Abstract
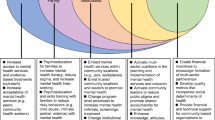
Young people´s perspectives on service quality in Therapeutic Residential Care (TRC) are commonly excluded or overshadowed by those of adults which has led to calls for better youth self-report indicators of quality healthcare. In response, we performed a systematic review of peer-reviewed literature to identify the most important quality indicators for young people by reviewing the literature on their beliefs and experiences regarding TRC and building on the four-pronged parsimonious framework (setting, staffing, treatment approach, and safety) proposed by Farmer et al., (2017). Following PRISMA guidelines, a systematic literature search was conducted in March 2022. Of the 17, 815 records screened, 15 articles, composed of 15 samples were included. A total of five domains and 13 quality indicators were identified: 1) Setting; 2) Staffing (professional skills and access to specialist support [doctor/therapist]); 3) Treatment approach (effective transition and aftercare support, rest and time to think, life skills, behavioural improvement, access to education and farm animals as therapeutic aides); 4) Safety (staff actions and structure and stability), and 5) Milieu factor (trusting relationships, family involvement, and relationship continuity). These four domains provide a practical framework for better-oriented treatment. The additional domain identified as the milieu factor places the critical quality indicators of TRC (e.g., trusting relationships) from the perception of the youth themselves, at the centre of attention, and encourages services to assess the extent to which they have the milieu factor, so they can strategically adapt and be responsive to the needs of young people. Policy and service delivery implications are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article [and/or] its supplementary materials.
References
Águila-Otero, A., Bravo, A., Santos, I., & Del Valle, J.F. (2020). Addressing the most damaged adolescents in the child protection system: An analysis of the profiles of young people in therapeutic residential care. Children and Youth Services Review, Elsevier, vol. 112©. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.104923
Ambresin, A., Bennett, K., Patton, G. C., Sanci, L. A., & Sawyer, S. M. (2013). Assessment of youth-friendly health care: A systematic review of indicators drawn from young people’s perspectives. The Journal of Adolescent Health: Official Publication of the Society for Adolescent Medicine, 52(6), 670–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2012.12.014
Anglin, J. P. (2004). Creating “well-functioning” residential care and defining its place in a system of care. Child & Youth Care Forum, 33, 175–192. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CCAR.0000029689.70611.0f
Anglin, J. P., & Henderson, B. (2023). A Critical dialogue on residential care for children and youth: what we really know and questions of quality residential treatment. Children & Youth. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886571X.2023.2284693
Archard, D. (2020), ‘How should we think about childhood and children? A provocation paper’, Medium. Retrieved January 6, 2022, from https://medium.com/reframing-childhood-past-and-present/how-should-we-think-about-childhood-and-children-66c5624092f
Attar-Schwartz, S., & Khoury-Kassabri, M. (2015). Indirect and verbal victimization by peers among at-risk youth in residential care. Child Abuse & Neglect, 42, 84–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2014.12.007
Bath, H. (2015a). Out of home care in Australia: Looking back and looking ahead. Children Australia, 40(4), 310–315. https://doi.org/10.1017/cha.2015.39
Bath, H. (2015b). The three pillars of TraumaWise care: Healing in the other 23 hours. Reclaiming Children and Youth, 23(4), 5.
Beiza, G., Capella, C., Dussert, D., Rodríguez, L., Águila, D., Gutiérrez, C., & Lama, X. (2015). Institutionalized adolescents in therapy: narratives of psychotherapy and healing from sexual abuse. https://doi.org/10.7411/RP.2016.004
Bjørlykhaug, K. I., Bank, R. M., & Karlsson, B. (2020). Social support and relational recovery in the age of individualism. Journal of Recovery in Mental Health, 4(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2156857X.2020.1868553
Boel-Studt, S. M. (2017). Latent subtypes of youth in psychiatric residential care. Children and Youth Services Review, 77, 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2017.04.005
Boel-Studt, S., Huefner, J. C., Bender, K., Huang, H., & Abell, N. (2018). Developing quality standards and performance measures for residential group care: Translating theory to practice. Residential Treatment for Children & Youth, 36(4), 260–281. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886571x.2018.1536494
Bowlby, J. (1988). A secure base: Parent–child attachment and healthy human development. Basic Books.
