Abstract
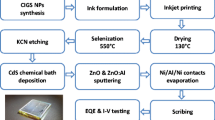
Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 (CZTSSe) is considered as the promising absorbing layer materials for solar cells due to its earth-abundant constituents and excellent semiconductor properties. Through solution-processing, such as various printing methods, the fabrication of high performance CZTSSe solar cell could be applied to mass production with extremely low manufacturing cost and high yield speed. To better fulfill this goal, environmentalfriendly inks/solutions are optimum for further reducing the capital investment on instrument, personnel and environmental safety. In this review, we summarized the recent development of CZTSSe thin films solar cells fabricated with benign solvents, such as water and ethanol. The disperse system can be classified to the true solution (consisting of molecules) and the colloidal suspension (consisting of nanoparticles).Three strategies for stabilization (i.e., physical method, chemical capping and selfstabilization) are proposed to prepare homogeneous and stable colloidal nanoinks. The one-pot self-stabilization method stands as an optimum route for preparing benign inks for its low impurity involvement and simple procedure. As-prepared CZTSSe inks would be deposited onto substrates to form thin films through spin-coating, spraying, electrodeposition or successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) method, followed by annealing in a chalcogen (S- or Se-containing) atmosphere to fabricate absorber. The efficiency of CZTSSe solar cell fabricated with benign solvents can also be enhanced by constituent adjustments, doping, surface treatments and blocking layers modifications, etc., and the deeper research will promise it a comparable performance to the nonbenign CZTSSe systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katagiri H, Jimbo K, Yamada S, Kamimura T, Maw WS, Fukano T, Ito T, Motohiro T. Enhanced conversion efficiencies of Cu2ZnSnS4- based thin film solar cells by using preferential etching technique. Applied Physics Express, 2008, 1(4): 041201
Schubert B A, Marsen B, Cinque S, Unold T, Klenk R, Schorr S, Schock HW. Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cells by fast coevaporation. Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 2011, 19(1): 93–96
Wang W, Winkler M T, Gunawan O, Gokmen T, Todorov T K, Zhu Y, Mitzi D B. Device characteristics of CZTSSe thin-film solar cells with 12.6% efficiency. Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(7): doi: 10.1002/aenm.201301465
Zhang H, Hu B, Sun L, Hovden R, Wise FW, Muller D A, Robinson R D. Surfactant ligand removal and rational fabrication of inorganically connected quantum dots. Nano Letters, 2011, 11 (12): 5356–5361
Kamoun N, Bouzouita H, Rezig B. Fabrication and characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis technique. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(15): 5949–5952
Zeng X, Tai K F, Zhang T, Ho C W J, Chen X, Huan A, Sum T C, Wong L H. Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 kesterite solar cell with 5.1% efficiency using spray pyrolysis of aqueous precursor solution followed by selenization. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2014, 124: 55–60
Vigil-Galán O, Courel M, Espindola-Rodriguez M, Izquierdo-Roca V, Saucedo E, Fairbrother A. Toward a high Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cell efficiency processed by spray pyrolysis method. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2013, 5(5): 053137
Yeh M Y, Lee C C, Wuu D S. Influences of synthesizing temperatures on the properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 prepared by sol–gel spin-coated deposition. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2009, 52(1): 65–68
Jiang M, Lan F, Yan X, Li G. Cu2ZnSn(S1-x Sex)4thin film solar cells prepared by water-based solution process. Physica Status Solidi (RRL)- Rapid Research Letters, 2014, 8(3): 223–227
Jiang M, Li Y, Dhakal R, Thapaliya P, Mastro M, Caldwell J, Kub F, Yan X. Cu2ZnSnS4 polycrystalline thin films with large densely packed grains prepared by sol-gel method. Journal of Photonics for Energy, 2011, 1(1): 019501
Tian Q, Huang L, Zhao W, Yang Y, Wang G, Pan D. Metal sulfide precursor aqueous solutions for fabrication of Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin film solar cells. Green Chemistry, 2015, 17(2): 1269–1275
