Abstract
Energy-sensitive photon counting detectors (PCDs) have recently been developed for medical X-ray computed tomography (CT) imaging and a handful of prototype PCD-CT systems have been built and evaluated. PCDs detect X-rays by using mechanisms that are completely different from the current CT detectors (i.e., energy integrating detectors or EIDs); PCDs count photons and obtain the information of the object tissues (i.e., the effective atomic numbers and mass densities) to be imaged. Therefore, these PCDs have the potential not only for evolution—to improve the current CT images such as providing dose reduction—but also for a revolution—to enable novel applications with a new concept such as molecular CT imaging. The performance of PCDs, however, is not flawless, and thus, it requires integrated efforts to develop PCD-CT for clinical use. In this article, we review the current status and the prediction for the future of PCDs, PCD-CT systems, and potential clinical applications.

Figures are reprinted with a modification from Taguchi and Iwanczyk (Ref. [1])

Figures are reprinted from Koenig et al. (Ref. [38])

The figure is reprinted from Xu et al. (Ref. [29])

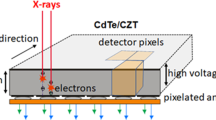
Figures are reprinted from Taguchi and Iwanczyk (Ref. [1])

Figures are reprinted from Taguchi et al. (Ref. [45])

Figures are reprinted from Taguchi and Iwanczyk (Ref. [1])

Figures are reprinted with modifications from Nakada et al. (Ref. [59])

