Abstract
Objective
This study examined the influence of linearization correction (LC) on brain perfusion single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Methods
The early onset group (<65 years old) consisted of 10 patients with AD, and the late onset group (≥65 years old) of 13 patients with AD. Age-matched controls included seven younger and seven older normal volunteers. Tc-99m hexamethyl propyleneamine oxine (HMPAO) SPECT images were reconstructed with or without LC [LC (+) or LC (−)] and a statistical analysis was performed using a three-dimensional stereotactic surface projection (3D-SSP). In addition, a fully automatic diagnostic system was developed, which calculated the proportion of the number of abnormal pixels in the superior and inferior parietal lobule, as well as in the precuneus and posterior cingulate gyrus.
Results
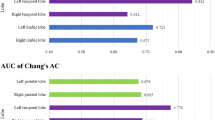
The areas under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUCs) of the early onset group for conventional axial SPECT images, SPECT + 3D-SSP images and the fully automatic diagnostic system were 0.71, 0.88, and 0.92 in LC (−) and 0.67, 0.85, and 0.91 in LC (+), respectively. The AUCs of the late onset group were 0.50, 0.61, and 0.79 in LC (−) and 0.49, 0.67, and 0.85 in LC (+), respectively.
Conclusion
LC on Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT did not significantly influence the diagnostic performance for differentiating between AD and normal controls in either early or late onset AD. Further examination with individuals suffering from very mild dementia is, therefore, expected to elucidate the effect of LC on minimally hypoperfused areas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Small GW, Rabins PV, Barry PP, Buckholtz NS, Dekosky ST, Ferris SH, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer disease and related disorders: consensus statement of the American Association for Geriatric Psychiatry, the Alzheimer’s Association, and the American Geriatrics Society. J Am Med Assoc. 1997;278:1363–71.
Iversen LL. Differences between early and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1987;8:554–5.
Ishii K, Kawachi T, Sasaki H, Kono AK, Fukuda T, Kojima Y, et al. Voxel-based morphometric comparison between early and late-onset mild Alzheimer’s disease and assessment of diagnostic performance of Z score images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005;26:333–40.
Mielke R, Herholz K, Grond M, Kessler J, Heiss WD. Differences of regional cerebral glucose metabolism between presenile and senile dementia of Alzheimer type. Neurobiol Aging. 1992;13:93–8.
Yasuno F, Imamura T, Hirono N, Ishii K, Sasaki M, Ikejiri Y, et al. Age at onset and regional cerebral glucose metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 1998;9:63–7.
Sakamoto S, Ishii K, Sasaki M, Hosaka K, Mori T, Matsui M, et al. Differences in cerebral metabolic impairment between early and late onset types of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci. 2002;200:27–32.
Steinling M, Defebvre L, Duhamel A, Lecouffe P, Lavenu I, Pasquier F, et al. Is there a typical pattern of brain SPECT imaging in Alzheimer’s disease? Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2001;12:371–8.
Minoshima S, Giordani B, Berent S, Frey KA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. Metabolic reduction in the posterior cingulate cortex in very early Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Neurol. 1997;42:85–94.
Neary D, Snowden JS, Shields RA, Burjan AW, Northen B, MacDermott N, et al. Single-photon emission tomography using 99mTc-HMPAO in the investigation of dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1987;50:1101–9.
Derouesne C, Rancurel G, Le Poncin Lafitte M, Rapin JR, Lassen MA. Variability of cerebral blood flow defects in Alzheimer’s disease on 123iodo-isopropyl-amphetamine and single photon emission tomography. Lancet. 1985;1:1282.
Muller H, Moller HJ, Stippel A, Fric M, Grunwald F, Laux G, et al. SPECT patterns in probable Alzheimer’s disease. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999;249:190–6.
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JP, Frith CD, Frackowiak RSJ. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp. 1995;2:189–210.
Minoshima S, Frey KA, Koeppe RA, Foster NL, Kuhl DE. A diagnostic approach in Alzheimer’s disease using three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections of fluorine-18-FDG PET. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:1238–48.
Lassen NA, Andersen AR, Friberg L, Paulson OB. The retention of [99mTc]-d, l-HMPAO in human brain after intracarotid bolus injection: a kinetic analysis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988;8:S13–22.
Murase K, Tanada S, Fujita H, Sasaki S, Hamamoto K. Kinetic behavior of technetium-99m-HMPAO in the human brain and quantification of cerebral blood flow using dynamic SPECT. J Nucl Med. 1992;33:135–43.
Ohnishi T, Hoshi H, Nagamachi S, Jinnouchi S, Flores LGII, Futami S, et al. High-resolution SPECT to assess hippocampal perfusion in neuropsychiatric disease. J Nucl Med. 1995;36:1163–9.
Kogure D, Matsuda H, Ohnishi T, Asada T, Uno M, Kunihiro T, et al. Longitudinal evaluation of early Alzheimer’s disease using brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2000;41:1155–62.
