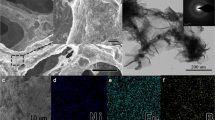
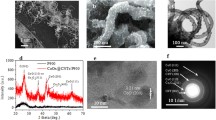
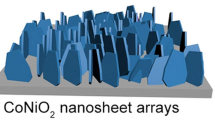
Abstract
Economical water electrolysis requires highly active non-noble electrocatalysts to overcome the sluggish kinetics of the two half-cell reactions, oxygen evolution reaction, and hydrogen evolution reaction. Although intensive efforts have been committed to achieve a hydrogen economy, the expensive noble metal-based catalysts remain under consideration. Therefore, the engineering of self-supported electrocatalysts prepared using a direct growth strategy on three-dimensional (3D) nickel foam (NF) as a conductive substrate has garnered significant interest. This is due to the large active surface area and 3D porous network offered by these electrocatalysts, which can enhance the synergistic effect between the catalyst and the substrate, as well as improve electrocatalytic performance. Hydrothermal-assisted growth, microwave heating, electrodeposition, and other physical methods (i.e., chemical vapor deposition and plasma treatment) have been applied to NF to fabricate competitive electrocatalysts with low overpotential and high stability. In this review, recent advancements in the development of self-supported electrocatalysts on 3D NF are described. Finally, we provide future perspectives of self-supported electrode platforms in electrochemical water splitting.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yan Y, Xia BY, Zhao B et al (2016) A review on noble-metal-free bifunctional heterogeneous catalysts for overall electrochemical water splitting. J Mater Chem A 4(45):17587–17603
Chaudhari NK, Jin H, Kim B et al (2017) Nanostructured materials on 3D nickel foam as electrocatalysts for water splitting. Nanoscale 9(34):12231–12247
Xing Z, Gan F, Wang J et al (2017) Experimental and theoretical insights into sustained water splitting with an electrodeposited nanoporous nickel hydroxide@nickel film as an electrocatalyst. J Mater Chem A 5(17):7744–7748
Wang W, Xu X, Zhou W et al (2017) Recent progress in metal-organic frameworks for applications in electrocatalytic and photocatalytic water splitting. Adv Sci 4(4):1600371
Mamtani K, Jain D, Dogu D et al (2018) Insights into oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) active sites for nitrogen-doped carbon nanostructures (CNx) in acidic media. Appl Catal B Environ 220:88–97
Wang K, She X, Chen S et al (2018) Boosting hydrogen evolution via optimized hydrogen adsorption at the interface of CoP3 and Ni2P. J Mater Chem A 6(14):5560–5565
Chi H, Lin J, Kuang S et al (2023) Self-supported ultrathin NiCo layered double hydroxides nanosheets electrode for efficient electrosynthesis of formate. J Energy Chem 85:267–275
Lan Q, Jin S, Yang B et al (2022) Metal-oxo cluster catalysts for photocatalytic water splitting and carbon dioxide reduction. Trans Tianjin Univ 28(3):214–225
Miao M, Pan J, He T et al (2017) Molybdenum carbide-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. Chemistry 23(46):10947–10961
Wang M, Zhang L, He Y et al (2021) Recent advances in transition-metal-sulfide-based bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A 9(9):5320–5363
Zhang H, Maijenburg AW, Li X et al (2020) Bifunctional heterostructured transition metal phosphides for efficient electrochemical water splitting. Adv Funct Mater 30(34):2003261
Dutta S, Indra A, Feng Y et al (2019) Promoting electrocatalytic overall water splitting with nanohybrid of transition metal nitride-oxynitride. Appl Catal B Environ 241:521–527
Sahoo DP, Das KK, Mansingh S et al (2022) Recent progress in first row transition metal Layered double hydroxide (LDH) based electrocatalysts towards water splitting: a review with insights on synthesis. Coord Chem Rev 469:214666
Yang H, Driess M, Menezes PW (2021) Self-supported electrocatalysts for practical water electrolysis. Adv Energy Mater 11(39):2102074
Geng B, Yan F, Zhang X et al (2021) Conductive CuCo-based bimetal organic framework for efficient hydrogen evolution. Adv Mater 33(49):e2106781
Zhao Y, Wei S, Xia L et al (2022) Sintered Ni metal as a matrix of robust self-supporting electrode for ultra-stable hydrogen evolution. Chem Eng J 430:133040
Katsounaros I, Cherevko S, Zeradjanin AR et al (2014) Oxygen electrochemistry as a cornerstone for sustainable energy conversion. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 53(1):102–121
Sun H, Xu X, Yan Z et al (2018) Superhydrophilic amorphous Co–B–P nanosheet electrocatalysts with Pt-like activity and durability for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 6(44):22062–22069
