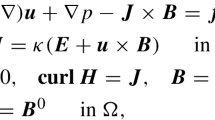Abstract
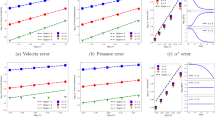
In this report, we present and study a fully discrete finite element variational multiscale scheme for the unsteady incompressible Navier–Stokes equations where high Reynolds numbers are allowed. The scheme uses conforming finite element pairs for spatial discretization and a three-point difference formula for temporal discretization which is of second-order, where a stabilization term based on two local Gauss integrations is employed to stabilize the numerical scheme. We prove stability of the scheme, derive a priori error estimates for the fully discrete solution, and finally, give some numerical results to verify the theoretical predictions and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed numerical scheme.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Girault, V., Raviart, P.A.: Finite Element Methods for Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Algorithms. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg (1986)
Glowinski, R.: Finite element methods for incompressible viscous flow. In: Ciarlet, P.G., Lions, J.L. (eds.) Handbook of Numerical Analysis, Numerical Methods for Fluids (Part 3), vol. 9. Elsevier Science Publisher, Amsterdam (2003)
Elman, H.C., Silvester, D.J., Wathen, A.J.: Finite Elements and Fast Iterative Solvers: With Applications in Incompressible Fluid Dynamics. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2005)
Zienkiewicz, O.C., Taylor, R.C., Nietharasu, P.: The Finite Element Method for Fluid Dynamics, 6th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Burlington (2005)
Feng, X.L., He, Y.N., Huang, P.Z.: A stabilized implicit fractional-step method for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations using equal-order pairs. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 392(2), 209–224 (2012)
He, Y.N.: Two-level method based on finite element and Crank–Nicolson extrapolation for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 41(4), 1263–1285 (2003)
He, Y.N., Liu, K.M.: A multilevel finite element method in space-time for the Navier–Stokes problem. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 21(6), 1052–1078 (2005)
Li, J., Chen, Z.X.: A new stabilized finite volume method for the stationary Stokes equations. Adv. Comput. Math. 30, 141–152 (2009)
Wen, G.B., Chen, Z.B.: Unsteady/steady numerical simulation of three-dimensional incompressible Navier–Stokes equations on artificial compressibility. Appl. Math. Mech. (English Edition) 25(1), 59–77 (2004)
Layton, W., Lee, H., Peterson, J.: A defect-correction method for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Math. Comput. 129, 1–19 (2002)
Wang, K.: A new defect correction method for the Navier–Stokes equations at high Reynolds numbers. Appl. Math. Comput. 11(216), 3252–3264 (2010)
Liu, Q.F., Hou, Y.R.: A two-level defect-correction method for Navier–Stokes equations. B. Aust. Math. Soc. 81, 442–454 (2010)
Kaya, S., Layton, W., Riviere, B.: Subgrid stabilized defect correction methods for the Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM. Numer. Anal. 44, 1639–1654 (2006)
Guermond, J.-L., Marra, A., Quartapelle, L.: Subgrid stabilized projection method for 2D unsteady flows at high Reynolds numbers. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 195, 5857–5876 (2006)
Galvin, K.J.: New subgrid artificial viscosity Galerkin methods for the Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 200, 242–250 (2011)
Zhang, Y., He, Y.N.: Assessment of subgrid-scale models for the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 234, 593–604 (2010)
Shang, Y.Q.: A two-level subgrid stabilized Oseen iterative method for the steady Navier–Stokes equations. J. Comput. Phys. 233, 210–226 (2013)
Hughes, T., Mazzei, L., Jansen, K.: Large eddy simulation and the variational multiscale method. Comput. Vis. Sci. 3, 47–59 (2000)
John, V., Kaya, S.: A finite element variational multiscale method for the Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 26, 1485–1503 (2005)
Li, J., He, Y.N.: A stabilized finite element method based on two local Gauss integrations for the Stokes equations. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 214, 58–65 (2008)
He, Y.N., Li, J.: A stabilized finite element method based on local polynomial pressure projection for the stationary Navier–Stokes equations. Appl. Numer. Math. 58, 1503–1514 (2008)
Zheng, H.B., Hou, Y.R., Shi, F., Song, L.N.: A finite element variational multiscale method for incompressible flows based on two local Gauss integrations. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 5961–5977 (2009)
