Abstract
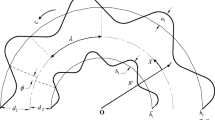
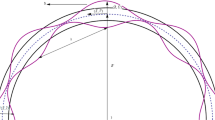
The effects of channel curvature on the performance of viscous micro-pumps with a circular channel were numerically investigated using the Navier-Stokes equations. Channel curvature was defined as the reciprocal of the radius of a circular arc along the centerline of the channel. The performance of viscous micro-pumps was studied in terms of the dimensionless mass flow rate and dimensionless driving power. To study the effects of channel curvature, various pumps were simulated by varying the radius and height of the channel, and the eccentricity of the rotor. Numerical results show that the channel curvature plays a significant role in the performance of viscous micro-pumps. The effects of channel curvature become more significant as the channel height increases and/or the clearance gap decreases. For a given pump geometry and operation conditions, there is an optimal channel height that results in a maximum dimensionless mass flow rate. The value of optimal channel height is shown to be quite dependent on the magnitude of channel curvature and the pressure load. The dimensionless driving power decreases monotonically with channel curvature; thus a viscous micro-pump with a circular channel is more efficient than a corresponding pump with a straight channel. A circular channel viscous micro-pump exhibits a larger mass flow rate than a corresponding pump with a straight channel for all the Reynolds numbers simulated in this paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Gad-el-Hak, The MEMS Handbook, CRC Press (2002).
A. Ritcher, A. Plettner, K. A. Hoffmann and H. Sandmaier, Micro-machined electro-hydrodynamic (EHD) pump, Sensors and Actuators, A 29 (1991) 159–168.
D. J. Harrison, A. Manz, A. and P. G. Glavina, Electroosmotic pumping within a chemical sensor system integrated on silicon, Proceedings of International Conference on Solid State Sensors and Actuators Transducers (1991) 792–795.
H. T. G. Van Lintel, F. C. M. Van De Pol and S. Bouwstra, A piezoelectric micro-pump based on micro-machining of silicon, Sensors and Actuators, 15 (1996) 153–167.
M. Sen, D. Wajerski and M. Gad-el-Hak, A novel pump for MEMS applications, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 118 (1996) 624–627.
M. I. Kilani, P. C. Galambos, Y. S. Haik and C. J. Chen, Design and analysis of a surface micro-machined spiralchannel viscous pump, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 15 (2003) 339–344.
M. C. Sharatchandra, M. Sen and Gad-el Hak, Navier-Stokes simulation of a novel viscous pump, Journal of Fluids Engineering, 119 (1997) 372–382.
L. Jianfeng and D. Jing, Flow dynamical behaviors and characteristics of aligned and staggered viscous pumps, International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 53 (2010) 2092–2099.
A. K. da Silva, M. H. Kobayashi and C. F. M. Coimbra, Optimal theoretical design of 2-D micro-scale viscous pumps for maximum mass flow rate and minimum power consumption, International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 28 (2007) 526–536.
M. R. H. Nobari and A. Malvandi, Torsion and curvature effects on fluid flow in a helical annulus, International journal of non-linear mechanics, 57 (2013) 90–101.
A. A. Avramenko and A. V. Kuznetsov, Instability of a slip flow in a curved channel formed by two concentric cylindrical surfaces, European Journal of Mechanics B/Fluids, 28 (2009) 722–727.
R. Tang and C. Y. Wu, An efficient micro-mixer based multidirectional vortices due to baffles and channel curvature, Biomicrofluidics, 5 (2011) 014103.
J. Zhu, R. C. Canter, G. Keten, P. Vedantam, T. R. J. Tzeng and X. Xuan, Continuous flow particle and cell separations in a serpentine micro-channel via curvature-induced dielectrophoresis, Microfluid Nanofluid, 11 (2011) 743–752.
D. J. Kang and S. S. Bae, Frequency effects of upstream wake on the unsteady boundary layer, Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 16 (10) (2002) 1303–1313.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor DAEJOONG KIM
Dong Jin Kang received his B.E. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Yeungnam University, Gyeungsan, Korea in 1985. He received his M.E. and Ph.D. degrees in Mechanical Engineering from KAIST, Daejeon, Korea in 1987 and 1991, respectively. He is currently Professor at the School of Mechanical Engineering of Yeungnam University, Gyeungsan, Korea. His research interests include simulations of fluid flow and heat transfer in micro devices.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, D.J. Effects of channel curvature on the performance of viscous micro-pumps. J Mech Sci Technol 28, 3733–3740 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0834-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-014-0834-7