Abstract
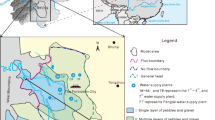
The Visual MODFLOW software has been used to simulate the flow behavior, while both a Genetic Algorithm and a Tabu Search Algorithm have been used to maximize the extracted flowrates and investigate the optimal groundwater management strategy of an unconfined aquifer, for the case when surface pumps are used. The procedure above is applied in the south-west area of the Eidomeni-Evzoni phreatic aquifer, located near the borderline of Greece and the Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia (FYROM). The optimal total pumping flowrate has been estimated at 4560.9 m3/d. It is proven that the non-linear Boussinesq equation rather than its linearized counterpart should be used. It is also demonstrated that a coarse uniform grid might underestimate the head drawdown induced by the well; accordingly, a more sophisticated grid, with two refinement zones around each well, should be adopted. The optimization results indicate that the Τabu Search approach is computationally more efficient than the Genetic Algorithms, while both give the same results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arostegui, M. A., Kadipasaoglu, S. N., and Khumawala, B. M. (2006). “An empirical comparison of Tabu search, simulated annealing, and genetic algorithms for facilities location problems.” International Journal of Production Economics, Vol. 103, No. 2, pp. 742–754. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2005.08.010.
Ayvaz, M. T. (2009). “Application of harmony search algorithm to the solution of groundwater management models.” Advances in Water Resources, Vol. 32, pp 916–924, DOI: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2009.03.003.
Basharat, M. and Tariq, A. (2013). “Spatial climate variability and its impact on irrigated hydrology in a canal command.” Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, Vol. 38 No. 3, pp. 507–522, DOI: 10.1007/s13369-012-0336-9.
Bear, J. (1979). Hydraulics of Groundwater. Mc-Graw-Hill, New York.
Fotakis, D. and Sidiropoulos, E. (2014). “Combined land-use and water allocation planning.” Annals of Operations Research, Vol. 219, No. 1, pp. 169–185.
Glover, F. (1989). Tabu search, part I., ORSA Journal on Computing, Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 190–206, DOI: 10.1007/s10479-012-1080-y.
Goldberg, D. E. (1989). Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning, Addison-Wesley-Longman, Reading, Mass.
Harbaugh, A. W. and McDonald M. G. (1996). “User’s Documentation for MODFLOW-96 an update to the US Geological Survey Modular Finite-Difference Ground-Water Flow Model U.S.” Geological Survey Open File Report 96-485, Reston Virginia.
Hill, M. C. (1990). “Preconditioned conjugate-gradient 2 (PCG2), a computer program for solving ground-water flow equations”. Department of the Interior, USGeological Survey.
Huang, C. L., Fan, J. C., Liao, K. W., and Lien, T. H. (2013). “A methodology to build a groutability formula via a heuristic algorithm.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 1, pp. 106–116, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-013-1847-y.
Jian-Xia, C., Qiang, H., and Yi-Min, W. (2005). “Genetic algorithms for optimal reservoir dispatching.” Water Resources Management, Vol. 19, No. 4, pp. 321–331, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-005-3018-5.
Jin, J., Crainic. T. G., and Løkketangen A. (2012). “A parallel multineighborhood cooperative Tabu search for capacitated vehicle routing problems.” European Journal of Operational Research, Vol. 222, No. 3, pp. 441–451, DOI: 10.1016/j.ejor.2012.05.025.
Karamouz, M., Tabari, M. M. R., and Kerachian, R. (2007). “Application of genetic algorithms and artificial neural networks in conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources.” Water International, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp. 163–17, DOI: 10.1080/02508060708691973.
Katsifarakis, K. L. (2008). “Groundwater pumping cost minimization–an analytical approach.” Water Resources Management, Vol. 22, No. 8, 1089–1099, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-007-9212-x.
Kerachian, R. and Karamouz, M. (2006). “Optimal reservoir operation considering the water quality issues: A stochastic conflict resolution approach.” Water Resources Research, Vol. 42, No. 12, DOI: 10.1029/2005WR004575.
Lee, S. M., Jin, Y. M., Woo, S K., and Shin D. H. (2013). “Approximate cost estimating model of eco-type trade for river facility construction using case-based reasoning and genetic algorithms.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 17, No. 2, pp. 292–300, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-013-1638-5.
Lee, Y. M. and Ellis, J. H. (1996). “Comparison of algorithms for nonlinear integer optimization: application to monitoring network design.” Journal of Environmental Engineering, Vol. 122, No. 6, pp. 524–531, DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9372(1996)122:6(524).
Mastrolilli, M. and Gambardella, L. M. (2000). “Effective neighborhood functions for the flexible job shop problem.” Journal of Scheduling, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 3–20.
Merabtene, T., Kawamura, A., Jinno, K., and Olsson, J. (2002). “Risk assessment for optimal drought management of an integrated water resources system using a genetic algorithm.” Hydrological Processes, Vol. 16, No. 11, pp. 2189–2208, DOI: 10.1002/hyp.1150.
Moharram, S. H., Gad, M. I., Saafan, T. A., and Allah, S. K. (2012). “Optimal groundwater management using genetic algorithm in El-Farafra oasis, western desert, Egypt.” Water Resources Management, Vol. 26, No. 4, pp. 927–948, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-011-9865-3.