Figures are reprinted with modifications from Cammin et al. (Ref. [67])
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taguchi K, Iwanczyk JS. Vision 20/20: single photon counting X-ray detectors in medical imaging. Med Phys. 2013;40:100901.
Mettler FA Jr, Wiest PW, Locken JA, Kelsey CA. CT scanning: patterns of use and dose. J Radiol Prot. 2000;20:353–9.
Swank RK. Absorption and noise in X-ray phosphors. J Appl Phys. 1973;44:4199–203.
Iwanczyk JS, Nygard E, Meirav O, Arenson J, Barber WC, Hartsough NE, et al. Photon counting energy dispersive detector arrays for X-ray imaging. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2009;56:535–42.
Schlomka JP, Roessl E, Dorscheid R, Dill S, Martens G, Istel T, et al. Experimental feasibility of multi-energy photon-counting K-edge imaging in pre-clinical computed tomography. Phys Med Biol. 2008;53:4031–47.
Shikhaliev PM. Energy-resolved computed tomography: first experimental results. Phys Med Biol. 2008;53:5595–613.
Barber WC, Nygard E, Iwanczyk JS, Zhang M, Frey EC, Tsui BMW, et al. Characterization of a novel photon counting detector for clinical CT: count rate, energy resolution, and noise performance. Lake Buena Vista: In: Presented at the SPIE medical imaging 2009: physics of medical imaging; 2009.
Feuerlein S, Roessl E, Proksa R, Martens G, Klass O, Jeltsch M, et al. Multienergy photon-counting K-edge imaging: potential for improved luminal depiction in vascular imaging. Radiology. 2008;249:1010–6.
Tomita Y, Shirayanagi Y, Matsui S, Aoki T, Hatanaka Y. X-ray color scanner with multiple energy discrimination capability. San Diego: In: Presented at the medical imaging 2005: physics of medical imaging; 2005.
Tomita Y, Shirayanagi Y, Matsui S, Misawa M, Takahashi H, Aoki T, et al. X-ray color scanner with multiple energy differentiate capability. Roma: In: Presented at the IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference; 2004.
Butler APH, Anderson NG, Tipples R, Cook N, Watts R, Meyer J, et al. Bio-medical X-ray imaging with spectroscopic pixel detectors. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 2008;591:141–6.
Ballabriga R, Campbell M, Heijne EHM, Llopart X, Tlustos L. The Medipix3 prototype, a pixel readout chip working in single photon counting mode with improved spectrometric performance. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2007;54:1824–9.
Firsching M, Butler AP, Scott N, Anderson NG, Michel T, Anton G. Contrast agent recognition in small animal CT using the Medipix2 detector. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 2009;607:179–82.
Kraft E, Fischer P, Karagounis M, Koch M, Krueger H, Peric I, et al. Counting and integrating readout for direct conversion X-ray imaging: concept, realization and first prototype measurements. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2007;54:383–90.
Steadman R, Herrmann C, Mulhens O, Maeding DG, Colley J, Firlit T, et al. ChromAIX: a high-rate energy-resolving photon-counting ASIC for spectral computed tomography. San Diego: In: Presented at the medical imaging 2010: physics of medical imaging; 2010.
Kappler S, Glasser F, Janssen S, Kraft E, Reinwand M. A research prototype system for quantum-counting clinical CT. San Diego: In: Presented at the medical imaging 2010: physics of medical imaging; 2010.
Barber WC, Arodzero A, Malakhov N, Damron MQ, Hartsough NE, Moraes D, et al. Guard ring elimination in CdTe and CdZnTe detectors. San Diego: In: Presented at the IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference; 2006.
Iwanczyk JS, Nygard E, Meirav O, Arenson J, Barber WC, Hartsough NE, et al. Photon counting energy dispersive detector arrays for X-ray imaging. Honolulu: In: Presented at the IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference; 2007.
Barber WC, Wessel JC, Nygard E, Malakhov N, Wawrzyniak G, Hartsough NE, et al. High flux X-ray imaging with CdZnTe arrays. Anaheim: In: Presented at the IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference; 2012.
Rupcich F, Gilat-Schmidt T. Experimental study of optimal energy weighting in energy-resolved CT using a CZT detector. Orlando: In: Presented at the medical imaging 2013: physics of medical imaging; 2013.
Cajipe VB, Calderwood RF, Clajus M, Hayakawa S, Jayaraman R, Tumer TO, et al. Multi-energy X-ray imaging with linear CZT pixel arrays and integrated electronics. In: Presented at the nuclear science symposium conference record, 2004. Rome: IEEE; 2004.
Xu C, Danielsson M, Karlsson S, Svensson C, Bornefalk H. Performance characterization of a silicon strip detector for spectral computed tomography utilizing a laser testing system. Orlando: In: Presented at the SPIE Medical Imaging 2011; 2011.
Fredenberg E, Hemmendorff M, Cederstrom B, Aslund M, Danielsson M. Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography with a photon-counting detector. Med Phys. 2010;37:2017–29.
Fredenberg E, Lundqvist M, Cederström B, Åslund M, Danielsson M. Energy resolution of a photon-counting silicon strip detector. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 2010;613:156–62.
