Abstract
Objective
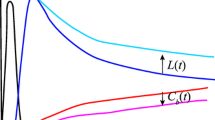
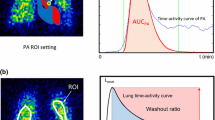
The \(\gamma\)-Ray Evaluation with Iodoamphetamine for Cerebral blood flow Assessment (REICA) method is a new method for cerebral blood flow (CBF) quantification with SPECT and [123I] IMP, which does not require invasive arterial blood sampling, or the use of a regression formula. Moreover, it takes into consideration tracer retention, while the Graph-Plot (GP) method does not. This study aims to confirm the reliability of the REICA method in calculating CBF by accounting for pulmonary tracer retention artefact.
Methods
Data of 100 patients were retrospectively analyzed. Washout rate (WR) was defined as 1- (max count /min count) in the lungs. The bias due to WR was analyzed by dividing the data into high/low WR groups and a multiple regression analysis was also performed.
Results
The REICA method did not show significant bias according to the \(\chi ^2\) test (\(p=0.07\)), while the GP method showed significant bias (\(p=0.0006\)). Both the REICA and GP methods showed significant correlation with autoradiography (ARG) method (\(p<0.0001\), \(p<0.0001\)) and WR (\(p=0.002\), \(p<0.0001\)) when analyzed via multiple regression analysis with covariates of age and sex.
Conclusions
The REICA method is a reliable method for CBF quantification, which is unaffected by tracer washout through the lungs unlike the GP method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iida H, Itoh H, Nakazawa M, Hatazawa J, Nishimura H, Onishi Y, et al. Quantitative mapping of regional cerebral blood flow using iodine-123-IMP and SPECT. J Nucl Med. 1994;35:2019–30.
Iida H, Itoh H, Bloomfield P, Munaka M, Higano S, Murakami M, et al. A method to quantitate cerebral blood flow using a rotating gamma camera and iodine-123 iodoamphetamine with one blood sampling. Eur J Nucl Med. 1994;21:1072–84.
Okamoto K, Ushijima Y, Okuyama C, Nakamura T, Nishimura T. Measurement of cerebral blood flow using graph plot analysis and I-123 iodoamphetamine. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27:191–6.
Yonekura Y, Fujita T, Nishizawa S, Iwasaki Y, Mukai T, Konishi J. Temporal changes in accumulation of N-isopropyl- p-iodoamphetamine in human brain: relation to lung clearance. J Nucl Med. 1989;30:1977–81.
Kameyama M, Watanabe K. A new non-invasive graphical method for quantification of cerebral blood flow with [\(^{123}\)I] IMP. Ann Nucl Med. 2018;32:620–6.
Matsuda H, Tsuji S, Shuke N, Sumiya H, Tonami N, Hisada K. A quantitative approach to technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime. Eur J Nucl Med. 1992;19:195–200.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ms. Natalie Okawa for English language editing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
MK is listed as an inventor on a patent application (2019–074369, 2017–199618) related to this work submitted by Nihon Medi-Physics to the Japan Patent Office. MK received research funding from Nihon Medi-Physics and Fujifilm Toyama Chemistry that supply [123I] IMP in Japan.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruko, M., Kameyama, M., Sakai, J. et al. The REICA method for quantification of cerebral blood flow is less affected by lung washout of [123I] IMP than the graph-plot method. Ann Nucl Med 34, 757–761 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-020-01499-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-020-01499-y