Bramsen, I., Kuiper, C., Willemse, K., & Cardol, M. (2019). My Path Towards Living on My Own: Voices of Youth Leaving Dutch Secure Residential care. Child Adolescent Social Work, 36, 365–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10560-018-0564-2
Briggs, E. C., Greeson, J. K., Layne, C. M., Fairbank, J. A., Knoverek, A. M., & Pynoos, R. S. (2012). Trauma exposure, psychosocial functioning, and treatment needs of youth in residential care: Preliminary findings from the NCTSN Core Data Set. Journal of Child & Adolescent Trauma, 5, 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/19361521.2012.646413
Brook, R. H., McGlynn, E. A., & Cleary, P. D. (1996). Quality of health care part II: Measuring quality of care. New England Journal of Medicine, 335, 966–970. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm199609263351311
Castro, E., Magalhães, E., & Del Valle, J. (2023). A systematic review of non-specific and specific treatment factors associated with lower or greater internalising and externalising symptoms in therapeutic residential care. Children & Youth Services Review, 147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2023.106840
Cunningham, M., & Rious, J. B. (2015). Listening to the voices of young people: Implications for working in diverse communities. The American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 85(6S), 86–92. https://doi.org/10.1037/ort0000132
Daly, D. L., Huefner, J. C., Bender, K. R., Davis, J. K., Whittaker, J. K., & Thompson, R. W. (2018). Quality care in therapeutic residential programs: Definition, evidence for effectiveness, and quality standards. Residential Treatment for Children & Youth., 35(3), 242–262. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886571X.2018.1478240
Donabedian, A. (2003). An introduction to quality assurance in health care. Oxford University Press.
Dunn, D. M., Culhane, S. E., & Taussig, H. N. (2010). Children´s appraisals of their experiences in out-of-home care. Children and Youth Services Review, 32(10), 1324–1330. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.childyouth.2010.05.001
Ennals, P., Lessing, K., Spies, R., Egan, R., Hemus, P., Droppert, K., Tidhar, M., Wood, T., van Dijk, C., Bride, R., Asche, A., Bendall, S., & Simmons, M. (2021). Co-producing to understand what matters to young people living in youth residential rehabilitation services. Early Intervention in Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1111/eip.13222
Ensign, J. (2004). Quality of health care: The views of homeless youth. Health Services Research, 39(4p1), 695–708. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6773.2004.00253.x
Farley, T. M., McWey, L. M., & Ledermann, T. (2020). Trauma and violence as predictors of internalizing and externalizing symptoms of youth in residential child welfare placements. Journal of Family Violence, 36, 249–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10896-020-00140-w
Farmer, E. M. Z., Murray, M. L., Ballentine, K., Rauktis, M. E., & Burns, B. J. (2017). Would we know it if we saw it? assessing quality of care in group homes for youth. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 25(1), 28–36. https://doi.org/10.1177/1063426616687363
Field, A., Sen, R., Johnston, C., & Ellis, K. (2021). Turning 18 in specialized residential therapeutic care: Independence or a cliff edge? Children & Society, 35(5), 784–798. https://doi.org/10.1111/chso.12450
Finkelhor, D., Hamby, S., Turner, H., & Walsh, W. (2016). Children's exposure to violence and sexual abuse. The Wiley handbook on the psychology of violence. 24. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118303092
Gallagher, B., & Green, A. (2012). In, out and after care: Young adults’ views on their lives, as children, in a therapeutic residential establishment. Children and Youth Services Review, 34(2), 437–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2011.11.014
Gazilj, I., Borić, I., & Ćosić, A. (2021). The experience of residential care from the perspective of adolescents and caregivers. Journal of Elementary Education, 14(Spec. Iss), 35–61. https://doi.org/10.18690/rei.14.Spec.Iss.35-61.2021
Geurts, E., Boddy, J., Noom, M., & Knorth, E. (2012). Family-centred residential care: The new reality? Child & Family Social Work, 17, 170–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2206.2012.00838.x
Gharabaghi, K., & Anderson-Nathe, B. (2015). The voice of young people. Child & Youth Services, 36, 95–97. https://doi.org/10.1080/0145935X.2015.1072406
Gilligan, R. (2007). Adversity, resilience and the educational progress of young people in public care. Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties, 12(2), 135–145. https://doi.org/10.1080/13632750701315631
Gilligan, R. (2015). Foreword. In J. K. Whittaker, J. F. del Valle, & L. Holmes (Eds.), Therapeutic residential care for children and youth: Developing evidence-based international research (pp. 11–22). Jessica Kingsley Publishers.
