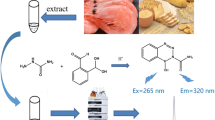
Abstract
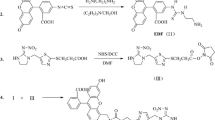
Semicarbazide (SEM) has been proven to extensively exist in foodstuffs due to anthropogenic factor in food processing and possesses various toxic effects on human health. Although many methods have been developed, they often require long analytical time, complex laboratory equipment, trained personnel, difficultly prepared antibodies, or relatively expensive equipment. The present study developed a new method for SEM determination by HPLC with fluorescence detection (FLD). The fluorescence reagent, 2-(11H-benzo[a]carbazol-11-yl) ethyl chloroformate (BCEC), was first used for SEM labeling. The fluorescent labeling conditions were optimized systematically. SEM can be labeled in only 10 min at 40 °C. The labeled SEM was analyzed on an eclipse XDB-C8 column in 8 min. The new method offered the low LOD of 0.4 μg/kg at a signal-to-noise ratio of 3 and also exhibited excellent reproducibility, precision, and accuracy. When applied to analyze several foodstuffs, it showed good applicability. The developed method has been proven to be simple, inexpensive, selective, sensitive, accurate, and reliable for SEM analysis in foodstuffs. Furthermore, this developed method should have a powerful potential in the analysis of SEM from many other food samples.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becalski A, Lau B, Lewis D, Seaman S (2004) Semicarbazide formation in azodicarbonamide-treated flour: a model study. J Agric Food Chem 52(18):5730–5734
Bezerra M, Santelli R, Oliveira E, Villar L, Escaleira L (2008) Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 76(5):965–977
Bogialli S, Di Corcia A (2009) Recent applications of liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry to residue analysis of antimicrobials in food of animal origin. Anal Bioanal Chem 395(4):947–966
Cháfer-Pericás C, Maquieira Á, Puchades R (2010) Fast screening methods to detect antibiotic residues in food samples. TrAC–Trend Anal Chem 29(9):1038–1049
Chen G, Li J, Zhang S, Song C, Li G, Sun Z, You J (2012) A sensitive and efficient method to systematically detect two biophenols in medicinal herb herbal products and rat plasma based on thorough study of derivatization and its convenient application to pharmacokinetics with semi-automated device. J Chromatogr A 1249:190–200
Chen G, Li J, Sun Z, Zhang S, Li G, Song C, Suo Y, You J (2014) Rapid and sensitive ultrasonic-assisted derivatisation microextraction (UDME) technique for bitter taste-free amino acids (FAA) study by HPLC–FLD. Food Chem 143:97–105
Cooper KM, Samsonova JV, Plumpton L, Elliott C, Kennedy DG (2007) Enzyme immunoassay for semicarbazide—the nitrofuran metabolite and food contaminant. Anal Chim Acta 592(1):64–71
de la Calle MB, Anklam E (2005) Semicarbazide: occurrence in food products and state-of-the-art in analytical methods used for its determination. Anal Bioanal Chem 382(4):968–977
Di Stefano V, Pitonzo R, Avellone G, Di Fiore A, Monte L, Ogorka A (2014) Determination of aflatoxins and ochratoxins in Sicilian sweet wines by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorometric detection and immunoaffinity cleanup. Food Anal Methods. doi:10.1007/s12161-014-9934-3
Jiang W, Luo P, Wang X, Chen X, Zhao Y, Shi W, Wu X, Wu Y, Shen J (2012) Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of nitrofurantoin metabolite 1-amino-hydantoin in animal tissues. Food Control 23(1):20–25
Jin W, Yang G, Wu L, Wang Q, Shao H, Qin A, Yu B, Li D, Cai B (2011) Detecting 5-morpholino-3-amino-2-oxazolidone residue in food with label-free electrochemical impedimetric immunosensor. Food Control 22(10):1609–1616
Kabashima T, Yu Z, Tang C, Nakagawa Y, Okumura K, Shibata T, Lu J, Kai M (2008) A selective fluorescence reaction for peptides and chromatographic analysis. Peptides 29(3):356–363
Li G, Dong L, Wang A, Wang W, Hu N, You J (2014) Simultaneous determination of biogenic amines and estrogens in foodstuff by an improved HPLC method combining with fluorescence labeling. LWT-Food Sci Technol 55(1):355–361
McCracken R, Hanna B, Ennis D, Cantley L, Faulkner D, Kennedy D (2013) The occurrence of semicarbazide in the meat and shell of Bangladeshi fresh-water shrimp. Food Chem 136(3):1562–1567
