Abstract
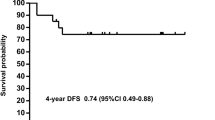
To explore the efficacy of treatment for childhood acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) with a combination of all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) and arsenic trioxide (As2O3) for remission induction, we reviewed the clinical course and outcome of 37 children with APL from January 1999 to December 2003. Among the 37 children (≤14 years) with newly diagnosed APL, we applied treatments that consisted of ATRA alone or in combination with As2O3 in induction followed by consolidation and maintenance treatment. Overall, 35 (94.6%) of 37 children achieved complete remission (CR). Two patients died of intracerebral hemorrhage on days 1 and 2. The 5-year estimates of event-free survival (EFS), disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS) rates for the 37 patients were 79.2, 83.7, and 91.5%, respectively. There were 27 patients with white blood cell (WBC) count lower than 10 × 109/L. In 27 patients with a WBC count <10 × 109/L, 17 patients (group-I) were treated with ATRA alone and 10 patients (group-II) were treated with ATRA which was switched to As2O3 due to the side effects of ATRA. Although the 5-year estimate of DFS between group-I and group-II showed no significant difference (P = 0.108), the DFS rate improved by 25% in group-II. Our results suggest that the combination of As2O3 and ATRA might decrease the relapse rate compared with ATRA alone in induction therapy for childhood APL, at least in those with a WBC count less than 10 × 109/L.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Testi AM, Biondi A, Lo Coco F, et al. GIMEMA-AIEOPAIDA protocol for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) in children. Blood. 2005;106:447–53.
Ortega JJ, Madero L, Martin G, et al. Treatment with all-trans retinoic acid and anthracycline monochemotherapy for children with acute promyelocytic leukemia: a multicenter study by the PETHEMA Group. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:7632–40.
de Botton S, Coiteux V, Chevret S, et al. Outcome of childhood acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans-retinoic acid and chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1404–12.
Mann G, Reinhardt D, Ritter J, et al. Treatment with all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia reduces early deaths in children. Ann Hematol. 2001;80:417–22.
Tallman MS. What is the role of arsenic in newly diagnosed APL? Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2008;21:659–66.
Lengfelder E, Haferlach C, Saussele S, et al. High dose ara-C in the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: long-term results of the German AMLCG. Leukemia. 2009;23:2248–58.
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, et al. Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood. 1997;89:3354–60.
Soignet SL, Frankel SR, Douer D, et al. United States multicenter study of arsenic trioxide in relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:3852–60.
Powell BL, Moser B, Stock W, et al. Arsenic trioxide improves event-free and overall survival for adults with acute promyelocytic leukemia: North American Leukemia Intergroup Study C9710. Blood. 2010;116:3751–7.
Shen ZX, Shi ZZ, Fang J, et al. All-trans retinoic acid/As2O3 combination yields a high quality remission and survival in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:5328–35.
Chen Y, Gu L, Zhou C, et al. Relapsed APL patient with variant NPM-RARalpha fusion responded to arsenic trioxide-based therapy and achieved long-term survival. Int J Hematol. 2010;91:708–10.
Hu J, Liu YF, Wu CF, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of all-trans retinoic acid/arsenic trioxide-based therapy in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:3342–7.
Gore SD, Gojo I, Sekeres MA, et al. Single cycle of arsenic trioxide-based consolidation chemotherapy spares anthracycline exposure in the primary management of acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:1047–53.
Ravandi F, Estey E, Jones D, et al. Effective treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with all-trans-retinoic acid, arsenic trioxide, and gemtuzumab ozogamicin. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:504–10.
Mantadakis E, Samonis G, Kalmanti M. A comprehensive review of acute promyelocytic leukemia in children. Acta Haematol. 2008;119:73–82.
George B, Mathews V, Poonkuzhali B, et al. Treatment of children with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide: a single center experience. Leukemia. 2004;18:1587–90.
Zhang L, Zhao H, Zhu X, Chen Y, et al. Retrospective analysis of 65 Chinese children with acute promyelocytic leukemia: a single center experience. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2008;51:210–5.
Wang H, Hao L, Wang X, et al. Retrospective study of arsenic trioxide for childhood acute promyelocytic leukemia in China: a single-center experience. Int J Hematol. 2010;91:820–5.
Zhou J, Zhang Y, Li J, et al. Single-agent arsenic trioxide in the treatment of children with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 2010;115:1697–702.
Avvisati G, Lo Coco F, Diverio D, et al. AIDA (all-trans retinoic acid + idarubicin) in newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: a Gruppo Italiano Malattie Ematologiche Maligne dell’Adulto (GIMEMA) pilot study. Blood. 1996;88:1390–8.
Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, standardization of response criteria, treatment outcomes, and reporting standards for therapeutic trials in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:4642–9.
Creutzig U, Ritter J, Zimmermann M, et al. Idarubicin improves blast cell clearance during induction therapy in children with AML: results of study AML-BFM 93 AML-BFM Study Group. Leukemia. 2001;15:348–54.
Sanz MA, Lo Coco F, Martin G, et al. Definition of relapse risk and role of nonanthracycline drugs for consolidation in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia: a joint study of the PETHEMA and GIMEMA cooperative groups. Blood. 2000;96:1247–53.
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS, et al. Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res. 2002;62:3893–903.
Mathews V, George B, Lakshmi KM, et al. Single-agent arsenic trioxide in the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: durable remissions with minimal toxicity. Blood. 2006;107:2627–32.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Professor Yizhou Zheng for the careful reading of our manuscript. They also thank Professor Hui Zhao for helpful suggestions. This study was supported in part by a grant from the Science and Technology Support Key Program of Tianjin(09ZCZDSF03800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Zhu, X., Zou, Y. et al. Effect of arsenic trioxide on the treatment of children with newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia in China. Int J Hematol 93, 199–205 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-011-0768-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-011-0768-0