Greenhalgh, T., & Taylor, R. (1997). Papers that go beyond numbers (qualitative research). BMJ (clinical Research Ed.), 315(7110), 740–743. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7110.740
Harder, A. T., & Knorth, E. J. (2015). Uncovering what is inside the ‘black box’ of effective therapeutic residential youth care. In J. K. Whittaker, J. F. del Valle, & L. Holmes (Eds.), Therapeutic residential care with children and youth: Developing evidence-based international practice (pp. 217–228). Jessica Kingsley Publishers. https://doi.org/10.7334/psicothema2016.172
Harder, A. T., Knorth, E. J., & Kalverboer, M. E. (2017). The Inside Out? Views of Young People, Parents, and Professionals Regarding Successful Secure Residential Care. Child & Adolescent Social Work Journal: C & A, 34(5), 431–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10560-016-0473-1
Hawkins-Rodgers, Y. (2007). Adolescents adjusting to a group home environment: A residential care model of re-organizing attachment behavior and building resiliency. Children and Youth Services Review, 29(9), 1131–1141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2007.04.007
Holden, M. J., Izzo, C., Nunno, M., Smith, E. G., Endres, T., Holden, J. C., & Kuhn, F. (2010). Children and residential experiences: A comprehensive strategy for implementing a research-informed program model for residential care. Child Welfare, 89(2), 131.
Holland, S. (2009). Listening to children in care: A review of methodological and theoretical approaches to understanding looked after children’s perspectives. Children & Society, 23(3), 226–235. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1099-0860.2008.00213.x
Hooper, S. R., Murphy, J., Devaney, A., & Hultman, T. (2000). Ecological outcomes of adolescents in a psychoeducational residential treatment facility. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 70(4), 491–500. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0087807
James, S. (2011). What works in group care? A structured review of treatment models for group homes and residential care. Children and Youth Services Review, 33, 308–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2010.09.014
James, S. (2017). Implementing evidence-based practice in residential care – how far have we come? Residential Treatment for Children & Youth, 34(2), 155–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886571X.2017.1332330
James, S., Alemi, Q., & Zepeda, V. (2013). Effectiveness and implementation of evidence-based practices in residential care settings. Children and Youth Services Review, 35(4), 642–656. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2013.01.007
January, S., Trout, L., Huscroft-D’Angelo, J., Duppong, H., & Thompson, D. (2018). Perspectives on factors impacting youth’s reentry into residential care: an exploratory study. Child & Family Studies, 27, 2584–2595. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-018-1093-5
Khan, K. S., Kunz, R., Kleijnen, J., & Antes, G. (2003). Five steps to conducting a systematic review. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, 96(3), 118–121. https://doi.org/10.1177/014107680309600304
Kim, J. (2016). Youth involvement in participatory action research (PAR): Challenges and barriers. Critical Social Work, 17(1), 38–53. https://doi.org/10.22329/csw.v17i1.5891
Knorth, E. J., Harder, A. T., Zandberg, T., & Kendrick, A. J. (2008). Under one roof: A review and selective meta-analysis on the outcomes of residential child and youth care. Children and Youth Services Review, 30, 123–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2007.09.001
Kor, K., Fernandez, E., & Spangaro, J. (2021). Interpretative phenomenological analysis of young people’s lived experiences of therapeutic residential care. Child & Family Social Work, 26, 89–99. https://doi.org/10.1111/cfs.12792
Lee, B. R., & McMillen, J. C. (2008). Measuring quality in residential treatment for children and youth. Residential Treatment for Children & Youth, 24(1–2), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1080/08865710802146622
Leipoldt, J., Harder, A., Kayed, N., Grietens, H., & Rimehaug, T. (2019). Determinants and outcomes of social climate in therapeutic residential youth care: A systematic review. Children and Youth Services Review. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2019.02.010
