Abstract
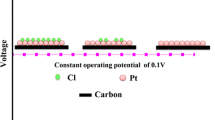
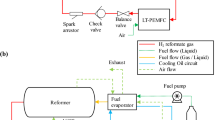
Carbon monoxide (CO), which is preferentially absorbed on the platinum catalyst layer of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC), is extremely detrimental to cell performance. Essentially, the carbon monoxide absorption diminishes the cell’s performance by blocking and reducing the number of catalyst sites available for the hydrogen oxidation reaction. In order to obtain a full understanding of CO poisoning characteristics and remediate CO-poisoned PEMFCs, a CO poisoning numerical model is developed and incorporated into a fully three-dimensional electrochemical and transport coupled PEMFC model. By performing CFD numerical simulations, this paper clearly demonstrates the CO poisoning mechanisms and characteristics of PEMFCs. The predictive capability for CO poisoning effects enables us to find major contributors to CO tolerance in a PEMFC and thus successfully integrate CO-resistant fuel cell systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Oetjen, V. M. Schmidt, U. Stimming and F. Trila, Performance data of a proton exchange membrane fuel cell using H2/CO as fuel gas, J. Electrochem. Soc., 143 (1996) 3838–3842.
T. E. Springer, T. Rockward, T. A. Zawodzinski and S. Gottesfeld, Model for polymer electrolyte fuel cell operation on reformate feed: effects of CO, H2 dilution, and high fuel utilization, J. Electrochem. Soc., 148 (2001) A11–A23.
M. Murthy, M. Esayian, A. Hobson, S. MacKenzie, füW. K. Lee and J. W. Van Zee, Performance of a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell exposed to transient CO concentrations, J. Electrochem. Soc., 148 (2001) A1141–A1147.
L. Brown, A comparative study of fuels for onboard hydrogen production for fuel-cell-powered automobiles, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 26 (2001) 381–397.
J. Divisek, H. F. Oetjen, V. Peinecke, V. M. Schmidt and U. Stimming, Components for PEM fuel cell systems using hydrogen and CO containing fuels, Electrochimica Acta, 43 (1998) 3811–3815.
J. Zhang, T. Thampan and R. Datta, Influence of anode flow rate and cathode oxygen pressure on CO poisoning of proton exchange membrane fuel cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 149(6) (2002) A765–A772.
G. A. Camara, E. A. Ticianelli, S. Mukerjee, S. J. Lee and J. McBreen, The CO poisoning mechanism of the hydrogen oxidation reaction in proton exchange membrane fuel cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 6 (2002) A748–A753.
S. Um, C. Y. Wang and K. S. Chen, Computational fluid dynamics modeling of proton exchange membrane fuel cells, J. Electrochem. Soc., 147 (2000) 4485–4493.
H. Ju and C. Y. Wang, Experimental validation of a PEM fuel cell model by current distribution data, J. Electrochem. Soc., 151 (2004) A1954–A1960.
H. Ju, H. Meng and C. Y. Wang, A single-phase, non-isothermal model for PEM fuel cells, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer, 48 (2005) 1303–1315.
T. E. Springer, T. A. Zawodzinski and S. Gottesfeld, Modeling of polymer electrolyte fuel cell performance with reformate feed stream: effects of low levels of CO in hydrogen, The Electrochemical Society Proceedings Series, PV 97-13 (1997) 15–24.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ju, H., Lee, KS. & Um, S. Multi-dimensional modeling of CO poisoning effects on proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). J Mech Sci Technol 22, 991–998 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0207-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-008-0207-1