Abstract
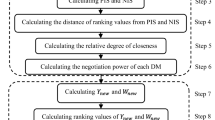
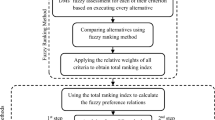
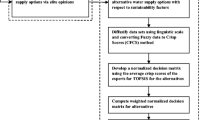
In this paper, the criteria set related to the priority preorders of water resources projects is introduced. A fuzzy multiple criteria group decision-making model is established, which incorporates quantitative analysis, judgments, experience and preferences of decision-makers. The model is used in practice to determine the priority preorders of five water resources projects, and the results show that the best choice can supply more new employment, domestic water and irrigation water, and has better quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
LeMoine G, Subramanian A, Xie M et al. Guide to the Formulating of Water Resources Strategy [R]. No. 263, The World Bank, Technical Paper, 1994
Karnib A. An approach to elaborate priority preorders of water resources projects based on multi-criteria evaluation and fuzzy sets analysis[J]. Water Resources Management, 2004, 18(1): 13–33.
Luo Zhihui, Chen Huiyuan, Feng Shangyou. The study on multi-objective optimization method for cascade water power development[J]. Journal of Water Conservancy, 1998,1: 29–32(in Chinese).
Kindler J. Planning and Decision-Making Frame Work, Environmentally Sound Water Management [M]. Oxford University Press, New York, 1990.
Loucks D P, Stedinger J R, Haith D A. Water Resources System Planning and Analysis [M]. The Southeast Book Company, Prentice-Hall, New York, 1981.
Louie P W, Yeh W W G, Hsu N. Multi-objective water resources management planning[J]. J Water Resour Plan Managt, 1984, 110(1): 39–56.
Seckler D. The New Era of Water Resources Management: From “Dry” to “Wet” Water Savings[R]. Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research, 1996.
Bardossy A, Duckstein L, Bogardi I. Combination of fuzzy numbers representing expert opinions[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1993, 57(2): 173–181.
Hsu H M, Chen C T. Aggregation of fuzzy opinions under group decision making[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1996, 79(3): 279–285.
Lee Hsuan Shih. Optimal consensus of fuzzy opinions under group decision making environment[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2002, 132(3): 303–315.
Chen Shouyu. Fuzzy System Decision-Making Theory and Its Application [M]. Dalian University of Technology Press, Dalian, 1994(in Chinese).
Chen Shouyu. Non-structured decision making analysis and fuzzy optimum seeking theory for multi-objective systems[J]. Journal of Fuzzy Mathematics, 1996, 4(2): 835–842(in Chinese).
Chen Shouyu. Fuzzy Set Theory and Application [M]. National Defense Industry Press, Beijing, 1998(in Chinese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
LIU Yingjie, born in 1978, female, doctorate student.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Feng, P. Fuzzy approach to determining priority preorders of water resources projects. Trans. Tianjin Univ. 15, 121–125 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-009-0021-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12209-009-0021-6