Kishore Kumar Y B, Suresh Babu G, Uday Bhaskar P, Sundara Raja V. Preparation and characterization of spray-deposited Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2009, 93(8): 1230–1237
Zhong J, Xia Z, Zhang C, Li B, Liu X, Cheng Y B, Tang J. One-pot synthesis of self-stabilized aqueous nanoinks for Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 solar cells. Chemistry of Materials, 2014, 26(11): 3573–3578
Woo K, Kim Y, Moon J. A non-toxic, solution-processed, earth abundant absorbing layer for thin-film solar cells. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(1): 5340–5345
Larramona G, Bourdais S, Jacob A, Choné C, Muto T, Cuccaro Y, Delatouche B, Moisan C, Péré D, Dennler G. Efficient Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells spray coated from a hydro-alcoholic colloid synthesized by instantaneous reaction. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(28): 14655–14662
Larramona G, Bourdais S, Jacob A, Choné C, Muto T, Cuccaro Y, Delatouche B, Moisan C, Péré D, Dennler G. 8.6% efficient CZTSSe solar cells sprayed from water–ethanol CZTS colloidal solutions. Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2014, 5(21): 3763–3767
Li Z, Ho J C W, Lee K K, Zeng X, Zhang T, Wong L H, Lam Y M. Environmentally friendly solution route to kesterite Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin films for solar cell applications. RSC Advances, 2014, 4(51): 26888–26894
Chen G, Yuan C, Liu J, Huang Z, Chen S, Liu W, Jiang G, Zhu C. Fabrication of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films using oxides nanoparticles ink for solar cell. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 276: 145–152
van Embden J, Chesman A S, Della Gaspera E, Duffy NW, Watkins S E, Jasieniak J J. Cu2ZnSnS4xSe4(1–x ) solar cells from polar nanocrystal inks. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(14): 5237–5240
Kang C C, Chen H F, Yu T C, Lin T C. Aqueous synthesis of wurtzite Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals. Materials Letters, 2013, 96: 24–26
Kush P, Ujjain S K, Mehra N C, Jha P, Sharma R K, Deka S. Development and properties of surfactant-free water-dispersible Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals: a material for low-cost photovoltaics. Chemphyschem: a European journal of Chemical Physics and Physical Chemistry, 2013, 14(12): 2793–2799
Liu W, Guo B, Mak C, Li A, Wu X, Zhang F. Facile synthesis of ultrafine Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals by hydrothermal method for use in solar cells. Thin Solid Films, 2013, 535: 39–43
Tian Q, Xu X, Han L, Tang M, Zou R, Chen Z, Yu M, Yang J, Hu J. Hydrophilic Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals for printing flexible, low-cost and environmentally friendly solar cells. CrystEngComm, 2012, 14 (11): 3847–3850
Hsu K C, Liao J D, Chao L M, Fu Y S. Fabrication and characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 powders by a hydrothermal method. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 52(6R): 061202
Camara S M, Wang L, Zhang X. Easy hydrothermal preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) nanoparticles for solar cell application. Nanotechnology, 2013, 24(49): 495401
Jiang H, Dai P, Feng Z, Fan W, Zhan J. Phase selective synthesis of metastable orthorhombic Cu2ZnSnS4. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(15): 7502–7506
Tiong V T, Bell J, Wang H. One-step synthesis of high quality kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals- a hydrothermal approach. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology, 2014, 5: 438–446
Tiong V T, Zhang Y, Bell J, Wang H. Phase-selective hydrothermal synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals: the effect of the sulphur precursor. CrystEngComm, 2014, 16(20): 4306–4313
Zhao Y, Zhou W H, Jiao J, Zhou Z J, Wu S X. Aqueous synthesis and characterization of hydrophilic Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystals. Materials Letters, 2013, 96: 174–176
Kovalenko M V, Scheele M, Talapin D V. Colloidal nanocrystals with molecular metal chalcogenide surface ligands. Science, 2009, 324(5933): 1417–1420
Kovalenko MV, Bodnarchuk MI, Zaumseil J, Lee J S, Talapin D V. Expanding the chemical versatility of colloidal nanocrystals capped with molecular metal chalcogenide ligands. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(29): 10085–10092