Aslund M, Cederstrom B, Lundqvist M, Danielsson M. Physical characterization of a scanning photon counting digital mammography system based on Si-strip detectors. Med Phys. 2007;34:1918–25.
Xu C, Danielsson M, Karlsson S, Svensson C, Bornefalk H. Preliminary evaluation of a silicon strip detector for photon-counting spectral CT. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 2012;677:45–51.
Kappler S, Hannemann T, Kraft E, Kreisler B, Niederloehner D, Stierstorfer K, et al. First results from a hybrid prototype CT scanner for exploring benefits of quantum-counting in clinical CT. San Diego: In: Presented at the Proceedings of the SPIE 8313, medical imaging, physics of medical imaging; 2012.
Gimenez EN, Ballabriga R, Campbell M, Horswell I, Llopart X, Marchal J, et al. Characterization of Medipix3 with synchrotron radiation. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2011;58:323–32.
Xu C, Chen H, Persson M, Karlsson S, Danielsson M, Svensson C, et al. Energy resolution of a segmented silicon strip detector for photon-counting spectral CT. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 2013;715:11–7.
Xu C, Danielsson M, Bornefalk H. Evaluation of energy loss and charge sharing in cadmium telluride detectors for photon-counting computed tomography. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2011;58:614–25.
Xu C, Persson M, Han C, Karlsson S, Danielsson M, Svensson C, et al. Evaluation of a second-generation ultra-fast energy-resolved ASIC for photon-counting spectral CT. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2013;60:437–45.
Roessl E, Proksa R. K-edge imaging in X-ray computed tomography using multi-bin photon counting detectors. Phys Med Biol. 2007;52:4679–96.
Tanguay J, Kim HK, Cunningham IA. The role of X-ray Swank factor in energy-resolving photon-counting imaging. Med Phys. 2010;37:6205–11.
Taguchi K, Polster C, Lee O, Stierstorfer K, Kappler S. Spatio-energetic cross talk in photon counting detectors: detector model and correlated Poisson data generator. Med Phys. 2016;43:6386–404.
Kappler S, Henning A, Kreisler B, Schoeck F, Stierstorfer K, Flohr T. Photon counting CT at elevated X-ray tube currents: contrast stability, image noise and multi-energy performance. San Diego: In: Presented at the SPIE medical imaging 2014: physics of medical imaging; 2014.
Kappler S, Hoelzer S, Kraft E, Stierstorfer K, Flohr TG. Quantum-counting CT in the regime of count-rate paralysis: introduction of the pile-up trigger method. Orlando: In: Presented at the proceedings of the SPIE 7661, medical imaging: physics of medical imaging; 2011.
Kappler S, Kraft E, Kreisler B, Schoeck F, Flohr TG. Imaging performance of a hybrid research prototype CT scanner with small-pixel counting detector. Geneva: In: Presented at the workshop on medical applications of spectroscopic X-ray detectors; 2013.
Koenig T, Hamann E, Procz S, Ballabriga R, Cecilia A, Zuber M, et al. Charge summing in spectroscopic X-ray detectors with high-Z sensors. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 2013;60:4713–8.
Gardner RP, Wielopolski L. A generalized method for correcting pulse-height spectra for the peak pileup effect due to double sum pulses. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 1977;140:289–96.
Hero AO, Clinthorne NH, Rogers WL. A lower bound on PET timing estimation with pulse pileup. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci. 1991;38:709–12.
Johns PC, Yaffe MJ. Correction of pulse-height spectra for peak pileup effects using periodic and random pulse generators. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 1987;255:559–81.
Wang AS, Harrison D, Lobastov V, Tkaczyk JE. Pulse pileup statistics for energy discriminating photon counting X-ray detectors. Med Phys. 2011;38:4265–75.
Taguchi K, Srivastava S, Tang Q, Caffo BS, Iwanczyk JS, Hartsough NE, et al. Pulse pileup statistics for energy sensitive photon counting detectors with pulse height analysis. San Diego: In: Presented at the SPIE medical imaging 2012: physics of medical imaging; 2012.
Cammin J, Xu J, Barber WC, Iwanczyk JS, Hartsough NE, Taguchi K. A cascaded model of spectral distortions due to spectral response effects and pulse pileup effects in a photon-counting X-ray detector for CT. Med Phys. 2014;41:041905.
Taguchi K, Frey EC, Wang X, Iwanczyk JS, Barber WC. An analytical model of the effects of pulse pileup on the energy spectrum recorded by energy resolved photon counting X-ray detectors. Med Phys. 2010;37:3957–69.
Taguchi K, Zhang M, Frey EC, Wang X, Iwanczyk JS, Nygard E, et al. Modeling the performance of a photon counting X-ray detector for CT: energy response and pulse pileup effects. Med Phys. 2011;38:1089–102.
Roessl E, Daerr H, Proksa R. A Fourier approach to pulse pile-up in photon-counting X-ray detectors. Med Phys. 2016;43:1295–8.
Hsieh SS, Pelc NJ. The feasibility of a piecewise-linear dynamic bowtie filter. Med Phys. 2013;40:031910.
Roessl E, Proksa R. Dynamic beam-shaper for high flux photon-counting computed tomography. Geneva: In: Presented at the workshop on medical applications of spectroscopic X-ray detectors; 2013.