Sun H, Yan Z, Liu F et al (2020) Self-supported transition-metal-based electrocatalysts for hydrogen and oxygen evolution. Adv Mater 32(3):1806326
Yan Z, Sun H, Chen X et al (2018) Anion insertion enhanced electrodeposition of robust metal hydroxide/oxide electrodes for oxygen evolution. Nat Commun 9(1):2373
Kwon J, Han H, Choi S et al (2019) Current status of self-supported catalysts for robust and efficient water splitting for commercial electrolyzer. ChemCatChem 11(24):5898–5912
Wang Y, Cao Q, Guan C et al (2020) Recent advances on self-supported arrayed bifunctional oxygen electrocatalysts for flexible solid-state Zn-air batteries. Small 16(33):e2002902
Ma TY, Dai S, Qiao SZ (2016) Self-supported electrocatalysts for advanced energy conversion processes. Mater Today 19(5):265–273
Shan X, Liu J, Mu H et al (2020) An engineered superhydrophilic/superaerophobic electrocatalyst composed of the supported CoMoSx chalcogel for overall water splitting. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 59(4):1659–1665
Liu JN, Zhao CX, Ren D et al (2022) Preconstructing asymmetric interface in air cathodes for high-performance rechargeable Zn-air batteries. Adv Mater 34(11):e2109407
Chen Y, Ren Z, Fu H et al (2018) NiSe-Ni0.85Se heterostructure nanoflake arrays on carbon paper as efficient electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Small 14(25):1800763
Ganesan P, Sivanantham A, Shanmugam S (2017) Nanostructured nickel-cobalt-titanium alloy grown on titanium substrate as efficient electrocatalyst for alkaline water electrolysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(14):12416–12426
Liu X, You B, Sun Y (2017) Facile surface modification of ubiquitous stainless steel led to competent electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. ACS Sustainable Chem Eng 5(6):4778–4784
Gultom NS, Abdullah H, Hsu CN et al (2021) Activating nickel iron layer double hydroxide for alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction and overall water splitting by electrodepositing nickel hydroxide. Chem Eng J 419:129608
Huang X, Gong L, Xu H et al (2020) Hierarchical iron-doped CoP heterostructures self-assembled on copper foam as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting. J Colloid Interface Sci 569:140–149
Zhang W, Li D, Zhang L et al (2019) NiFe-based nanostructures on nickel foam as highly efficiently electrocatalysts for oxygen and hydrogen evolution reactions. J Energy Chem 39:39–53
Li J, Zhang J, Shen J et al (2023) Self-supported electrocatalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. Mater Chem Front 7(4):567–606
Wang P, Jia T, Wang B (2020) A critical review: 1D/2D nanostructured self-supported electrodes for electrochemical water splitting. J Power Sources 474:228621
Ratsoma MS, Poho BLO, Makgopa K et al (2023) Application of nickel foam in electrochemical systems: a review. J Electron Mater 52(4):2264–2291
Zhang T, Sun J, Guan J (2023) Self-supported transition metal chalcogenides for oxygen evolution. Nano Res 16(7):8684–8711
Zhang Y, Xiao J, Lv Q et al (2018) Self-supported transition metal phosphide based electrodes as high-efficient water splitting cathodes. Front Chem Sci Eng 12(3):494–508
Zhang J, Si C, Kou T et al (2020) Recent progress in self-supported two-dimensional transition metal oxides and (oxy)hydroxides as oxygen evolution reaction catalysts. Sustain Energy Fuels 4(6):2625–2637
Liu J, Zhu D, Zheng Y et al (2018) Self-supported earth-abundant nanoarrays as efficient and robust electrocatalysts for energy-related reactions. ACS Catal 8(7):6707–6732
Verma S, Sinha-Ray S, Sinha-Ray S (2020) Electrospun CNF supported ceramics as electrochemical catalysts for water splitting and fuel cell: a review. Polymers 12(1):238
Yang G, Park SJ (2019) Conventional and microwave hydrothermal synthesis and application of functional materials: a review. Materials 12(7):1177
Ashik UPM, Kudo S, Hayashi J et al (2018) Synthesis of inorganic nanomaterials. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge
Kim HY, Shin J, Jang IC et al (2019) Hydrothermal synthesis of three-dimensional perovskite NiMnO3 oxide and application in supercapacitor electrode. Energies 13(1):36
Kang Y, Deng C, Chen Y et al (2020) Binder-free electrodes and their application for Li-ion batteries. Nanoscale Res Lett 15(1):112
Tang C, Cheng N, Pu Z et al (2015) NiSe nanowire film supported on nickel foam: an efficient and stable 3D bifunctional electrode for full water splitting. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54(32):9351–9355
