Abstract
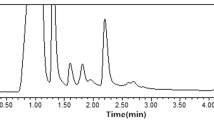
In this work, a 4-chloro-7-nitrobenzodioxazole (NBD-Cl) derivatization coupled with the ultrasound-assisted cloud point extraction (UACPE) method prior to high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection (HPLC-FLD) analysis was developed for the determination of four widely used fluoroquinolones (FQs) including norfloxacin (NOR), ciprofloxacin (CIP), sarafloxacin (SAR), and gatifloxacin (GAT) in eggs. The derivatives of FQs with NBD-Cl were extracted into the Triton X-114 surfactant-rich phase, which was analyzed by reversed-phase HPLC-FLD. Ultrasound was applied to accelerate the phase separation in extraction and enhance the extraction efficiency of target analytes. Variable parameters affecting the derivatization and UACPE procedure were systematically evaluated and optimized. Under the optimum conditions, four FQs were successfully separated within 30 min through an Agilent TC-C18 column. Good recoveries of 86.2–103.5 %, which were calculated using a range of spiked samples at three concentrations, were obtained by UACPE. The calibration graphs were linear over the range of 1.2–73.0 μg kg−1 for four FQs with correlation coefficients (R) no less than 0.9957. The limits of detection were 0.2, 0.5, 0.3, and 0.4 μg kg−1 for NOR, CIP, SAR, and GAT, respectively. The precisions indicated by relative standard deviations ranged from 0.6 to 4.3 % for both intraday and interday analysis. The proposed method proved to be a selective, sensitive, and eco-friendly approach which was successfully applied to analyze FQs in eggs at the local farmers market, and none of the target analytes were detected in these samples.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Drlica K, Malik M, Kerns RJ, Zhao X (2008) Quinolone-mediated bacterial death. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52:385
Duan CF, Shen Z, Wu DP, Guan YF (2011) Recent developments in solid-phase microextraction for on-site sampling and sample preparation. Trends Anal Chem 30:1568
Ebrahimzadeh H, Tavassoli N, Sadeghi O, Amini MM (2012) Optimization of solid-phase extraction using artificial neural networks and response surface methodology in combination with experimental design for determination of gold by atomic absorption spectrometry in industrial wastewater samples. Talanta 97:211
Han F, Yin R, Shi XL, Jia Q, Liu HZ, Yao HM, Xu L, Li SM (2008) Cloud point extraction–HPLC method for determination and pharmacokinetic study of flurbiprofen in rat plasma after oral and transdermal administration. J Chromatogr B 868:64
Hartmann G, Schuster M (2013) Species selective preconcentration and quantification of gold nanoparticles using cloud point extraction and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 761:27
Jia GF, Lv CG, Zhu WT, Qiu J, Wang XQ, Zhou ZQ (2008) Applicability of cloud point extraction coupled with microwave-assisted back-extraction to the determination of organophosphorous pesticides in human urine by gas chromatography with flame photometry detection. J Hazard Mater 159:300
Jiménez V, Rubies A, Centrich F, Companyó R, Guiteras J (2011) Development and validation of a multiclass method for the analysis of antibiotic residues in eggs by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1218:1443
Minovski N, Vračko M, Šolmajer T (2011) Quantitative structure–activity relationship study of antitubercular fluoroquinolones. Mol Divers 15:417
Moema D, Nindi MM, Dube S (2012) Development of a dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction method for the determination of fluoroquinolones in chicken liver by high performance liquid chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 730:80
Parham H, Rahbar N (2009) Solid phase extraction–spectrophotometric determination of fluoride in water samples using magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Talanta 80:664
Pourreza N, Fat’hi MR, Hatami A (2012) Indirect cloud point extraction and spectrophotometric determination of nitrite in water and meat products. Microchem J 104:22
Saleh A, Yamini Y, Faraji M, Rezaee M, Ghambarian M (2009) Ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction method based on applying low density organic solvents followed by gas chromatography analysis for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. J Chromatogr, A 1216:6673
Santalad A, Srijaranai S, Burakham R, Glennon JD, Deming RL (2009) Cloud-point extraction and reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of carbamate insecticide residues in fruits. Anal Bioanal Chem 394:1307
Shamsipur M, Hassan J (2010) A novel miniaturized homogenous liquid–liquid solvent extraction-high performance liquid chromatographic-fluorescence method for determination of ultra traces of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediment samples. J Chromatogr, A 1217:4877
Shi ZH, Jiang HX, Yan JJ, Zhang HY (2012) Determination of Anthraquinone Derivatives in Chang-Qing Tea by Using Cloud-Point Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Food Anal Method 5:659
Sikalos TI, Paleologos EK (2005) Cloud Point Extraction Coupled with Microwave or Ultrasonic Assisted Back Extraction as a Preconcentration Step Prior to Gas Chromatography. Anal Chem 77:2544
Stoilova NA, Surleva AR, Stoev G (2013) Simultaneous Determination of Nine Quinolones in Food by Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Food Anal Method 6:803
Tang T, Qian K, Shi TY, Wang F, Li JQ, Cao YS (2010) Determination of triazole fungicides in environmental water samples by high performance liquid chromatography with cloud point extraction using polyethylene glycol 600 monooleate. Anal Chim Acta 680:26
Ulu ST (2009) Highly sensitive spectrofluorimetric determination of lomefloxacin in spiked human plasma, urine and pharmaceutical preparations. Eur J Med Chem 44:3402
Völgyi G, Vizserálek G, Takács-Novák K, Avdeef A, Tam KY (2012) Predicting the exposure and antibacterial activity of fluoroquinolones based on physicochemical properties.Eur J Pharm Sci 47:21
Wang T, Gao XL, Tong J, Chen LG (2012) Determination of formaldehyde in beer based on cloud point extraction using 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine as derivative reagent. Food Chem 131:1577
Wei W, Yin XB, He XW (2008) pH-mediated dual-cloud point extraction as a preconcentration and clean-up technique for capillary electrophoresis determination of phenol and m-nitrophenol. J Chromatogr A 1202:212
Yan HY, Qiao JD, Wang H, Yang GL, Row KH (2011) Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction combined with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for the determination of four Sudan dyes in sausage samples. Analyst 136:2629
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 20961012) and National Innovation Fund for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (10C26215305131). The Analytical and Testing Center of Kunming University of Science and Technology is also thanked for its help in the analysis of practical samples.
Conflict of Interest
Qinghai Xia declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yang Jiao declares that he has no conflict of interest. Wei Xiong declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yaling Yang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Mousheng Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 135 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, Q., Jiao, Y., Xiong, W. et al. Development of a Precolumn Derivatization Procedure Prior to Ultrasound-Assisted Cloud Point Extraction for Sensitive Determination of Fluoroquinolones in Eggs by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Fluorescence Detection. Food Anal. Methods 7, 1130–1138 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9725-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9725-2