Alvarez RE. Estimator for photon counting energy selective X-ray imaging with multibin pulse height analysis. Med Phys. 2011;38:2324–34.
Lee O, Kappler S, Polster C, Taguchi K. Estimation of basis line-integrals for spectral distortion compensation in photon counting CT using low-order polynomial approximation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2016 (in press).
Lee O, Polster C, Kappler S, Taguchi K. Spectral response effect-compensated estimator in photon counting CT using low-order Gram polynomials. In: Presented at the forth international conference on image formation in X-ray computed tomography, Bamberg, 2016.
Xu J, Zbijewski W, Gang G, Stayman JW, Taguchi K, Lundqvist M et al. Cascaded systems analysis of photon counting detectors. Med Phys. 2014; 41:101907.
Shikhaliev PM. Beam hardening artefacts in computed tomography with photon counting, charge integrating and energy weighting detectors: a simulation study. Phys Med Biol. 2005;50:5813–27.
Leng S, Yu L, Wang J, Fletcher JG, Mistretta CA, McCollough CH. Noise reduction in spectral CT: reducing dose and breaking the trade-off between image noise and energy bin selection. Med Phys. 2011;38:4946–57.
Schirra CO, Roessl E, Koehler T, Brendel B, Thran A, Pan D, et al. Statistical reconstruction of material decomposed data in spectral CT. IEEE Trans Med Imag. 2013;32:1249–57.
Nakada K, Taguchi K, Fung GSK, Amaya K. Joint estimation of tissue types and linear attenuation coefficients for photon counting CT. Seoul: In: Presented at the IEEE nuclear science symposium and medical imaging conference; 2013.
Nakada K, Taguchi K, Fung GSK, Amaya K. Maximum a posteriori reconstruction of CT images using pixel-based latent variable of tissue types. In: Presented at the third international conference on image formation in X-ray computed tomography, Salt Lake City, 2014.
Nakada K, Taguchi K, Fung GSK, Amaya K. Joint estimation of tissue types and linear attenuation coefficients for photon counting CT. Med Phys. 2015;42:5329–41.
Nakada K. Joint estimation of tissue types and linear attenuation coefficients using image segmentation algorithm for photon counting CT. Master of science thesis. Department of Systems and Control Engineering, School of Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology; 2016. p. 58.
Zhicong Y, Shuai L, Steven MJ, Zhoubo L, Ralf G, Baiyu C, et al. Evaluation of conventional imaging performance in a research whole-body CT system with a photon-counting detector array. Phys Med Biol. 2016;61:1572.
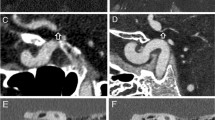
Pourmorteza A, Symons R, Sandfort V, Mallek M, Fuld MK, Henderson G, et al. Abdominal imaging with contrast-enhanced photon-counting CT: first human experience. Radiology. 2016;279:239–45.
Muenzel D, Bar-Ness D, Roessl E, Blevis I, Bartels M, Fingerle AA, et al. Spectral photon-counting CT: initial experience with dual-contrast agent K-edge colonography. Radiology 2016; 160890 (online doi:10.1148/radiol.2016160890).
Cormode DP, Roessl E, Thran A, Skajaa T, Gordon RE, Schlomka J-P, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque composition: analysis with multicolor CT and targeted gold nanoparticles. Radiology 2010;256: 774–82.
Pan D, Williams TA, Senpan A, Allen JS, Scott MJ, Gaffney PJ, et al. Detecting vascular biosignatures with a colloidal, radio-opaque polymeric nanoparticle. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:15522–7.
Pan D, Roessl E, Schlomka J-P, Caruthers SD, Senpan A, Scott MJ, et al. Computed tomography in color: nanoK-enhanced spectral CT molecular imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:9635–9.
Cammin J, Srivastava S, Fung GSK, Taguchi K. Spectral response compensation for photon counting clinical X-ray CT and application to coronary vulnerable plaque detection. In: Proceedings of the second international meeting on image formation in X-ray computed tomography, Salt Lake City; 2012. pp. 186–189.
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful for the financial support received from Siemens Healthcare GmbH (Nos. JHU-2015-CT-1-01-Taguchi-C00218347, JHU-2015-CT-1xx-01-Taguchi-C00219287, and JHU-2016-CT-1-01-Taguchi_C0022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author received financial supports from Siemens Healthcare GmbH (Nos. JHU-2015-CT-1-01-Taguchi-C00218347, JHU-2015-CT-1xx-01-Taguchi-C00219287, and JHU-2016-CT-1-01-Taguchi_C0022). The author is a consultant to LISIT, Co., Ltd. (Life Saving Imaging Technologies) (Tokyo, Japan) and JOB Corporation (Yokohama, Japan).
Animal and human research
There is no animal nor humans involved in this work.
Informed consent
There is no subject to inform to, as there is no human subjects involved in this work.
About this article
Cite this article
Taguchi, K. Energy-sensitive photon counting detector-based X-ray computed tomography. Radiol Phys Technol 10, 8–22 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-017-0390-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12194-017-0390-9