sáez, E.: Two limit cycles in a Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with additive Allee effect. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 10, 1401–1416 (2009)
Kar, T.K., Das, U., Jana, S.: Dynamical behavior of delayed stage structured predator prey model with non monotonic functional response. Int. J. Dyn. Control (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-014-0110-9
Roy, B., Roy, S.K.: Analysis of prey-predator three species models with vertebral and invertebral predators. Int. J. Dyn. Control 3, 306–312 (2015)
Pal, D., Mahapatra, G.S., Samanta, G.P.: Bifurcation analysis of predator-prey model with time delay and harvesting efforts using interval parameter. Int. J. Dyn. Control (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40435-014-0083-8
Sen, M., Banerjee, M., Morozov, A.: Bifurcation analysis ratio-dependent prey-predator model with the Allee effect. Ecol. Complex. 11, 12–27 (2012)
Molla, H., Rahman, M.S., Sarwardi, S.: Dynamical study of a prey-predator model incorporating nonlinear prey refuge and additive Allee effect acting on prey species. Model Earth Syst. Environ. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-020-01049-5
Holling, C.S.: The functional response of prey-predator to prey density and its role mimicry and population regulation. Mem. Entomol. Soc. Can. 45, 3–60 (1965)
Holling, C.S.: The components of predation as revealed by a study of small-mammal predation of the European pine sawfly. Can. Entomol. 91, 293–320 (1959)
Holling, C.S.: Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol. 91, 385–398 (1959)
Ardity, R., Ginzburg, L.R.: Coupling in predator-prey dynamics : ratio dependence. J. Theor. Biol. 139, 311–326 (1989)
Beddington, J.R.: Mutual interference between parasites or predators and its effect on searching efficiency. J. Anim. Ecol. 44, 331–340 (1975)
DeAngelis, D.L., Goldstein, R.A., ONeill, R.V.: A model for trophic interactions. Ecology 56, 881–892 (1975)
Cantrell, R.S., Cosner, C.: On the dynamics of predator-prey models with the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 257, 206–222 (2001)
Pal, P.J., Mandal, P.K.: Bifurcation analysis of a modified Leslie-Gower predator-preymodel with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and strong Allee effect. Math. Comput. Simul. 97, 123–146 (2014)
Meng, X., Huo, H., Zhang, X.: The effect of harvesting and delay on predator-prey system with beddington-DeAngelis fubctional response. Int. J. Biomath. 5, 23 (2012)
Hwang, T.W.: Global analysis of the predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 281, 395–401 (2003)
Damian, Y.V., Vidal, C., Olivares, E.G.: Dynamics and bifurcations of a modified Leslie-Gower-type model considering a Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 42(9), 3179–3210 (2019)
Khellaf, W., Hamri, N.: Boundedness and Global Stability for a predator-prey System with the Beddington-DeAngelis functional response. Differ. Equ. Nonlinear Mech. 24 (2010)
Lata, K., Misra, A.K., Upadhyay, R.K.: A mathematical model for the conservation of forestry resources with two discrete time delays. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 3, 1011–1027 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-017-0349-1
Tripathi, J.P., Abbas, S., Thakur, M.: Dynamical analysis of a prey predator model with Beddington-DeAngelis type functional response incorporating a prey refuge. Nonlinear Dyn. 80, 177–196 (2015)
Xin, Y., Meng, Y., Qian, W.: Bifurcation analysis in a singular Beddington-DeAngelis predator-prey model with two delays and non-linear predator harvesting. Math. Biosci. Eng. 16(4), 2668–2696 (2019)
Lv, Y., Zhang, Z., Yuan, R., Pei, Y.: Effect of harvesting and prey refuge in a prey-predator system. J. Biol. Syst. 22, 133–150 (2014)
Gan, S.Y., Azman, B.A.R., Yoshida, T., Majid, A.M., Toda, T., Takahashi, K., Othman, B.H.R.: Comparison of day and night mysid assembages traps, with key to species occurring at Pulau Tinggi. Coast. Mar. Sci. Malays. 34(1), 74–81 (2010)
Bullard, S.G., Hay, M.E.: Plankton tethering to assess spatial patterns of predation risk over a coral reef and seagrass bed. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 225, 17–28 (2002)
Ma, Z., Li, W., Zhao, Y., Wang, W., Zhang, H., Li, Z.: Effects of prey refuges on a predator-prey model with a class of functional responses: the role of refuges. Math. Biosci. 218(2), 73–79 (2009)
McNair, J.M.: The effects of refuges on predator-prey interactions: a reconsideration. Theor. Popul. Biol. 29, 38 (1986)
Sih, A.: Prey refuges and predator-prey stability. Theor. Popul. Biol. 31, 1 (1987)
Chakraborty, K., Chakraborty, M., Kar, T.K.: Regulation of a prey-predator fishery incorporating prey refuge by taxation: a dynamic reaction model. J. Biol. Syst. 19(03), 417–445 (2011)