Magalhães, E., Pinheiro, M., & Calheiros, M. (2022). Participation of young people in residential care: Professionals’ perceptions about barriers and facilitators in Portugal. In Claudia Equit & Jade Purtell (Eds.), Children’s rights to participate in out-of-home care: International social work contexts. London: Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003319368
Mallon, G. P. (2001). Cow as co-therapist: Utilisation of farm animals as therapeutic aides with children in residential treatment. Child & Adolescent Social Work, 11, 455–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01876570
McLean, S. (2015). Managing behaviour in child residential group care: Unique tensions. Child & Family Social Work, 20(3), 344–353. https://doi.org/10.1111/cfs.12083
McMillen, J. C., Proctor, E. K., Megivern, D., Striley, C. W., Cabassa, L. J., Munson, M. R., & Dickey, B. (2005). Quality of care in the social services: Research agenda and methods. Social Work Research, 29(3), 181–191. https://doi.org/10.1093/swr/29.3.181
McPherson, L., Gatwiri, K., Cameron, N., & Parmenter, N. (2019). The evidence base for therapeutic group care. A systematic scoping review. Retrieved December 6, 2021, from https://professionals.childhood.org.au/app/uploads/2019/03/Research-Report-Evidence-Base-for-Therapeutic-Group-Care-16Feb19-1.pdf
McPherson, L., Vosz, M., Gatwiri, K., Parmenter, N., Macnamara, N., Mitchell, J. & Tucci, J. (2021). What does research tell us about young people’s participation in decision-making in residential care? A systematic scoping review. Children and Youth Services Review, 105899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105899
Megivern, D. M., McMillen, J. C., Proctor, E. K., Striley, C. L., Cabassa, L. J., & Munson, M. R. (2007). Quality of care: Expanding the social work dialogue. Social Work, 52(2), 115–124. https://doi.org/10.1093/sw/52.2.115
Munro, E. (2001). Empowering looked-after children. Child & Family Social Work, 6, 129–137. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2206.2001.00192.x
Munson, M. R., Lee, B. R., Miller, D., Cole, A., & Nedelcu, C. (2013). Emerging adulthood among former system youth: The ideal versus the real. Children and Youth Services Review, 35(6), 923–929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2013.03.003
Ness, O., Kvello, Ø., Borg, M., Semb, R., & Davidson, L. (2017). “Sorting things out together”: Young adults’ experiences of collaborative practices in mental health and substance use care. American Journal of Psychiatric Rehabilitation, 20(2), 126–142. https://doi.org/10.1080/15487768.2017.1302369
Nickerson, A. B., Brooks, J. L., & Colby, S. A. (2006). Family involvement in residential treatment: staff, parent, and adolescent perspectives. Child & Family StudiEs, 15, 681–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-006-9041-1
Nijhof, K. S. (2011). Crossing barriers: Evaluation of a new compulsory residential treatment program for youth. (PhD). Radboud Universiteit Nijmegen.
Page, M., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ, 372, n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71
Pazaratz, D. (1999). An impressionistic evaluation of the efficacy of a residential treatment facility for emotionally disturbed youth. Residential Treatment for Children and Youth, 16(3), 15–35. https://doi.org/10.1300/j007v16n03_02
Pecora, P. J., & English, D. J. (2016). Elements of effective practice for children and young people served by therapeutic residential care: Research brief. Casey Family Programs. Retrieved November 7, 2021, from https://www.casey.org
Pérez-García, S., Águila-Otero, A., González-García, C., Santos, I., & Del Valle, J. F. (2019). No one ever asked us Young people’s evaluation of their residential childcare facilities in three different programs. Psicothema, 31(3), 319–326. https://doi.org/10.7334/psicothema2019.129
Rivard, J. C., Bloom, S. L., McCorkle, D., & Abramovitz, R. (2005). Preliminary results of a study examining the implementation and effects of a trauma informed recovery framework for youths in residential treatment. Therapeutic Community: The International Journal for Therapeutic and Supportive Organisations, 26(1), 83–96.