Jiang C, Lee J S, Talapin D V. Soluble precursors for CuInSe2, CuIn1–x GaxSe2, and Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 based on colloidal nanocrystals and molecular metal chalcogenide surface ligands. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(11): 5010–5013
Zhou H, Duan H S, Yang W, Chen Q, Hsu C J, Hsu WC, Chen C C, Yang Y. Facile single-component precursor for Cu2ZnSnS4 with enhanced phase and composition controllability. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(3): 998–1005
Su Z, Sun K, Han Z, Cui H, Liu F, Lai Y, Li J, Hao X, Liu Y, Green M A. Fabrication of Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells with 5.1% efficiency via thermal decomposition and reaction using a non-toxic sol–gel route. Journal of Materials Chemistry. A, Materials for Energy and Sustainability, 2014, 2(2): 500–509
Kim S, Kim J. Effect of selenization on sprayed Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cell. Thin Solid Films, 2013, 547: 178–180
Scragg J J, Berg D M, Dale P J A. 3.2% efficient Kesterite device from electrodeposited stacked elemental layers. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 2010, 646(1–2): 52–59
Araki H, Kubo Y, Mikaduki A, Jimbo K, Maw W S, Katagiri H, Yamazaki M, Oishi K, Takeuchi A. Preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films by sulfurizing electroplated precursors. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2009, 93(6–7): 996–999
Scragg J J, Dale P J, Peter L M. Towards sustainable materials for solar energy conversion: preparation and photoelectrochemical characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4. Electrochemistry Communications, 2008, 10(4): 639–642
Scragg J J, Dale P J, Peter L M. Synthesis and characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber layers by an electrodeposition-annealin88g route. Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517(7): 2481–2484
Iljina J, Zhang R, Ganchev M, Raadik T, Volobujeva O, Altosaar M, Traksmaa R, Mellikov E. Formation of Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber layers for solar cells by electrodeposition-annealing route. Thin Solid Films, 2013, 537: 85–89
Ennaoui A, Lux-Steiner M, Weber A, Abou-Ras D, Kötschau I, Schock H W, Schurr R, Hölzing A, Jost S, Hock R, Voß T, Schulze J, Kirbs A. Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cells from electroplated precursors: Novel low-cost perspective. Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517 (7): 2511–2514
Wang Y, Ma J, Liu P, Chen Y, Li R, Gu J, Lu J, Yang S, Gao X. Cu2ZnSnS4 films deposited by a co-electrodeposition-annealing route. Materials Letters, 2012, 77: 13–16
Pawar S M, Pawar B S, Moholkar A V, Choi D S, Yun J H, Moon J H, Kolekar S S, Kim J H. Single step electrosynthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films for solar cell application. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(12): 4057–4061
Schurr R, Hölzing A, Jost S, Hock R, Voß T, Schulze J, Kirbs A, Ennaoui A, Lux-Steiner M, Weber A, Kötschau I, Schock HW. The crystallisation of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cell absorbers from coelectroplated Cu–Zn–Sn precursors. Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517 (7): 2465–2468
Chan C P, Lam H, Surya C. Preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 films by electrodeposition using ionic liquids. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2010, 94(2): 207–211
Mali S S, Patil B M, Betty C A, Bhosale P N, Oh Y W, Jadkar S R, Devan R S, Ma Y R, Patil P S. Novel synthesis of kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 nanoflakes by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction echnique: characterization and application. Electrochimica Acta, 2012, 66: 216–221
Mali S S, Shinde P S, Betty C A, Bhosale P N, Oh Y W, Patil P S. Synthesis and characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films by SILAR method. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2012, 73(6): 735–740
Shinde N M, Dubal D P, Dhawale D S, Lokhande C D, Kim J H, Moon J H. Room temperature novel chemical synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) absorbing layer for photovoltaic application. Materials Research Bulletin, 2012, 47(2): 302–307
Shinde N M, Deshmukh P R, Patil S V, Lokhande C D. Aqueous chemical growth of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films: air annealing and photoelectrochemical properties. Materials Research Bulletin, 2013, 48(5): 1760–1766
