Abstract
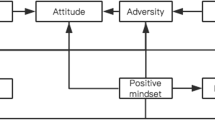
Research on growth mindset has increased dramatically in recent years, and the school climate is critical to growth mindset of middle school students, yet the underlying mediating mechanism is rarely known. This study investigated the chain mediating effect of perceived social support, positive personality between school climate and growth mindset of middle school students. To be specific, 992 junior high school students were taken as the study sample, in which participants completed questionnaires on growth mindset, perceived social support, and positive personality. After controlling for age and socioeconomic status, this study found that there was no gender difference in growth mindset, and school climate was not directly correlated with growth mindset of junior high school students. Moreover, perceived social support and positive personality could mediate the chain between school climate and growth mindset of junior high school students.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All authors ensure that all data and materials and software applications and custom code support publishable statements and conform to standards.
References
Anderson, J. C., & Gerbing, D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103(3), 411–423.
Azimi, M., Fahami, F., & Mohamadirizi, S. (2018). The relationship between perceived social support in the first pregnancy and fear of childbirth. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research, 23(3), 235–239.
Baldridge, M. C. (2010). The Effects of a Growth Mindset Intervention on the Beliefs about Intelligence, Effort Beliefs, Achievement Goal Orientations, and Academic Self-Efficacy of LD Students with Reading Difficulties.ProQuest LLC,789
Barrera, M. (1986). Distinctions between social support concepts, measures, and models. American Journal of Community Psychology, 14(4), 413–445.
Brandisauskiene, A., Kemeryte-Ivanauskiene, E., Buksnyte-Marmiene, L., Cesnaviciene, J., Daugirdiene, A., & Nedzinskaite-Maciuniene, R. (2021). Connection between teacher support and Student’s achievement (13 vol., p. 13632). Could Growth Mindset Be the Moderator? Sustainability. 24.
Burnette, J. L., O’Boyle, E., VanEpps, E., Pollack, J., & Finkel, E. (2012). Mind-sets matter: A meta-analytic review of implicit theories and self-regulation. Psychological Bulletin, 139(3), 655–701.
Chan, R. C. H. (2022). Gender nonconformity, peer victimization, and internalizing problems among youth: Differential moderating effects of school climate by sex assigned at birth. Psychology of Violence, 12(5), 347–360.
Chen, C. J. (2022). The Influence of school climate on student engagement in Learning: A moderated chain mediation analysis (Master’s thesis, Guangzhou University).
Chen, L. (2022). A study on the influence of junior high school students’ perceived school atmosphere on their learning engagement (Master’s Thesis, Central China Normal University).
Clark, K. N., & Malecki, C. K. (2019). Academic grit scale: Psychometric properties and associations with achievement and life satisfaction. Journal of School Psychology, 72, 49–66.
Claro, S., Paunesku, D., & Dweck, C. S. (2016). Growth mindset tempers the effects of poverty on academic achievement. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(31), 8664–8668.
Coelho, V. A., Bear, G. G., & Bras, P. (2020). A multilevel analysis of the importance of School Climate for the Trajectories of Students’ self-concept and self-esteem throughout the Middle School Transition. Journal of youth and adolescence, 49(9), 1793–1840.
Colarossi, L. G., & Eccles, J. S. (2003). Differential effects of support providers on adolescents’ mental health. Social Work Research, 27(1), 19–30.
Conigrave, J. H., Bradshaw, E. L., Devine, E. K., Ciarrochi, J., & Sahdra, B. J. (2019). The link between self-esteem and implicit malleability theories: A meta-analysis Unpublished manuscript.
Cornell, D., Maeng, J. L., Burnette, A. G., Jia, Y., Huang, F., Konold, T., Datta, P., Malone, M., & Meyer, P. (2018). Student threat assessment as a standard school safety practice: Results from a statewide implementation study. School Psychology Quarterly, 33(2), 213–222.
