Abstract
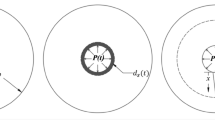
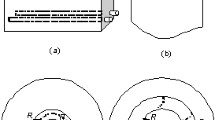
An analytical model for predicting the corrosion-induced cracking of concrete cover of reinforced concrete (RC) structures was developed. The effects of influence factors such as practical initial defects, corrosion rate, strength and elastic modulus of concrete on the corrosion-induced cracking of concrete cover were investigated. It was found that the size of practical initial defects was the most effective factor. Therefore, improving the compactness of concrete is an effective way to improve the durability of RC structures. It was also demonstrated that the accelerated corrosion tests may be unfavorable in the study of the relationship between cracking time and crack width.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu Chunhua, Jin Weiliang, Liu Ronggui. Reinforcement corrosion-induced cover cracking and its time prediction for reinforced concrete structures [J]. Corrosion Science, 2011, 53(4): 1337–1347.
Leon C, Dimitri V Val. Prediction of corrosion-induced cover cracking in reinforced concrete structures [J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2011, 25(4): 1854–1869.
Li C Q, Yang S T. Prediction of concrete crack width under combined reinforcement corrosion and applied load [J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2011, 137(11): 722–731.
Zhang Xiaogang, Song Yupu, Wu Zhimin. Calculation model of equivalent strength for induced crack based on double-K fracture theory and its optimizing setting in RCC arch dam [J]. Transactions of Tianjin University, 2005, 11(1): 59–65.
Zhang Xiaogang, Wang Xuezhi, Lu Zhaohui et al. Analytic model of non-uniform corrosion induced cracking of reinforced concrete structure [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2011, 18(3): 940–945.
Zhang Xiaogang, Zhao Yangang, Xing Feng et al. Coupling effects of influence factors on probability of corrosion initiation time of reinforced concrete [J]. Journal of Central South University of Technology, 2011, 18(1): 223–229.
Zhang Xiaogang, Zhao Yangang, Lu Zhaohui. Dynamic corrosion-induced cracking process of RC considering effect of initial defects [J]. Journal of Asian Architecture and Building Engineering, 2010, 9(2): 439–446.
Liu Y P, Weyers R E. Modeling the time-to-corrosion cracking in chloride contaminated reinforced concrete structures [J]. ACI Materials Journal, 1998, 95(6): 675–680.
Xu Shilang, Reinhardt H W. Determination of double-K criterion for crack propagation in quasi-brittle fracture. Part III. Compact tension specimens and wedge splitting specimens [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1999, 98(2): 179–193.
Xu S L, Reinhardt H W. Crack extension resistance and fracture properties of quasi-brittle softening materials like concrete based on the complete process of fracture [J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1998, 92(1): 71–99.
Reinhardt H W, Xu S L. Crack extension resistance based on the cohesive force in concrete [J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1999, 64(5): 563–587.
Bhargava K, Ghosh A K, Mori Y et al. Modeling of time to corrosion-induced cover cracking in reinforced concrete structures [J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2005, 35(11): 2203–2218.
Liu Hongwen. Advanced Mechanics of Materials[M]. Higher Education Press, Beijing, 1985 (in Chinese).
Torres-Acosta A A, Sagüés A A. Concrete cracking by localized steel corrosion-Geometric effects [J]. ACI Materials Journal, 2004, 101(6): 501–507.
Wu Zhimin, Xu Shilang, Ding Yining et al. The double-K fracture parameter of concrete for non-standard three point bending beam specimens [J]. China Engineering Science, 2001, 3(4): 76–81(in Chinese).
Andrade C, Alonso C, Molina F J. Cover cracking as a function of bar corrosion. Part I. Experimental test [J]. Materials and Structures, 1993, 26(8): 453–464.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50908148), Natural Science Foundation for Team Project of Guangdong Province(No. 9351806001000001), Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, Ministry of Education (41 Batch), and Open Fund of State Key Laboratory of Coastal and Offshore Engineering of Dalian University of Technology (No. LP1111).
ZHANG Xiaogang, born in 1978, male, associate Prof.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Wang, J. & Zhou, Y. Analytical modeling for corrosion-induced cover cracking of corrosive reinforced concrete structures. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 18, 285–290 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-012-1905-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-012-1905-4