Abstract
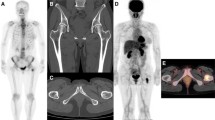
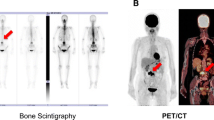
Distant metastases from breast cancer most frequently occur in the skeleton. Although 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography (PET), with or without computed tomography (CT), is superior to bone scintigraphy for the detection of osteolytic bone metastases, it has been reported that sclerotic bone metastases frequently show no or only a low degree of FDG uptake on PET and PET/CT. Since both lytic and sclerotic metastases can occur in breast cancer patients, bone scintigraphy may remain of additional value in these patients. In this case series, we describe four breast cancer patients in whom FDG PET/CT has clearly visualized sclerotic bone metastases because of increased FDG uptake. Not so much the type of metastasis (sclerotic or lytic), but possibly the characteristics of the primary tumor or treatments prior to the FDG PET/CT scan might influence the degree of FDG uptake of bone metastases. The ability to detect sclerotic bone metastases based on increased FDG uptake supports the use of FDG PET/CT as a staging procedure in breast cancer patients, but knowledge of factors determining the visibility of bone metastases with FDG PET/CT is crucial.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Hoeven JJM, Krak NC, Hoekstra OS, Comans EFI, Boom RPA, van Geldere D, et al. 18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography in staging of locally advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1253–9.
Mahner S, Schirrmacher S, Brenner W, Jenicke L, Habermann CR, Avril N, et al. Comparison between positron emission tomography using 2-[fluorine-18]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose, conventional imaging and computed tomography for staging of breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2008;19:1249–54.
Fuster D, Duch J, Paredes P, Velasco M, Muñoz M, Santamaría G, et al. Preoperative staging of large primary breast cancer with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography compared with conventional imaging procedures. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:4746–51.
Hodgson NC, Gulenchyn KY. Is there a role for positron emission tomography in breast cancer staging? J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:712–20.
Fletcher JW, Djulbegovic B, Soares HP, Siegel BA, Lowe VJ, Lyman GH, et al. Recommendations on the use of 18F-FDG PET in oncology. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:480–508.
Kennecke H, Yerushalmi R, Woods R, Cheang MCU, Voduc D, Speers CH, et al. Metastatic behavior of breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3271–7.
Kasem AR, Desai A, Daniell S, Sinha P. Bone scan and liver ultrasound scan in the preoperative staging for primary breast cancer. Breast J. 2006;12:544–8.
Yang SN, Liang JA, Lin FJ, Kao CH, Lin CC, Lee CC. Comparing whole body (18)F-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography and technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate bone scan to detect bone metastases in patients with breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2002;128:325–8.
Cook GJ, Houston S, Rubens R, Maisey MN, Fogelman I. Detection of bone metastases in breast cancer by 18FDG PET: differing metabolic activity in osteoblastic and osteolytic lesions. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:3375–9.
Abe K, Sasaki M, Kuwabara Y, Koga H, Baba S, Hayashi K, et al. Comparison of 18FDG-PET with 99mTc-HMDP scintigraphy for the detection of bone metastases in patients with breast cancer. Ann Nucl Med. 2005;19:573–9.
Nakai T, Okuyama C, Kubota T, Yamada K, Ushijima Y, Taniike K, et al. Pitfalls of FDG-PET for the diagnosis of osteoblastic bone metastases in patients with breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:1253–8.
Du Y, Cullum I, Illidge TM, Ell PJ. Fusion of metabolic function and morphology: sequential [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/computed tomography studies yield new insights into the natural history of bone metastases in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3440–7.
Fogelman I. Osteoblastic bone metastases in breast cancer: is not seeing believing? Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2005;32:1250–2.
Groheux D, Giacchetti S, Moretti J-L, Porcher R, Espié M, Lehmann-Che J, et al. Correlation of high 18F-FDG uptake to clinical, pathological and biological prognostic factors in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:426–35.
Gil-Rendo A, Martínez-Regueira F, Zornoza G, García-Velloso MJ, Beorlegui C, Rodriguez-Spiteri N. Association between [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake and prognostic parameters in breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2009;96:166–70.
Shie P, Cardarelli R, Brandon D, Erdman W, Abdulrahim N. Meta-analysis: comparison of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography and bone scintigraphy in the detection of bone metastases in patients with breast cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2008;33:97–101.
Morris PG, Lynch C, Feeney JN, Patil S, Howard J, Larson SM, et al. Integrated positron emission tomography/computed tomography may render bone scintigraphy unnecessary to investigate suspected metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3154–9.
Hall FM. Imaging bone metastases in breast cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185:1082. author reply 1082–3.
Ohta M, Tokuda Y, Suzuki Y, Kubota M, Makuuchi H, Tajima T, et al. Whole body PET for the evaluation of bony metastases in patients with breast cancer: comparison with 99Tcm-MDP bone scintigraphy. Nucl Med Commun. 2001;22:875–9.
Israel O, Goldberg A, Nachtigal A, Militianu D, Bar-Shalom R, Keidar Z, et al. FDG-PET and CT patterns of bone metastases and their relationship to previously administered anti-cancer therapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006;33:1280–4.
Segaert I, Mottaghy F, Ceyssens S, De Wever W, Stroobants S, Van Ongeval C, et al. Additional value of PET-CT in staging of clinical stage IIB and III breast cancer. Breast J. 2010;16:617–24.
Conflicts of interest
No fundings, grants or technical support were received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koolen, B.B., Vegt, E., Rutgers, E.J.T. et al. FDG-avid sclerotic bone metastases in breast cancer patients: a PET/CT case series. Ann Nucl Med 26, 86–91 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-011-0538-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-011-0538-3