Moutsopoulos S. H., Drossakis C., Papaspyros J. N. E., and Tsihrintzis V. A. (2012) “Optimization of water resources management of the Eidomeni-Evzoni aquifer.” Proceedings of the 11th. International Conference “Protection and Restoration of the Environment”, July 3-6, Thessaloniki, Greece, pp. 748–756.
Park, M., Chung, G., Yoo, C., and Kim, J. H. (2012). “Optimal design of stormwater detention basin using the genetic algorithm.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, Vol. 16, No. 4, pp. 660–666, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-012-0991-0.
Peaceman, D. W. (1978). “Interpretation of well-block pressures in numerical reservoir simulation.” Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, Vol. 18, No. 3, pp. 183–194.
Pisinaras, V., Petalas, C., Tsihrintzis V. A., and Karatzas, G. P. (2012). “Integrated modeling as a decision-aiding tool for groundwater management in a Mediterranean agricultural watershed.” Hydrological Process, Vol. 27, No. 14, pp.1973–1987.
Pliakas, F., Petalas, C., Diamantis, I., and Kallioras, A. (2005). “Modeling of groundwater artificial recharge by reactivating an old stream bed.” Water Resources Management, Vol. 19, No. 3, pp. 279–294, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-005-3472-0.
Psilovikos, A. A. (1996). “Optimum Management in Aquifer Studies Using the Linear Programming (LP) method. An application to Eidomeni -Evzoni area.”, M.Sc. Thesis, Thessaloniki, Greece [in Greek].
Psilovikos, A. (2006). “Response matrix minimization used in groundwater management with mathematical programming: A case study in a transboundary aquifer in northern Greece.” Water Resources Management, Vol. 20, No. 2, pp. 277–290, DOI: 10.1007/s11269-006-0324-5.
Psilovikos, A. A. (1999). “Optimization models in groundwater management, based on linear and mixed integer programming. An application to a Greek hydrogeological basin.” Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part B: Hydrology, Oceans and Atmosphere. Vol. 24, Nos. 1-2, pp. 139–144, DOI: 10.1016/S1464-1909(98)00025-2.
Psilovikos, A. and Tzimopoulos, C. (2004). “Comparison of quadratic and non-linear programming (QP and NLP) optimization models in groundwater management.” Journal of Hydroinformatics, Vol. 6, No. 3, pp. 175–185.
RACM (2010). “Monitoring of surface-water and groundwater resources of Central Macedonia, in the time period 2008-2009.” Regional Authority of Central Macedonia, October 2010.” Thessaloniki, Greece [in Greek].
Sidiropoulos, P., Mylopoulos, N., and Loukas, A. (2013). “Optimal management of an overexploited aquifer under climate change: the lake Karla case.” Water Resources Management, Vol. 27, No. 6, pp. 1635–1649, DOI 10.1007/s11269-012-0083-4.
Tan, C. C., Tung, C. P., Chen, C. H., and Yeh, W. W. G. (2008). “An integrated optimization algorithm for parameter structure identification in groundwater modeling.” Advances in Water Resources, Vol. 31, No. 3, pp. 545–560, DOI: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2007.11.007.
Tselepidou, K. and Katsifarakis, K. L. (2010). “Optimization of the exploitation system of a low enthalpy geothermal aquifer with zones of different transmissivities and temperatures.” Renewable Energy, Vol. 35, No.7, pp. 1408–1413, DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2009.11.004.
Tung, C. P. and Chou, C. A. (2004). “Pattern classification using Tabu search to identify the spatial distribution of groundwater pumping. Hydrogeology Journal, Vol. 12, No. 5, pp. 488–496, DOI: 10.1007/s10040-004-0344-2.
Wang, M. and Zheng, C. (1997). Optimal remediation policy selection under general conditions. Ground Water, Vol. 35, No. 5, pp. 757–764, DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-6584.1997.tb00144.x.
Wang, M. and Zheng, C. (1998). “Ground water management optimization using genetic algorithms and simulated annealing: formulation and comparison.” Journal of the American Water Resources Association. Vol. 34, pp. 519–530, DOI: 10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb00951.x.
Waterloo Hydrogeologic Inc. (2006). “Visual MODFLOW version 4.2 User’s Manual.” Waterloo Hydrogeologic Inc.
Yoo, D. G., Chung, G., Sadollah, A., and Kim, J. H. (2015). “Applications of network analysis and multi-objective genetic algorithm for selecting optimal water quality sensor locations in water distribution networks.” KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering. Vol. 19, No.7, pp. 2333–2344, DOI: 10.1007/s12205-015-0273-8.
Zheng C. and Wang P. (2003). “MGO-A Modular Groundwater Optimizer Incorporating MODFLOW/MT3DMS. Documentation and User’s Guide.” University of Alabama and Groundwater Systems Research Ltd, Tuscaloosa, Alabama.
Zheng, C. and Wang, P. P. (1999). “An integrated global and local optimization approach for remediation system design.” Water Resources Research, Vol. 35, No.1, pp. 137–148, DOI: 10.1029/1998WR900032.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moutsopoulos, K.N., Papaspyros, J.N.E. & Tsihrintzis, V.A. Management of groundwater resources using surface pumps: Optimization using Genetic Algorithms and the Tabu Search method. KSCE J Civ Eng 21, 2968–2976 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1013-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12205-017-1013-z