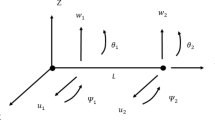
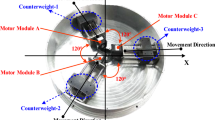
Abstract
Even a moderate mass imbalance of a high-precision rotor produces a significant level of vibration when it spins at high revolutionary speed such as 10,000 rpm or faster. As a result, many attempts have been made for the development of dynamic rotor balancing methods mostly by the precision mechanical system industry; however, intensive studies about the fundamental principles from a theoretical point of view should be carried out further. In the present paper, a new dual axes dynamic imbalance correction method is introduced and tested through simulations. The proposed method is more efficient and effective than its predecessors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Robert, Disk clamp with tabs shaped to apply equal forces at equally spaced locations around an axis of rotation of a disk drive, U.S. Patent 5,790,345, (1998).
Hiroshi Kawaguchi, Shizuo Yamazaki, Makoto Horisaki, Katsumi Watanabe, Kenji Tomida and Kusagaya, Servo pattern writing method and apparatus thereof, U. S. Patent 6,947,244, (2005).
Keiko Watanabe, Tetsuya Hamaguchi, Takashi Matsuki and Shizuo Yamazaki, Method for assembling disc apparatus, U. S. Patent 6,839,956, (2005).
Lealon R. McKenzie and Robert D. Murphy, Method and apparatus for minimizing once per revolution positional errors in a dis drive, U. S. Patent 6,421,199, (2002).
Branislav Hredzak and Guoxial Guo, New electromechanical balancing device for active imbalance compensation, Journal of Sound and Vibration, 294(4–5) (2006) 737–751.
Toshiki Hirano, Method for adjusting rotation balance of disk and device for the same, U. S. Patent 5,811,678, (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jung Kwan Lee is currently a masteral student in the School of Mechanical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University Korea. He received his B.S. degree from Sungkyunkwan University. His primary research interests are rotor design, analysis, and rotor dynamics.
Hyungpil Moon received his Ph.D. degree in mechanical engineering from the University of Michigan in 2005. He was a postdoctoral fellow at Carnegie Mellon University. He joined the faculty of the School of Mechanical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University in 2008.
Dongho Oh received his Ph.D. degree from KAIST in 1996. He worked as a Principal En-gineer of Samsung Electronics and SAIT. Dr. Oh is currently an Associate Professor at the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Chungnam National University.
Ja Choon Koo is an associate professor of the School of Mechanical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University Korea. He was an engineer at IBM Corporation, San Jose, California. He received his Ph.D from the University of Texas at Austin. His primary research interests are analysis, and control of dynamic systems, mechatronics, sensors, and actuators.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.K., Lee, S.B., Moon, H. et al. An enhanced real-time dynamic imbalance correction for precision rotors. J Mech Sci Technol 23, 1050–1053 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0339-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-009-0339-y