Mulder P, Beumer B, Van Rhijn J (2007) The determination of biurea: a novel method to discriminate between nitrofurazone and azodicarbonamide use in food products. Anal Chim Acta 586(1):366–373
Noonan GO, Warner CR, Hsu W, Begley TH, Perfetti GA, Diachenko GW (2005) The determination of semicarbazide (N-aminourea) in commercial bread products by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 53(12):4680–4685
Noonan GO, Begley TH, Diachenko GW (2008) Semicarbazide formation in flour and bread. J Agric Food Chem 56(6):2064–2067
O’Mahony J, Moloney M, McConnell RI, Benchikh EO, Lowry P, Furey A, Danaher M (2011) Simultaneous detection of four nitrofuran metabolites in honey using a multiplexing biochip screening assay. Biosens Bioelectron 26(10):4076–4081
Rezaee M, Yamini Y, Faraji M (2010) Evolution of dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method. J Chromatogr A 1217(16):2342–2357
Sheng L, Chen M, Chen S, Du N, Liu Z, Song C, Qiao R (2013) High-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection for the determination of nitrofuran metabolites in pork muscle. Food Addit Contam A 12:2114–2122
Tang Y, Xu J, Wang W, Xiang J, Yang H (2011) A sensitive immunochromatographic assay using colloidal gold–antibody probe for the rapid detection of semicarbazide in meat specimens. Eur Food Res Technol 232(1):9–16
Valera-Tarifa NM, Plaza-Bolaños P, Romero-González R, Martínez-Vidal JL, Garrido-Frenich A (2013) Determination of nitrofuran metabolites in seafood by ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled to triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J Food Compos Anal 30(2):86–93
Vass M, Diblikova I, Kok E, Stastny K, Frgalova K, Hruska K, Franek M (2008) In-house validation of an ELISA method for screening of semicarbazide in eggs. Food Addit Contam 25(8):930–936
Xie Y, Li P, Zhang J, Wang H, Qian H, Yao W (2013) Comparative studies by IR Raman and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of azodicarbonamide biurea and semicarbazide hydrochloride. Spectrochim Acta A 114:80–84
Ye J, Wang XH, Sang YX, Liu Q (2011) Assessment of the determination of azodicarbonamide and its decomposition product semicarbazide: investigation of variation in flour and flour products. J Agric Food Chem 59(17):9313–9318
You J, Zhao W, Liu L, Zhao X, Suo Y, Wang H, Li Y, Ding C (2007) Determination of amines using 2-(11H-benzo [a] carbazol-11-yl) ethyl chloroformate (BCEC-Cl) as labeling reagent by HPLC with fluorescence detection and identification with APCI/MS. Talanta 72(3):914–925
Yu Z, Kabashima T, Tang C, Shibata T, Kitazato K, Kobayashi N, Lee M, Kai M (2010) Selective and facile assay of human immunodeficiency virus protease activity by a novel fluorogenic reaction. Anal Biochem 397(2):197–201
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31301595, 21475075, 21475074, and 21275089), the Open Project Program of Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Aquatic Products Processing and Safety, Guangdong Ocean University (GDPKLAPPS1401), PhD research start-up funds of Qufu Normal University (bsqd 2012017), and the Soft Science Project of Shandong Province (2013RKA08020).
Conflict of Interest
Guoliang Li declares that he has no conflict of interest. Chenhong Tang declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ying Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Jing Yang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Hongliang Wu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Guang Chen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Weiheng Kong declares that he has no conflict of interest. Xiaojian Kong declares that he has no conflict of interest. Shucheng Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Jinmao You declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Chenhong Tang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Tang, C., Wang, Y. et al. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for Semicarbazide Screening in Foodstuffs by HPLC with Fluorescence Detection. Food Anal. Methods 8, 1804–1811 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-0063-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-014-0063-9