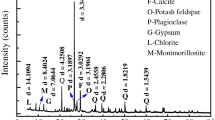
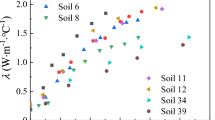
Abstract
Soil thermal conductivity is an important indicator for developing and utilizing geothermal resources. In this study, the impact of underground environmental factors on the thermal conductivity of loess was explored by studying the thermal conductivity of saturated and unsaturated loess under varying water content, dry density, and temperature using the Hot Disk thermal constant analyzer. The results show that the thermal conductivity of unsaturated undisturbed and remolded loess presents different growth trends as the water content increases. When the water content is less than 9%, the thermal conductivity of undisturbed soil increases slowly. The thermal conductivity of unsaturated loess gradually increases with temperature. When the temperature rises above 30°C, the latent heat transfer of steam gradually strengthens, accelerating the increase in thermal conductivity, which is most noticeable at intermediate saturation. However, the thermal conductivity of saturated loess rises slowly as the temperature rises. A weighted geometric average model is proposed in this study to predict the thermal conductivity of loess under temperature conditions, considering the effects of soil water content, dry density, and mineral content. The model accuracy was corroborated by the measured soil thermal conductivity and the data collected from six regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Air
- D :
-
Diffusion coefficient of water vapor in air
- da :
-
Dry air
- H L :
-
Latent heat of vaporization
- min :
-
Minerals
- n :
-
Soil porosity
- P :
-
Pressure
- q :
-
Quartz
- s :
-
Solids
- Sr :
-
Saturation
- T :
-
Kelvin temperature
- vs :
-
Water vapour
- w :
-
Water
- λ :
-
Thermal conductivity
- θ :
-
Volumetric content
References
Akrouch GA, Sánchez M, Briaud JL (2014) Thermo-mechanical behavior of energy piles in high plasticity clays. Acta Geotech 9:399–412, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-014-0312-5
Ali MA, Bouazza A, Singh RM, Gates WP (2016) Thermal conductivity of geosynthetic clay liners. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 53(9): 1510–1521, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2015-0585
Barry-Macaulay D, Bouazza A, Wang B, Singh RM (2015) Evaluation of soil thermal conductivity models. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 52(11):1–9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0518
Bauer ML, Saltonstall CB, Leseman ZC, Beechem TE, Hopkins PE, Norris PM (2016) Thermal conductivity of turbostratic carbon nanofiber networks. Journal of Heat Transfer: Transactions of the ASME 138(6), DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4032610
Boersma L, Sepaskhah AR (1979) Thermal conductivity of soils as a function of temperature and water content. Soil Science Society of America Journal 43(3):439–444, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1979.03615995004300030003x
Campbell GS, Jungbauer JD,JR, Bidlake WR (1994) Predicting the effect of temperature on soil thermal conductivity. Soil Science 158(5):307–313, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-199411000-00001
Corasaniti S, Gori F (2002) Theoretical prediction of the soil thermal conductivity at moderately high temperatures. Journal of Heat Transfer 124:1001–1008, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1513573
Côté J, Konrad JM (2005) A generalized thermal conductivity model for soils and construction materials. Canadian Geotechnical Journal 42(2):443–458, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1139/t04-106
De Vries DA (1963) Thermal properties of soils. In: Physics of plant environment. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 210–235
Dehghanpoor A, Branch S, Wong HS, Buenfeld NR (2013) Modelling the diffusivity of mortar and concrete using a three-dimensional mesostructure with several aggregate shapes. Computational Materials Science 78:63–73, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.05.024
Dong Y, Cartney JS, Lu N (2015) Critical review of thermal conductivity models for unsaturated soils. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 33:207–221, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9843-2
Feng L, Zhang SS, Liu XB, Jin Z, Peng JB (2021) The genesis, development, and evolution of original vertical joints in loess. Earth-Science Reviews 214:103526, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103526
Garber D, Choudhary R, Soga K (2013) Risk based lifetime costs assessment of a ground source heat pump (GSHP) system design: Methodology and case study. Building and Environment 60:66–80, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2012.11.011
Genuchten MTV (1980) A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal 44:892–898, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1980.0361599500440
Helms TC, Deckard E, Goos RJ (1996) Soil moisture, temperature, and drying influence on soybean emergence. Agronomy Journal 88:662–667, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1996.00021962008800040027
Hong B (2020) Experimental study on heat transfer characteristics and heat and moisture transport law of loess water and gas. PhD Thesis, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China (in Chinese)