Destin, M., Hanselman, P., Buontempo, J., Tipton, E., & Yeager, D. S. (2019). Do student mindsets differ by socioeconomic status and explain disparities in academic achievement in the United States? AERA open, 5(3), 2332858419857706.
Dong, D. (2019). The relationship between family socioeconomic status and reasoning and attention of secondary vocational School students with left-behind experience: The role of growth Mentality and its intervention[Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Anhui Normal University.
Dong, Q. & Lin, C. D. (2011). Key indicators and evaluation of mental development of children and adolescents aged 6~15 in China. Beijing: Science Press.
Duckworth, A. L., Peterson, C., Matthews, M. D., & Kelly, D. R. (2007). Grit: Perseverance and passion for long-term goals. Journal of personality and social psychology, 92(6), 1087–1101.
Dweck, C. S. (2006). Mindset: The new psychology of success. New York, NY: Random House.
Dweck, C. S., Chiu, C. Y., & Hong, Y. Y. (1995). Implicit theories and their role in judgments and reactions: A word from two perspectives. Psychological inquiry, 6(4), 267–285.
Dweck, C., & Simmons, R. (2014). Why do women fail? Retrieved from http://www.cnn.com/2014/07/29/opinion/dweck-simmons-girls-confidence-failure/
Eccles, J., Lord, L., & Roester, R. (1996). Round holes, square pegs, rocky roads, and sore feet: The impact of stage-environment fit on young adolescents’experiences in schools and families In Adolescence: Opportunities and challenges, Rochester Symposium on Developmental Psychopathology, Vol. 7. Rochester, NY: University of Rochester Press.
Eccles, J. S., & Roser, R. W. (2011). Schools as Developmental Contexts during Adolescence. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(1), 225–241.
Espelage, D. L., Low, S. K., & Jimerson, S. R. (2014). Understanding school climate, aggression, peer victimization, and bully perpetration: Contemporary science, practice, and policy. School Psychology Quarterly, 29, 233–237.
Faul, F., Erdfelder, E., Buchner, A., & Lang, A. G. (2009). Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behavior Research Methods, 41(4), 1149–1160.
Fraser, D. M. (2018). An exploration of the application and implementation of growth mindset principles within a primary school. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 88(4), 645–658.
Furnham, A., Rakow, T., & Mak, T. (2002). The determinants of parents’beliefs about the intelligence of their children: A study from HongKong. International Journal of Psychology, 37(6), 343–352.
Furnham, A., & Wu, C. (2014). The little emperor: Chinese parents’assessment of their own, their partner’s and their only child’s intelli-gence. High Ability Studies, 25(2), 121–141.
Fu, Z. G. (2016). Study on the Relationship and Intervention between College Students’ Life Events, General Self-Efficacy and Post-Stress Growth [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Guangxi Normal University.
Ge, M. G. & Yu, Y. B. (2006). A research report on the School Climate Questionnaire (Junior High School Edition). Psychological science, (02), 460–464.
Ge, M. G., & Yu, Y. B. (2006). Research report of school Climate Questionnaire (Junior High school version). Psychological science, (02), 460–464.
Gálvez, R. H., Tiffenberg, V., & Altszyler, E. (2019). Half a century of stereotyping associations between gender and intellectual ability in films. Sex Roles, 81(9–10), 643–654.
Gurung, R. A., R, Sarason, B. R., & Sarason, I. G. (2005). Personal characteristics, relationship quality, and social support perceptions and behavior in young adult romantic relationships. Personal Relationships, 4(4).
Halpin, A. W., & Croft, D. B. (1962). The Organizational Climate of School. Chicago, IL: Chicago University Press.
Hausmann, M. (2014). Arts versus science ? Academic background implicitly activates gender stereotypes on cognitive abilities with threat raising men’s (but lowering women’s) performance. Intelligence, 46, 235–245.