Xiao, D., Jennings, L.S.: Bifurcations of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system with constant rate harvesting. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 65(3), 737–753 (2005)
Chen, J., Huang, J., Ruan, S., Wang, J.: Bifurcations of invariant tori in predator-prey models with seasonal prey harvesting. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 73(5), 1876–1905 (2013)
May, R.M., Beddington, J.R., Clark, C.W., Holt, S.J., Laws, R.M.: Management of multispecies fisheries. Science 205(4403), 267–277 (1979)
Huang, J., Gong, Y., Ruan, S.: Bifurcation analysis in a predator-prey model with constant-yield predator harvesting. Discret. Contin. Dyn. Syst. Ser. B 18, 2101–2121 (2013)
Huang, J., Gong, Y., Chen, J.: Multiple bifurcations in a predator-prey system of Holling and Leslie type with constant-yield prey harvesting. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 23(10), 1350164 (2013)
Clark, C.W.: Aggregation and fishery dynamics: a theoretical study of schooling and the purse seine tuna fisheries. Fish. Bull. 77(2), 317–337 (1979)
Agnew, T.T.: Optimal exploitation of a fishery employing non-linear harvestingfunction. Ecol. Model. 6, 47–57 (1979)
Kong, L., Zhu, C.: Bogdanov-Takens bifurcations of codimensions 2 and 3 in a Leslie-Gower predator-prey model with Michaelis-Menten-type prey harvesting. Math. Methods Appl Sci. 40(18), 6715–6731 (2017)
Hu, D., Cao, H.: Stability and bifurcation analysis in a predator-prey system with Michaelis-Menten type predator harvesting. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 33, 58–82 (2017)
Debnath, S., Majumdar, P., Sarkar, S., Ghosh, U.: Global dynamics of a prey-predator model with Holling type iii functional response in the presence of harvesting. J. Biol. Syst. 30(01), 225–260 (2022)
Majumdar, P., Debnath, S., Mondal, B., Sarkar, S., Ghosh, U.: Complex dynamics of a prey-predator interaction model with Holling type-II functional response incorporating the effect of fear on prey and non-linear predator harvesting. Rend. Circ. Mat. Palermo Ser. 2, 1–32 (2022)
Santra, P., Mahapatra, G.S., Pal, D.: Prey-predator nonlinear harvesting model with functional response incorporating prey refuge. Int. J. Dyn. Control 4(3), 293–302 (2015)
Debnath, S., Ghosh, U., Sarkar, S.: Global dynamics of a tritrophic food chain model subject to the Allee effects in the prey population with sexually reproductive generalized-type top predator. Comput. Math. Methods (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/cmm4.1079
Perko, L.: Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems. Texts in Applied Mathematics, third ed., vol. 7, Springer-Verlag, New York (2001)
La Salle, J.: The Stability of Dynamical Systems. SIAM (1976)
Sotomayor, J.: Generic bifurcations of dynamical systems. In: Peixoto, M.M. (ed.) Dynamical Systems. Academic Press, New York (1973)
Ghosh, U., Majumdar, P., Ghosh, J.K.: Bifurcation analysis of a two-dimensional predator-prey model with Holling type IV functional response and nonlinear predator harvesting. J. Biol. Syst. 28(04), 839–864 (2020)
Majumdar, P., Debnath, S., Sarkar, S., Ghosh, U.: The complex dynamical behavior of a prey-predator model with Holling type III functional response and non-linear predator harvesting. Int. J. Model. Simul. 42(2), 287–304 (2022)
Kuznetsov, Y.A.: Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 112. Springer, (1998) New York
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their careful reading, useful comments and constructive suggestions for the improvement of the manuscript of the present research work.
Funding
This research does not receive any funding from government or private bodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There is no conflict of interest in this research work as declared by authors.
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any animal model/experiment and hence does not require any ethical approval.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendices
Appendices
Appendix I
The coefficient of six degree polynomial equation (6) is given by MAPLE software in the following:
Appendix II
Appendix III
Appendix IV
Appendix V Expressions of \(k_{ij}\) and \(l_{ij}\)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Majumdar, P., Ghosh, U., Sarkar, S. et al. Study of co-dimension two bifurcation of a prey–predator model with prey refuge and non-linear harvesting on both species. Rend. Circ. Mat. Palermo, II. Ser 72, 4067–4100 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12215-023-00881-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12215-023-00881-9
Keywords
- Beddington–DeAngelis functional response
- Non-linear harvesting
- Prey refuge
- Transcritical bifurcation
- Hopf bifurcation
- Saddle-node bifurcation
- Bogdanov–Takens bifurcation