Hu WL, Cheng WC, Wang L, Xue ZF (2022) Micro-structural characteristics deterioration of intact loess under acid and saline solutions and resultant macro-mechanical properties. Soil and Tillage Research 220:105382, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2022.105382
Hu WL, Cheng WC, Wen SJ (2023) Investigating the effect of degree of compaction, initial water content, and electric field intensity on electrokinetic remediation of an artificially Cu- and Pb-contaminated loess. Acta Geotechnica 18(2):937–949, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11440-022-01602-9
Hu HJ, Li T, Thornton C, Jiang MJ (2014) DEM analyses of one-dimensional compression and collapse behavior of unsaturated structural loess. Computers and Geotechnics 60:47–60, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2014.04.002
Leong WH, Tarnawski VR, Gori F, Buchan GD, Sundberg J (2005) Inter-particle contact heat transfer model: An extension to soils at elevated temperatures. International Journal of Energy Research 29(2):131–144, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/er.1046
Li D, Sun X, Khaleel M (2013) Comparison of different upscaling methods for predicting thermal conductivity of complex heterogeneous materials system: Application on nuclear waste forms. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 44:61–69, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-012-1269-3
Likos WJ (2015) Pore-scale model for thermal conductivity of unsaturated sand. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering 33:179–192, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9744-9
Liu CH, Zhou D, Wu H (2011) Measurement and prediction of temperature effects of thermal conductivity of soils. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering 33(12):1877–1886, DOI: 1000-4548(2011)33:12<1877: TRRDLD>2.0.TX;2-#
Nikolaev IV, Leong WH, Rosen MA (2013) Experimental investigation of soil thermal conductivity over a wide temperature range. International Journal of Thermophysics 34:1110–1129, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-013-1456-5
Smits KM, Sakaki T, Howington SE (2013) Temperature dependence of thermal properties of sands across a wide range of temperatures (30–70°C). Review and Analysis 12(1):2256–2265, DOI: https://doi.org/10.2136/vzj2012.0033
Song XY, Fan HH, Liu JW, Yang XJ (2020) An improved thermal conductivity model for unsaturated clay. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering 24(8)2364–2371, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-020-1812-5
Tarnawski VR, Gori F, Wagner B, Wagner B, Buchan GD (2000a) Modelling approaches to predicting thermal conductivity of soils at high temperatures. International Journal of Energy Research 24(5): 403–423, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6701(00)94755-6
Tarnawski VR, Leong WH (2012) A series-parallel model for estimating the thermal conductivity of unsaturated soils. International Journal of Thermophysics 33:1191–1218, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-012-1282-1
Tarnawski VR, Leong WH, Bristow KL (2000b) Developing a temperature-dependent Kersten function for soil thermal conductivity. International Journal of Energy Research 24:1335–1350, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-114x(200012)24:15<1335::aid-er652>3.0.co;2-x
Tarnawski VR, Leong WH, Gori F, Buchan GD, Sundberg J (2002) Inter-particle contact heat transfer in soil systems at moderate temperatures. International Journal of Energy Research 26(15): 1345–1358, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/er.853
Wang TH, Liu ZC, Lu J (2007) Experimental study on thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity of loess. Geotechnical Mechanics 28(4): 655–658, DOI: https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2007.04.004 (in Chinese)
Xu YS, Sun DA, Zeng ZT, Lv HB (2019) Effect of temperature on thermal conductivity of lateritic clays over a wide temperature range. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 138:562–570, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.04.077
Zhang N, Wang Z (2017) Review of soil thermal conductivity and predictive models. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 117:172–183, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.03.013
Zhao ZK, Wang T, Zhang L (2023) Measurement and modeling of the evaporation rate of loess under high temperature. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 215:124486, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2023.124486
Zhou Z, Adjali MH, Thomas HR, Rees SW, Davies M (2015) Ground heat transfer effects on the thermal performance of earth-contact structures. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 4(3):213–265, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1364-0321(99)00018-0
Acknowledgments
This presented work is supported by the Shaanxi Provincial Science and Technology Integrated Innovation Project (No.2012KTCQ03-01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Deng, J., Zheng, J. et al. Thermal Conductivity of Loess: Experimental Studies and Empirical Model. KSCE J Civ Eng 28, 644–654 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-023-0773-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-023-0773-x