Huang, Y., Li, P., Lai, Z., Jia, X., Xiao, D., Wang, T., Guo, L., & Lu, C. (2018). Association between sexual minority status and suicidal behavior among chinese adolescents: A moderated mediation model. Journal of Affective Disorders, 239, 85–92.
Janssen, T. W. P., & Atteveldt, N. V. (2022). Explore your brain: A randomized controlled trial into the effectiveness of a growth mindset intervention with psychosocial and psychophysiological components. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 12572
Jia, Y., Way, N., Ling, G. M., Yoshikawa, H., & Lu, Z. (2009). The influence of student perceptions of school climate on socioemotional and academic a nutriment: A comparison of chinese and american adolescents. Child Development, 80(05), 1514–1530.
Kapasi, A., & Pei, J. (2021). Mindset theory and school psychology. Canadian Journal of School Psychology, 08295735211053961.
Kim, J. J., Fung, J., Wu, Q., Fang, C., & Lau, A. S. (2017). Parenting variables associated with growth mindset: An examination of three chinese-heritage samples. Asian American Journal of Psychology, 8(2), 115–125.
Kim, Y. J. (2021). The Mediating Effect of Growth Mindset on the Relationship between Self-Esteem and Depression in the Elderly Koreans. Review of International Geographical Education Online, 11(8), 660–674.
Kleiman, E. M., & Riskind, J. H. (2013). Utilized social support and self-esteem mediate the relationship between perceived social support and suicide ideation: A test of a multiple mediator model. Crisis: The Journal of Crisis Intervention and Suicide Prevention, 34(1), 42–49.
Konishi, C., Hymel, S., Zumbo, B. D., & Li, Z. (2010). Do school bullying and student teacher and academic achievement. Canadian Journal of School Psychology, 25(1), 19–39.
Konold, T., Cornell, D., Shukla, K., & Huang, F. (2017). Racial/ethnic differences in perceptions of school climate and its association with student engagement and peer aggression. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 46(6), 1289–1303.
Lakey, B., & Orehek Edward. (2011). Relational regulation theory: A new approach to explain the link between perceived social support and mental health. Psychological Review, 118(3), 482–495.
Lin, D. H. (2022). What is the secret to lifelong learning and growth -- talk about the role of growth mindset.Educators, (16),6–7.
Lin, J. & Tu, W. (2015). The relationship between positive psychological quality, coping style and understanding of Social support in college students. Chinese Journal of Health Psychology, (2), 225–228.
Lou, N. M., & Noels, K. A. (2019). Promoting growth in foreign and second language education: A research agenda for mindsets in language learning and teaching. System, 86, 102–126.
Luo, X. F., Chen, Q. S., & Mu, S. K. (2017). Revision and preliminary application of the chinese version of the child and adolescent social support scale. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 04, 671–674.
Macnamara, B. N., & Rupani, N. S. (2017). The relationship between intelligence and mindset. Intelligence, 64, 52–59.
Malecki, C. K., & Demaray, M. K. (2006). Social support as a buffer in the relationship between socioeconomic status and academic performance. School Psychology Quarterly, 21(4), 375–395.
Malinauskas, R., & Malinauskiene, V. (2020). The Relationship between Emotional Intelligence and Psychological Well-Being among Male University Students: The Mediating Role of Perceived Social Support and Perceived Stress. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(5).
Ma, Y. (2022). The relationship between positive psychological quality and psychological well-being of urban and rural middle school students (Master’s thesis, Tianjin Normal University).
Moeller, C., & Chung-Yan, G. A. (2013). Effects of social support on professors’ work stress. International Journal of Educational Management, 27 No(3), 188–202.
National School Climate Council (2007). The school climate challenge: Narrowing the gap between school climate research and school climate policy, Practice Guidelines and Teacher Education Policy.
Park, D., Tsukayama, E., Yu, A., & Duckworth, A. L. (2020). The development of grit and growth mindset during adolescence. Journal of Experimental Child Psychology, 198, 104889.