Görlin M, Chernev P, Ferreira de Araújo J et al (2016) Oxygen evolution reaction dynamics, faradaic charge efficiency, and the active metal redox states of Ni-Fe oxide water splitting electrocatalysts. J Am Chem Soc 138(17):5603–5614
Burke MS, Kast MG, Trotochaud L et al (2015) Cobalt-iron (oxy)hydroxide oxygen evolution electrocatalysts: the role of structure and composition on activity, stability, and mechanism. J Am Chem Soc 137(10):3638–3648
Dinh KN, Zheng P, Dai Z et al (2018) Ultrathin porous NiFeV ternary layer hydroxide nanosheets as a highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201703257
Zhang Y, Fu J, Zhao H et al (2019) Tremella-like Ni3S2/MnS with ultrathin nanosheets and abundant oxygen vacancies directly used for high speed overall water splitting. Appl Catal B Environ 257:117899
Zhao Y, Chang C, Teng F et al (2017) Defect-engineered ultrathin δ-MnO2 nanosheet arrays as bifunctional electrodes for efficient overall water splitting. Adv Energy Mater 7(18):1700005
Yao L, Zhang N, Wang Y et al (2018) Facile formation of 2D Co2P@Co3O4 microsheets through in-situ toptactic conversion and surface corrosion: bifunctional electrocatalysts towards overall water splitting. J Power Sources 374:142–148
Shi H, Liang H, Ming F et al (2017) Efficient overall water-splitting electrocatalysis using lepidocrocite VOOH hollow nanospheres. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56(2):573–577
Kölbach M, Fiechter S, van de Krol R et al (2017) Evaluation of electrodeposited α-Mn2O3 as a catalyst for the oxygen evolution reaction. Catal Today 290:2–9
Liu J, Yang Y, Ni B et al (2017) Fullerene-like nickel oxysulfide hollow nanospheres as bifunctional electrocatalysts for water splitting. Small. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201602637
Shit S, Chhetri S, Jang W et al (2018) Cobalt sulfide/nickel sulfide heterostructure directly grown on nickel foam: an efficient and durable electrocatalyst for overall water splitting application. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(33):27712–27722
Ren JT, Yuan ZY (2017) Hierarchical nickel sulfide nanosheets directly grown on Ni foam: a stable and efficient electrocatalyst for water reduction and oxidation in alkaline medium. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(8):7203–7210
Liu D, Lu Q, Luo Y et al (2015) NiCo2S4 nanowires array as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for full water splitting with superior activity. Nanoscale 7(37):15122–15126
Zhong X, Tang J, Wang J et al (2018) 3D heterostructured pure and N-doped Ni3S2/VS2 nanosheets for high efficient overall water splitting. Electrochim Acta 269:55–61
Zhang X, Zhang S, Li J et al (2017) One-step synthesis of well-structured NiS–Ni2P2S6 nanosheets on nickel foam for efficient overall water splitting. J Mater Chem A 5(42):22131–22136
Ren H, Huang ZH, Yang Z et al (2017) Facile synthesis of free-standing nickel chalcogenide electrodes for overall water splitting. J Energy Chem 26(6):1217–1222
Zhu W, Yue X, Zhang W et al (2016) Nickel sulfide microsphere film on Ni foam as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Chem Commun 52(7):1486–1489
Zhang B, Wang H, Zuo Z et al (2018) Tunable CoFe-based active sites on 3D heteroatom doped graphene aerogel electrocatalysts via annealing gas regulation for efficient water splitting. J Mater Chem A 6(32):15728–15737
Lu Y, Li Z, Xu Y et al (2021) Bimetallic Co-Mo nitride nanosheet arrays as high-performance bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Chem Eng J 411:128433
Chen MT, Duan JJ, Feng JJ et al (2022) Iron, rhodium-codoped Ni2P nanosheets arrays supported on nickel foam as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. J Colloid Interface Sci 605:888–896
Faraji S, Ani FN (2014) Microwave-assisted synthesis of metal oxide/hydroxide composite electrodes for high power supercapacitors–a review. J Power Sources 263:338–360
Sun J, Wang W, Yue Q (2016) Review on microwave-matter interaction fundamentals and efficient microwave-associated heating strategies. Materials 9(4):231
Gerard O, Numan A, Krishnan S et al (2022) A review on the recent advances in binder-free electrodes for electrochemical energy storage application. J Energy Storage 50:104283
Rosa R, Ponzoni C, Leonelli C (2014) Direct energy supply to the reaction mixture during microwave-assisted hydrothermal and combustion synthesis of inorganic materials. Inorganics 2(2):191–210
Duan Y, Huang Z, Zhao C et al (2021) In-situ generated trimetallic molybdate nanoflowers on Ni foam assisted with microwave for highly enhanced oxygen evolution reaction. Chem 27(35):9044–9053
