Abstract
Objective
AQCEL enables automatic reconstruction of single-photon emission computed tomogram (SPECT) without image degradation and quantitative analysis of cerebral blood flow (CBF) after the input of simple parameters. We ascertained the usefulness and quality of images obtained by the application software AQCEL in clinical practice.
Methods
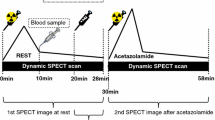
Twelve patients underwent brain perfusion SPECT using technetium-99m ethyl cysteinate dimer at rest and after acetazolamide (ACZ) loading. Images reconstructed using AQCEL were compared with those reconstructed using conventional filtered back projection (FBP) method for qualitative estimation. Two experienced nuclear medicine physicians interpreted the image quality using the following visual scores: 0, same; 1, slightly superior; 2, superior. For quantitative estimation, the mean CBF values of the normal hemisphere of the 12 patients using ACZ calculated by the AQCEL method were compared with those calculated by the conventional method. The CBF values of the 24 regions of the 3-dimensional stereotaxic region of interest template (3DSRT) calculated by the AQCEL method at rest and after ACZ loading were compared to those calculated by the conventional method.
Results
No significant qualitative difference was observed between the AQCEL and conventional FBP methods in the rest study. The average score by the AQCEL method was 0.25 ± 0.45 and that by the conventional method was 0.17 ± 0.39 (P = 0.34). There was a significant qualitative difference between the AQCEL and conventional methods in the ACZ loading study. The average score for AQCEL was 0.83 ± 0.58 and that for the conventional method was 0.08 ± 0.29 (P = 0.003). During quantitative estimation using ACZ, the mean CBF values of 12 patients calculated by the AQCEL method were 3–8% higher than those calculated by the conventional method. The square of the correlation coefficient between these methods was 0.995. While comparing the 24 3DSRT regions of 12 patients, the squares of the correlation coefficient between AQCEL and conventional methods were 0.973 and 0.986 for the normal and affected sides at rest, respectively, and 0.977 and 0.984 for the normal and affected sides after ACZ loading, respectively.
Conclusions
The quality of images reconstructed using the application software AQCEL were superior to that obtained using conventional method after ACZ loading, and high correlations were shown in quantity at rest and after ACZ loading. This software can be applied to clinical practice and is a useful tool for improvement of reproducibility and throughput.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vorstrup S, Brun B, Lassen NA. Evaluation of the cerebral vasodilatory capacity by the acetazolamide test before EC–IC bypass surgery in patients with occlusion of the internal carotid artery. Stroke. 1986;17:1291–8.
Widder B, Kleiser B, Krapf H. Course of cerebrovascular reactivity in patients with carotid artery occlusions. Stroke. 1994;25:1963–7.
Gur AY, Bova I, Bornstein NM. Is impaired cerebral vasomotor reactivity a predictive factor of stroke in asymptomatic patients? Stroke. 1996;27:2188–90.
Nakagawara J, Takeda R, Suematsu K, Nakamura J. Quantification of regional cerebral blood flow and vascular reserve in childhood moyamoya disease using [123I]IMP-ARG method. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 1997;99(Suppl 2):S96–9.
Nakagawara J. Quantitative stratification of hemodynamic cerebral ischemia in cerebral revascularization surgery. Surg Cereb Stroke. 2002;30:7–14.
Mimura H, Ono S, Yanagimoto S, Tomomitsu T, Ikenaga H, Muranaka A, et al. A fundamental study for diamox load scintigraphy using 99mTc-HMAPAO. Kaku Igaku. 1991;28:665–73.
Matsuda H, Tsuji S, Shuke N, Sumiya H, Tonami N, Hisada K. A quantitative approach to technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime. Eur J Nucl Med. 1992;19:195–200.
Matsuda H, Tsuji S, Shuke N, Sumiya H, Tonami N, Hisada K. Noninvasive measurements of regional cerebral blood flow using technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime. Eur J Nucl Med. 1993;20:391–401.
Matsuda H, Nakano S, Tanaka M. Noninvasive regional cerebral blood flow measurements at pre- and post-acetazolamide test using 99mTc-ECD. Kaku Igaku. 1996;33:759–66.
Takeuchi R, Matsuda H, Sakahara H, Konishi J. Noninvasive quantitative measurements of regional cerebral blood flow using technetium-99m-L, L-ECD SPECT activated with acetazolamide. Kaku Igaku. 1996;33:1213–20.
Takeuchi R, Matsuda H, Yonekura Y, Sakahara H, Konishi J. Noninvasive quantitative measurements of regional cerebral blood flow using technetium-99m-L, L-ECD SPECT activated with acetazolamide: quantification analysis by equal-volume-split 99mTc-ECD consecutive SPECT method. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1997;17:1020–32.
Takaki A, Yoshioka K, Teraoka S, Souma T, Yano K, Miyasaka T, et al. Development of an automatic analytical tool for quantitative cerebral blood flow measurement using 99mTc-ECD, and verification of clinical examples. Jpn J Radiol Technol. 2006;62:729–33.
Takaki A, Yoshioka K, Teraoka S, Souma T, Kawakami K, Yokoi T, et al. Development and assessment of an automatic quantitative cerebral vascular reserve estimation tool for use with triple-injection 99mTc-ECD SPECT. Jpn J Radiol Technol. 2007;63:563–9.
Yokoi T, Shinohara H, Takaki A. Improvement of signal-to-noise ratio using iterative reconstruction in a 99mTc-ECD split-dose injection protocol. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30:1125–33.
Takeuchi R, Yonekura Y, Matsuda H, Konishi J. Usefulness of a three-dimensional stereotaxic ROI template on anatomically standardised 99mTc-ECD SPET. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2002;29:331–41.
Takeuchi R, Matsuda H, Yoshioka K, Yonekura Y. Cerebral blood flow SPET in transient global amnesia with automated ROI analysis by 3DSRT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;31:578–89.
Takeuchi R, Yonekura Y, Takeda SK, Fujita K, Konishi J. Fully automated quantification of regional cerebral blood flow with three-dimensional stereotaxic region of interest template: validation using magnetic resonance imaging—technical note. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2003;43:153–62.
Lassen NA, Andersen AR, Friberg L, Paulson OB. The retention of [99mTc]-d, l-HM-PAO in the human brain after intracarotid bolus injection: a kinetic analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1998;8:S13–22.
Friberg L, Andersen AR, Lassen NA, Holm S, Dam M. Retention of 99mTc-bicisate in the human brain after intracarotid injection. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1994;14:S19–27.
Takaki A, Yoshioka K, Teraoka S, Souma T, Okada K, Yokoi T, et al. Improvement in accuracy of quantitative assessment of the regional cerebral blood flow with 99mTc-ECD. Kaku Igaku. 2005;42:11–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momose, M., Takaki, A., Matsushita, T. et al. Usefulness of the automatic quantitative estimation tool for cerebral blood flow: clinical assessment of the application software tool AQCEL. Ann Nucl Med 25, 13–19 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-010-0422-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-010-0422-6