Robinson, C. (2021). Lost in translation: The reality of implementing children’s right to be heard. Journal of the British Academy, 8(s4), 29–39. https://doi.org/10.5871/jba/008s4.029
Robinson, C., Quennerstedt, A., & I’Anson, J. (2020). The translation of articles from the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child into education legislation: The narrowing of Article 12 a consequence of translation. The Curriculum Journal, 31(3), 517–538. https://doi.org/10.1002/curj.6
Schaefer, C. E. (1972). Residential treatment: A view from the child. Child & Youth Care Forum, 1, 173–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01543432
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, LiberatiA, Petticrew M et al. (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BJMP, 349. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g7647
Somers, C. L., Day, A. G., Sepsey, A. M., Allegoet, D., Baroni, B. A., & Hong, J. S. (2021). Understanding the residential treatment center school academic environment: perspectives of students and teachers. Residential Treatment for Children & Youth, 38(2), 118–136. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886571X.2019.1622167
Sulimani-Aidan, Y., & Paldi, Y. (2020). Youth perspectives on parents’ involvement in residential care in Israel. Journal of Social Work., 20(1), 64–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/1468017318793619
Sunseri, P. A. (2004). Family functioning and residential treatment outcomes. Residential Treatment for Children & Youth, 22(1), 33–53. https://doi.org/10.1300/J007v22n01_03
Sunseri, P. A. (2020). Hidden figures: Is improving family functioning a key to better treatment outcomes for seriously mentally ill children? Residential Treatment for Children & Youth, 37(1), 46–64. https://doi.org/10.1080/0886571X.2019.1589405
Tisdall, E. (2018). Challenging competency and capacity? Due weight to children’s views in family law proceedings. International Journal of Children’s Rights, 26(1), 159–182. https://doi.org/10.1163/15718182-02601003
Trout, A., Hagaman, J., Chmelka, M., Gehringer, R., Epstein, M., & Reid, R. (2008). The academic, behavioral, and mental status of children and youth at entry to residential care. Residential Treatment for Children & Youth, 25(4), 359–374. https://doi.org/10.1080/08865710802533654
Tylee, A., Haller, D. M., Graham, T., Churchill, R., & Sanci, L. A. (2007). Youth-friendly primary-care services: How are we doing and what more needs to be done? Lancet (london, England), 369(9572), 1565–1573. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60371-7
Usher, C. L., Randolph, K., & Gogan, H. C. (1999). Placement patterns in foster care. Social Service Review, 73, 22–29. https://doi.org/10.1086/515794
Weiner, A., & Kupermintz, H. (2001). Facing adulthood alone: The long-term impact of family break-up and infant institutions, a longitudinal study. British Journal of Social Work, 31(2), 213–234.
Whittaker, J. K., Greene, K., Schubert, D., Blum, R., Cheng, K., Blum, K., Reed, N., Scott, K., Roy, R., & Savas, S. A. (2006). Integrating evidence-based practice in the child mental health agency: A template for clinical and organizational change. The American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 76(2), 194–201. https://doi.org/10.1037/0002-9432.76.2.194
Whittaker, J. K., Del Valle, J. F., & Holmes, L. (Eds.). (2015). Therapeutic residential care with children and youth: Developing evidence-based international practice. Jessica Kingsley Publishers. https://doi.org/10.1093/bjsw/bcv013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Castro, E., Magalhães, E. & del Valle, J.F. A Systematic Review of Quality Indicators in Therapeutic Residential Care Drawn from Young People´s Beliefs and Experiences. Child Ind Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-024-10118-5
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12187-024-10118-5