Zheng, H.B., Hou, Y.R., Shi, F.: Adaptive finite element variational multiscale method for incompressible flows based on two local Gauss integrations. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 7030–7041 (2010)
Shi, F., Zheng, H.B., Yu, J., Li, Y.: On the convergence of variational multiscale methods based on Newton’s iteration for the incompressible flows. Appl. Math. Model. 38, 5726–5742 (2014)
Li, Y., Mei, L.Q., Li, Y., Zhao, K.: A two-level variational multiscale method for incompressible flows based on two local Gauss integrations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 29, 1986–2003 (2013)
Xie, C., Zheng, H.B.: A parallel variational multiscle method for incompressible flows based on the partition of unity. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Model. 11(4), 854–865 (2014)
Shang, Y.Q.: A parallel two-level finite element variational multiscale method for the Navier–Stokes equations. Nonlinear Anal. 84, 103–116 (2013)
Shang, Y.Q., Qin, J.: A finite element variational multiscale method based on two-grid discretization for the steady incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 300, 182–198 (2016)
Shang, Y.Q., Qin, J.: Parallel finite element variational multiscale algorithms for incompressible flow at high Reynolds numbers. Appl. Numer. Math. 117, 1–21 (2017)
Jiang Y, Mei LQ, Wei HM, Tian WJ, Ge JT: A finite element variational multiscale method based on two local Gauss integrations for stationary conduction–convection problems. Math. Probl. Eng. article ID 747391 (2012)
Shang, Y.Q.: Error analysis of a fully discrete finite element variational multiscale method for time-dependent incompressible Navier–Stokes equations. Numer. Methods Partial Differ. Equ. 29(6), 2025–2046 (2013)
He, Y.N., Sun, W.W.: Stability and convergence of the Crank–Nicolson/Adams–Bashforth scheme for the time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 45(6), 837–869 (2007)
He, Y.N.: The Euler implicit/explicit scheme for the 2D time-dependent Navier–Stokes equations with smooth or non-smooth initial data. Math. Comp. 77, 2097–2124 (2008)
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis. North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Adams, R.: Sobolev Spaces. Academic Press Inc, New York (1975)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R.: Finite element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problem I: regularity of solutions and second-order error estimates for spatial discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 19(2), 275–311 (1982)
Hood, P., Taylor, C.: A numerical solution of the Navier–Stokes equations using the finite element technique. Comput. Fluids 1, 73–100 (1973)
Fortin, M.: Calcul Num\(\acute{e}\)rique des Ecoulements Fluides de Bingham et des Fluides Newtoniens Incompressible Par desm\(\acute{e}\)thodes D’el\(\acute{e}\)ments Finis. Doctoral thesis (1972)
Crouzeix, M., Raviart, P.A.: Conforming and nonconforming finite element methods for solving the stationary Stokes equations. RAIRO Anal. Numérique 7(R–3), 33–76 (1973)
Mansfield, L.: Finite element subspaces with optimal rates of convergence for stationary Stokes problem. RAIRO Anal. Numérique 16, 49–66 (1982)
Case, M., Ervin, V., Linke, A., Rebholz, L.: A connection between Scott–Vogelius elements and grad-div stabilized Taylor–Hood FE approximations of the Navier–Stokes equations. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 49(4), 1461–1481 (2011)
Heywood, J.G., Rannacher, R.: Finite element approximation of the nonstationary Navier–Stokes problem IV: error analysis for second-order time discretization. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 27(2), 353–384 (1990)
Shan, L., Hou, Y.R., Zheng, H.B.: Variational mulstiscale method based on the Crank–Nicolson extrapolation scheme for the nonstationary Navier–Stokes equations. Int. J. Comput. Math. 89, 2198–2223 (2012)
Hecht, F.: New development in FreeFem++. J. Numer. Math. 20(3–4), 251–265 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11361016) and the Basic and Frontier Research Program of Chongqing Municipality, China (No. cstc2016jcyjA0348).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, J., Shang, Y. A second-order finite element variational multiscale scheme for the fully discrete unsteady Navier–Stokes equations. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 58, 95–110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-017-1135-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12190-017-1135-y