Abstract
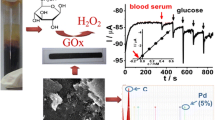
In this study, we report the construction of amperometric screen-printed glucose biosensors for food analysis by using two procedures for Prussian Blue (PB) deposition and different membranes for enzymatic immobilisation. The comparison between the screen-printed electrodes modified with PB by electrochemical and chemical deposition showed higher analytical performance (detection limit of 1 μM, linear range from 0.5 to 500 μM and a sensitivity of 823 μA mM−1 cm−2) when the latter was employed. Then, the immobilisation of glucose oxidase (GOD) by silica sol–gel and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hydrogel was performed on electrochemically modified PB electrodes. The electrochemical response of two glucose biosensors was evaluated by flow injection analysis. Biosensors constructed by silica sol–gel entrapment showed a wider linear range (0.005–1 mM) and a detection limit (0.02 mM) that was 10-fold lower than using entrapped GOD in PVA. The selected glucose biosensor showed negligible interference from ascorbic acid when the Nafion membrane was used to cover the PB-modified electrode surface. Additionally, it exhibited an operating lifetime of 8 h under continuous glucose injections ranging from 0.01 to 2 mM. Finally, the biosensor was applied for specific determination of glucose in red and white wines, juices and dried fruit.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karyakin AA (2001) Electroanal 10:13
Koncki R (2002) Anal Chem 32:79
de Tacconi NR, Rajeshwar K, Lenza RO (2003) Chem Mater 15:3046
Chaubey A, Malhorta BD (2002) Biosens Bioelectron 17:441
Zen JM, Kumar AS, Tsai DM (2003) Electroanal 15:1073
Newman JD, White SF, Tothill IE, Turner APF (1995) Anal Chem 67:4594
Ricci F, Palleschi G (2005) Biosens Bioelectron 21:389
De Mattos IL, Gorton L, Ruzgas T (2003) Biosens Bioelectron 18:193
Liang R, Jiang J, Qiu J (2008) Electroanal 24:2642
Karyakin AA, Kotelnikova EA, Lukachova LV, Karyakina EE, Wang J (2002) Anal Chem 74:1597
Derwinska K, Miecznikowski K, Koncki R, Kulesza PJ, Glab S, Malik MA (2003) Electroanal 15:1843
Li T, Yao Z, Ding L (2004) Sensors Actuators B 101:155
Dominguez Renedo O, Alonso-Lomillo MA, Arcos Martınez MJ (2007) Talanta 73:202
Ricci F, Amine A, Palleschi G, Moscone D (2003) Biosens Bioelectron 18:165
O'Halloran MP, Pravda M, Guilbault GG (2001) Talanta 55:605
Tudorache M, Bala C (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 388:565
Habib O, Demirkol DO, Timur S (2012) Food Anal Meth 5:188
Wang B, Li B, Deng Q, Dong S (1998) Anal Chem 70:3170
Lozinsky VI (1998) Russ Chem Rev 67:573
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2001) Chem Rev 101:1869
Lozinsky VI, Plieva FM (1998) Enzyme Microb Technol 23:227
Tsai Y, Huang J, Chiu C (2007) Biosens Bioelectron 22:3051
Kumar J, D'Souza SF (2008) Talanta 75:183
Imai K, Shiomi T, Uchida K, Miya M (1986) Biotechnol Bioeng 28:1721
Albanese D, Liguori C, Paciello V, Pietrosanto A (2011) IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 60:1909
Guan J, Miao Y, Chen J (2004) Biosens Bioelectron 19:789
Zuo S, Teng Y, Yuan H, Lan M (2008) Sensors Actuators B 133:555
Albanese D, Di Matteo M, Crescitelli A (2010) Comput Aided Chem Eng 28:283
Itaya K, Shoji N, Uchida I (1984) J Am Chem Soc 106:3423
Rejeb IB, Arduini F, Aminec A, Gargouri M, Palleschi G (2007) Anal Chim Acta 594:1
Haghighi B, Varma S, Alizadeh SFM, Yigzaw Y, Gorton L (2004) Talanta 64:3
Mello LD, Kubota LT (2002) Food Chem 77:237
Li Y, Song YY, Yang C, Xia XH (2007) Electrochem Commun 9:981
Lupu A, Compagnone D, Palleschi Anal G (2004) Chim Acta 513:67
Castro SL, Balbo VR, Barbeira PJS, Stradiotto NR (2001) Talanta 55:249
Pournaghi-Azar MH, Ojani R (1995) Talanta 42:1839
Pan S, Arnold MA (1996) Talanta 43:1157
Gibson TD (1999) Analysis 27:630
Karyakin AA, Karyakina EE, Gorton L (1999) Electrochem Commun 2:78
Conflict of Interest
Donatella Albanese declares that she has no conflict of interest. Adriana Sannini declares that she has no conflict of interest. Francesca Malvano declares that she has no conflict of interest. Roberto Pilloton declares that he has no conflict of interest. Marisa Di Matteo declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albanese, D., Sannini, A., Malvano, F. et al. Optimisation of Glucose Biosensors Based on Sol–Gel Entrapment and Prussian Blue-Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes for Real Food Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 7, 1002–1008 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9705-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-013-9705-6