Patel K, Shah D V, Kheraj V. Influence of deposition parameters and annealing on Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films grown by SILAR. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2015, 622: 942–947
Su Z, Yan C, Sun K, Han Z, Liu F, Liu J, Lai Y, Li J, Liu Y. Preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films by sulfurizing stacked precursor thin films via successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(19): 7678–7682
Gao C, Shen H, Jiang F, Guan H. Preparation of Cu2ZnSnS4 film by sulfurizing solution deposited precursors. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 261: 189–192
Wangperawong A, King J S, Herron S M, Tran B P, Pangan-Okimoto K, Bent S F. Aqueous bath process for deposition of Cu2ZnSnS4 photovoltaic absorbers. Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(8): 2488–2492
Moriya K, Tanaka K, Uchiki H. Characterization of Cu2ZnSnS4thin films prepared by photo-chemical deposition. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2005, 44(1B): 715–717
Shinde N M, Lokhande C D, Kim J H, Moon J H. Low cost and large area novel chemical synthesis of Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) thin films. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A Chemistry, 2012, 235: 14–20
Chen S, Walsh A, Gong X G, Wei S H. Classification of lattice defects in the kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 and Cu2ZnSnSe4 earth-abundant solar cell absorbers. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(11): 1522–1539
Hergert F, Hock R. Predicted formation reactions for the solid-state syntheses of the semiconductor materials Cu2SnX3 and Cu2ZnSnX4 (X = S, Se) starting from binary chalcogenides. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(15): 5953–5956
Shin SW, Pawar SM, Park C Y, Yun J H, Moon J H, Kim J H, Lee J Y. Studies on Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) absorber layer using different stacking orders in precursor thin films. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2011, 95(12): 3202–3206
Mitzi D B, Gunawan O, Todorov T K, Wang K, Guha S. The path towards a high-performance solution-processed kesterite solar cell. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2011, 95(6): 1421–1436
Polizzotti A, Repins I L, Noufi R, Wei S H, Mitzi D B. The state and future prospects of kesterite photovoltaics. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(11): 3171–3182
Vigil-Galán O, Courel M, Andrade-Arvizu J A, Sánchez Y, Espíndola-Rodríguez M, Saucedo E, Seuret-Jiménez D, Titsworth M. Route towards low cost-high efficiency second generation solar cells: current status and perspectives. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(8): 5562–5573
Chen S, Gong X G, Walsh A, Wei S H. Defect physics of the kesterite thin-film solar cell absorber Cu2ZnSnS4. Applied Physics Letters, 2010, 96(2): 021902
Vigil-Galán O, Espíndola-Rodríguez M, Courel M, Fontané X, Sylla D, Izquierdo-Roca V, Fairbrother A, Saucedo E, Pérez-Rodríguez A. Secondary phases dependence on composition ratio in sprayed Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films and its impact on the high power conversion efficiency. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2013, 117: 246–250
Wen Q, Li Y, Yan J, Wang C. Crystal size-controlled growth of Cu2ZnSnS4 films by optimizing the Na doping concentration. Materials Letters, 2015, 140: 16–19
Prabhakar T, Jampana N. Effect of sodium diffusion on the structural and electrical properties of Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2011, 95(3): 1001–1004
Tong Z, Yan C, Su Z, Zeng F, Yang J, Li Y, Jiang L, Lai Y, Liu F. Effects of potassium doping on solution processed kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cells. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 105(22): 223903
Johnson M, Baryshev S V, Thimsen E, Manno M, Zhang X, Veryovkin I V, Leighton C, Aydil E S. Alkali-metal-enhanced grain growth in Cu2ZnSnS4thin films. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(6): 1931–1938
Zhou H, Song T B, Hsu WC, Luo S, Ye S, Duan H S, Hsu C J, Yang W, Yang Y. Rational defect passivation of Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 photovoltaics with solution-processed Cu2ZnSnS4:Na nanocrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(43): 15998–16001
