Abstract
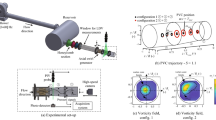
The combined effects of channel curvature and rotor configuration on the performance of two-stage viscous micropumps were studied numerically. The Navier-Stokes equations were simulated to investigate the performance of two-stage micropumps. The performance of two-stage micropumps was studied in terms of the dimensionless mass flow rate and dimensionless driving power. Four different rotor configurations were designed by changing placement of two rotors inside a microchannel: Two aligned and two staggered configurations. The aligned rotor configuration of type 1 is to place the two rotors along the convex wall, while type 2 is to place them along the concave wall. Numerical results show that the rotor configuration plays a significant role in the performance of two-stage micropumps. The channel curvature acts in a different way according to the rotor configuration. The mass flow rate of aligned rotor configuration of type 1 is greatly improved by the channel curvature, while it diminishes the mass flow rate of type 2. The maximum mass flow rate for the aligned rotor configuration of type 1 is obtained when the two rotors are placed at the junction of the circular and straight sections of the channel. The performance of staggered configurations is negligibly affected by the channel curvature. This characteristics is found due to rotation direction of the rotors. As the two rotors rotate in the opposite direction for the staggered configurations, the flow characteristics in the circular section is little affected by the channel curvature. The circumferential distance between the two rotors can be optimized in terms of the mass flow rate. The optimal value of the circumferential distance is about L = 1.4 for the staggered rotor configurations, and it is almost independent of the channel curvature. As the channel height increases, the circumferential distance becomes less significant for the staggered rotor configurations while it becomes significant for the aligned rotor configurations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. K. da Silva, M. H. Kobayashi and C. F. M. Coimbra, Optimal theoretical design of 2-D microscale viscous pumps for maximum mass flow rate and minimum power consumption, International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 28 (2007) 526–536.
M. I. Kilani, A. Al-Salaymeh and A.T. Al-Halhouli, Effect of channel aspect ratio on the flow performance of a spiralchannel viscous micropump, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 128 (2006) 618–627.
S. F. Bart, L. S. Tavrow, M. Mehregany and G. H. Lang, Microfabricated Electrohydrodynamic pumps, Sensors and Actuators, A 21 (1990) 193–197.
R. M. Moroney, R. M. White and R. T. Howe, Ultrasonically induced microtransport, Proceedings IEEE MEMS (1991) 277–282.
D. J. Harrison, A. A. Manz and P. G. Glavina, Electroosmotic pumping within a chemical sensor system integrated on silicon, Proceedings of International Conference on Solid State Sensors and Actuators Transducers (1991) 792–795.
H. T. G. Van Lintel, F. C. M. Van De Pol and S. Bouwstra, A piezoelectric micropump based on micromachining of silicon, Sensors and Actuators, 15 (1996) 153–167.
M. Sen, D. Wajerski and M. Gad-el-Hak, A novel pump for MEMS applications, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 118 (1996) 624–627.
N. T. Nguyen and S. T. Wereley, Fundamentals of and applications of microfluidics, Norwood, Artech House (2006) 293–337.
H. A. Arafa and T. A. Osman, Viscous pumps: comparative assessment of effectiveness, Proceedings of Institution of Mechanical Engineers, 217 Part J. (2003) 167–174.
M. Abdelgawad, I. Hasan and N. Esmail, Transient behavior of the viscous micropump, Microscale Thermophysical Engineering, 8 (2004) 361–384.
L. Jianfeng and D. Jing, Flow dynamical behaviors and characteristics of aligned and staggered viscous pumps, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 53 (2010) 2092–2099.
M. I. Kilani, P. C. Galambos, Y. S. Haik and C. J. Chen, Design and analysis of a surface micromachined spiralchannel viscous pump, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 15 (2003) 339–344.
D. J. Kang, Effects of channel curvature on the performance of viscous micro pumps, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 28 (9) (2014) 3733–3740.
ANSYS Fluent product, http://www.ansys.com/Products/Simulation+Technology/Fluid+Dynamics/ANSYS +Fluent.
M. C. Sharatchandra, M. Sen and Gad-el Hak, Navier-Stokes simulation of a novel viscous pump, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 119 (1997) 372–382.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Seongwon Kang
Dong Jin Kang received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Yeungnam University, Gyeungsan, Korea in 1985. He received his M.E. and Ph.D. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from KAIST, Daejeon, Korea in 1987 and 1991, respectively. He is currently a Professor at the School of Mechanical Engineering of Yeungnam University, Gyeungsan, Korea. His research interests include simulations of fluid flow and heat transfer in micro devices.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, D.J. Combined effects of channel curvature and rotor configuration on the performance of two-stage viscous micropumps. J Mech Sci Technol 31, 2813–2820 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0524-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-017-0524-3