Guo ML, Wu ZY, Zhang MM et al (2023) Coupling interface constructions of FeOOH/NiCo2S4 by microwave-assisted method for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Rare Met 42(6):1847–1857
Ren J, Du Y, Wang Y et al (2023) Modulating amorphous/crystalline heterogeneous interface in RuCoMoyOx grown on nickel foam to achieve efficient overall water splitting. Chem Eng J 469:143993
Cao X, Wang T, Qin H et al (2023) Crystalline—amorphous interfaces of NiO-CrOx electrocatalysts for boosting the urea oxidation reaction. Nano Res 16(3):3665–3671
Guo C, Shi Y, Lu S et al (2021) Amorphous nanomaterials in electrocatalytic water splitting. Chin J Catal 42(8):1287–1296
Nadarajan R, Gopinathan AV, Dileep NP et al (2023) Heterointerface engineering of cobalt molybdenum suboxide for overall water splitting. Nanoscale 15(37):15219–15229
Nunes D, Pimentel A, Santos L et al (2019) Metal Oxide Nanostructures for sensor applications. Semicond Sci Technol 34:043001
Sonawane GH, Patil SP, Sonawane SH et al (2018) Applications of nanomaterials. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge
Ma ZY, Yu ZL, Xu ZL et al (2020) Origin of batch hydrothermal fluid behavior and its influence on nanomaterial synthesis. Matter 2(5):1270–1282
Biswal HJ, Kaur JJ, Vundavilli PR et al (2022) Recent advances in energy field assisted hybrid electrodeposition and electroforming processes. CIRP J Manuf Sci Technol 38:518–546
Shojaei Z, Khayati GR, Darezereshki E (2022) Review of electrodeposition methods for the preparation of high-entropy alloys. Int J Miner Metall Mater 29(9):1683–1696
Percival SJ, Lu P, Lowry DR et al (2022) Electrodeposition of complex high entropy oxides via water droplet formation and conversion to crystalline alloy nanoparticles. Langmuir 38(5):1923–1928
Lee YJ, Park SK (2022) Metal-organic framework-derived hollow CoSx nanoarray coupled with NiFe layered double hydroxides as efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Small 18(16):2200586
Yang Y, Xie Y, Yu Z et al (2021) Self-supported NiFe-LDH@CoSx nanosheet arrays grown on nickel foam as efficient bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Chem Eng J 419:129512
Yang R, Zhou Y, Xing Y et al (2019) Synergistic coupling of CoFe-LDH arrays with NiFe-LDH nanosheet for highly efficient overall water splitting in alkaline media. Appl Catal B Environ 253:131–139
Mittal M, Sardar S, Jana A et al (2021) Handbook of nanomaterials for sensing applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Li K, He J, Guan X et al (2023) Phosphorus-modified amorphous high-entropy CoFeNiCrMn compound as high-performance electrocatalyst for hydrazine-assisted water electrolysis. Small 19(42):2302130
Lai D, Kang Q, Gao F et al (2021) High-entropy effect of a metal phosphide on enhanced overall water splitting performance. J Mater Chem A 9(33):17913–17922
Wang R, Huang J, Zhang X et al (2022) Two-dimensional high-entropy metal phosphorus trichalcogenides for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Nano 16(3):3593–3603
Joo J, Kim T, Lee J et al (2019) Morphology-controlled metal sulfides and phosphides for electrochemical water splitting. Adv Mater 31(14):e1806682
Sun M, Gao B, Wang S et al (2020) Study on the electrocatalytic performance of porous conductive materials based on an in situ growth of bimetal phosphides with plasma. Int J Electrochem Sci 15(4):3242–3254
Feng Z, Sui Y, Sun Z et al (2021) Controllable synthesis of flower-like Mn–Co–P nanosheets as bifunctional electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 615:126265
Salem KE, Saleh AA, Khedr GE et al (2023) Unveiling the optimal interfacial synergy of plasma-modulated trimetallic Mn–Ni–Co phosphides: tailoring deposition ratio for complementary water splitting. Energy Environ Mater 6(2):e12324
Fan H, Chen W, Chen G et al (2020) Plasma-heteroatom-doped Ni-V-Fe trimetallic phospho-nitride as high-performance bifunctional electrocatalyst. Appl Catal B Environ 268:118440
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) President’s International Fellowship Initiative (No. 2023VCB0014), The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52203284), Shenzhen Science and Technology Program (Nos. GJHZ20220913143801003 and RCBS20221008093057026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare there is no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Wang, X., Huang, Z. et al. Engineering of Self-Supported Electrocatalysts on a Three-Dimensional Nickel Foam Platform for Efficient Water Electrolysis. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 30, 103–116 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-024-00389-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-024-00389-y