Tang BNT, Minoshima S, George J, Robert A, Swine C, Laloux P, et al. Diagnosis of suspected Alzheimer’s disease is improved by automated analysis of regional cerebral blood flow. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004;31:1487–94.
Imabayashi E, Matsuda H, Asada T, Ohnishi T, Sakamoto S, Nakano S, et al. Superiority of 3-dimensional stereotactic surface projection analysis over visual inspection in discrimination of patients with very early Alzheimer’s disease from controls using brain perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med. 2004;45:1450–7.
Ansar MAB, Osaki Y, Kazui H, Oku N, Takasawa M, Kimura Y, et al. Effect of linearization correction on statistical parametric mapping (SPM): a 99mTc-HMPAO brain perfusion SPECT study in mild Alzheimer’s disease. Ann Nucl Med. 2006;20:511–7.
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology. 1984;34:939–44.
Yoshida T, Kuwabara Y, Ichiya Y, Sasaki M, Fukumura T, Ichimiya A, et al. Cerebral muscarinic acetylcholinergic receptor measurement in Alzheimer’s disease patients on 11C-N-methyl-4-piperidyl benzilate: comparison with cerebral blood flow and cerebral glucose metabolism. Ann Nucl Med. 1998;12:35–42.
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. Mini-Mental State. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975;12:189–98.
Yonekura Y, Nishizawa S, Mukai T, Fujita T, Fukuyama H, Ishikawa M, et al. SPECT with [99mTc]-d, l-hexamethyl-propylene amine oxime (HMPAO) compare with regional cerebral blood flow measured by PET: effect of linearization. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1988;8:S82–9.
Talairach J, Tournoux P. Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of human brain. New York: Thiem Medical Publishers; 1988.
Talbot PR, Lloyd JJ, Snowden JS, Neary D, Testa HJ. Choice of reference region in the quantification of single photon emission computed tomography in primary degenerative dementia. Eur J Nucl Med. 1994;21:503–8.
Pickut BA, Dierckx RA, Dobbeleir A, Audenaert K, Van Laere k, Vervaet A, et al. Validation of the cerebellum as a reference region for SPECT quantification in patients suffering from dementia of the Alzheimer type. Psychiatry Res. 1999;90:103–12.
Sjobeck M, Englund E. Alzheimer’s disease and the cerebellum: a morphologic study on neuronal and glial changes. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2001;12:211–8.
Mizumura S, Kumita S, Cho K, Ishihara M, Nakajo H, Toda M, et al. Development of quantitative analysis method for stereotactic brain image: assessment of reduced accumulation in extent and severity using anatomical segmentation. Ann Nucl Med. 2003;17:289–95.
Metz CE. ROC methodology in radiologic imaging. Invest Radiol. 1986;21:720–33.
Kubota T, Ushijima Y, Okuyama C, Nishimura T. A region-of-interest template for three-dimensional stereotactic surface projection images: Initial application to the analysis of Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Nucl Med Commun. 2006;27:37–44.
Kuwabara Y, Ichiya Y, Sasaki M, Akashi Y, Yoshida T, Fukumura T, et al. Cerebellar vascular response to acetazolamide in crossed cerebellar diaschisis: a comparison of 99mTc-HMPAO single-photon emission tomography with 15O-H2O positron emission tomography. Eur J Nucl Med. 1996;23:683–9.
Ishii K, Willoch F, Minoshima S, Drzezqa A, Ficaro EP, Cross DJ, et al. Statistical brain mapping of 18F-FDG PET in Alzheimer’s disease: validation of anatomical standardization for atrophied brains. J Nucl Med. 2001;42:548–57.
Matsuda H, Mizumura S, Nagao T, Ota T, Iizuka T, Nemoto K, et al. Automated discrimination between very early Alzheimer’s disease and controls using an easy Z-score imaging system for multicenter brain perfusion single-photon emission tomography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007;28:731–6.
Ishii K, Kono AK, Sasaki H, Miyamoto N, Fukuda T, Sakamoto S, et al. Fully automatic diagnostic system for early- and late-onset mild Alzheimer’s disease using FDG PET and 3D-SSP. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2006;33:575–83.
Yamamoto Y, Haramoto M, Komatsu A, Uchida K. Study of the normal database that affects 3D-SSP Z-score mapping. Nippon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi (Japanese). 2004;60:406–14.
Rasmusson DX, Brandt J, Steele C, Hedreen JC, Troncoso JC, Folstein MF. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer disease and clinical features of patients with non-Alzheimer disease neuropathology. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1996;10:180–8.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff in the Department of Radiology and Medical Technology, Kyushu University Hospital for their valuable clinical support and also thank Dr. Brian Quinn in Japan Medical Communication Inc. for their editorial assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitsumoto, T., Ohya, N., Ichimiya, A. et al. Diagnostic performance of Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT for early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease: a clinical evaluation of linearization correction. Ann Nucl Med 23, 487–495 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-009-0266-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12149-009-0266-0