Nagaoka A, Miyake H, Taniyama T, Kakimoto K, Nose Y, Scarpulla M A, Yoshino K. Effects of sodium on electrical properties in Cu2ZnSnS4 single crystal. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(15): 152101
Todorov T, Mitzi D B. Direct liquid coating of chalcopyrite lightabsorbing layers for photovoltaic devices. European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2010, 2010(1): 17–28
Zhong J, Xia Z, Luo M, Zhao J, Chen J, Wang L, Liu X, Xue D J, Cheng Y B, Song H, Tang J. Sulfurization induced surface constitution and its correlation to the performance of solutionprocessed Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 solar cells. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6288–6296
Walter T, Herberholz R, Müller C, Schock H W. Determination of defect distributions from admittance measurements and application to Cu(In,Ga)Se2 based heterojunctions. Journal of Applied Physics, 1996, 80(8): 4411
Shin B, Bojarczuk N A, Guha S. On the kinetics of MoSe2 interfacial layer formation in chalcogen-based thin film solar cells with a molybdenum back contact. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(9): 091907
Cui H, Lee C Y, Li W, Liu X, Wen X, Hao X. Improving efficiency of evaporated Cu2ZnSnS4 thin film solar cells by a thin Ag intermediate layer between absorber and back contact. International Journal of Photoenergy, 2015, 170507
Liu X, Cui H, Li W, Song N, Liu F, Conibeer G, Hao X. Improving Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) solar cell performance by an ultrathin ZnO intermediate layer between CZTS absorber and Mo back contact. Physica Status Solidi (RRL)- Rapid Research Letters, 2014, 8(12): 966–970
Shin B, Gunawan O, Zhu Y, Bojarczuk N A, Chey S J, Guha S. Thin film solar cell with 8.4%power conversion efficiency using an earthabundant Cu2ZnSnS4 absorber. Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 2013, 21(1): 72–76
Liu F, Sun K, Li W, Yan C, Cui H, Jiang L, Hao X, Green M A. Enhancing the Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cell efficiency by back contact modification: inserting a thin TiB2 intermediate layer at Cu2ZnSnS4/ Mo interface. Applied Physics Letters, 2014, 104(5): 051105
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Cheng Zhang was an undergraduate student at Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (WNLO) at Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He obtained his bachelor degree under the supervision of Dr. Jie Zhong and Prof. Jiang Tang from 2014 to 2015. He will start his Ph.D. study in Prof. Jian Lin’s group at the Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering at University of Missouri-Columbia. His research focuses on advanced materials synthesis and processing.
Jie Zhong currently is an associate professor at State Key Laboratory of Advanced Technology for Materials Synthesis and Processing, Wuhan University of Technology (WHUT). Before that, he worked at Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics (WNLO) at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST) as a postdoctoral researcher and lecturer. He received his Ph.D. degree in materials science and engineering in Central South University (CSU) in 2012. From 2008 to 2012, he conducted research as a visiting student and later as a research assistant at Department of Materials Engineering in Monash University. Jie’s research interest is now focused on synthesizing green inks of semiconductors (copper zinc tin sulfoselenide, perovskite and etc.), and producing photovoltaic and sensing devices via printing routes.
Jiang Tang is now a professor at Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. He received his bachelor’s degree from University of Science and Technology of China and his Ph.D. degree from University of Toronto in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering under the supervision of Prof. Edward H. Sargent. His research interest is chalcogenide thin film solar cells and colloidal quantum dot optoelectronic devices. He is the research pioneer of antimony selenide (Sb2Se3) thin film photovoltaics.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Zhong, J. & Tang, J. Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin film solar cells fabricated with benign solvents. Front. Optoelectron. 8, 252–268 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-015-0539-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-015-0539-2