Peterson, C., & Seligman, M. E. P. (2004). Strengths of Character and Well-Being: A closer look atHope and modesty. Journal of Social & Clinical Psychology, 23(5), 603–619.
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Lee, J. Y., & Podsakoff, N. P. (2003). Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology, 88(5), 879–903.
Qin, G. H., Jiang, Z. F., & Wang, D. M. (2020). The relationship between the current status of growth mindset mode and academic performance of primary and middle school students. parents, (20), 122–124.
Rina, T. S. U. C. H. I. E., & FUKUDA Seiji. (2021). Factors Associated with Self-Esteem in Junior High School Students. Shimane Journal of Medical Science, 38(4), 111–118.
Rivera, L. A., & Tilcsik, A. (2019). Scaling down inequality: Rating scales,gender bias, and the architecture of evaluation. American Sociological Review, 84(2), 248–274.
Roeser, R. W., Marachi, R., & Gehlbach, H. (2002). A Goal Theory Perspective on Teachers’ Professional Identities and the Contexts of Teaching.Goals, Goal Structures, and Patterns of Adaptive Learning, 223–260.
Roeser, R. W., Midgley, C., & Urdan, T. C. (1996). Perceptions of the school psychological environment and early adolescents? psychological and behavioral functioning in school:The mediating role of goals and belonging. Journal of Educational Psychology, 88, 408–422.
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2017). Self-determination theory: Basic psychological needs in motivation, development, and wellness. New York: Guilford Publishing.
Saunders, S. A. (2013). The impact of a growth mindset intervention on the reading achievement of at-riskadolescent students. University of Virginia.
Schmiedl, A., Schulte, E. M., & Kauffeld, S. (2022). The Demands-Buffering Role of Perceived and Received Social Support for Perceived Stress and Cortisol Levels. European Journal of Health Psychology.
Schneider, S. H., & Duran, L. (2010). School climate in middle schools: A cultural perspective. Journal of Research in Character Education, 8(2), 25–37.
Schwarzer, R. & Jerusalem, M. (1981). Fragebogen zur Erfassung von "Selbstwirksamkeit. Skalen zur Befindlichkeit und Persoenlichkeit In R. Schwarzer (Hrsg.). (Forschungsbericht No. 5). Berlin: Freie Universitaet, Institut fuer Psychologie.
Sedillo, Hamann, & Dayna (2021). Building Adolescent Self-efficacy and Resilience Through Social Action. Child and Adolescent Social Work Journal, pp.1–9.
Seligman, M. E. P., Ernst, R. M., et al. (2009). Positive education: Positive psychology and classroom interventions. Oxford review of education, 35(3), 293–311.
Shu, Y., Hu, Q., Xu, F., & Bian, L. (2022). Gender stereotypes are racialized: A cross-cultural investigation of gender stereotypes about intellectual talents. Developmental Psychology.
Snyder, C. R., & Lopez Shane, J. (2009). Oxford handbook of positive psychology (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press.
Soenens, B., & Vansteenkiste, M. (2010). A theoretical upgrade of the concept of parental psychological control: Proposing new insights on the basis of self-determination theory. Developmental Review, 30(1), 74–99.
Song, L. L., Qiu, Y., Wang, Y., Qiu, Z. F. & Yin, Y. Y. (2021). Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of 12-item grit scale in Chinese adolescent. China Journal of Health Psychology, (9), 1354–1359.
Spencer, M. B., Dupree, D., & Hartmann, T. (1997). A phenomenological variant of ecological systems theory (PVEST): A self-organization perspective in context. Development and Psychopathology, 9(4), 817–833.
Spinath, B., Spinath, F. M., Riemann, R., & Angleitner, A. (2003). Implicit theories aboutpersonality and intelligence and their relationship to actual personality and in-telligence. Personality and Individual Differences, 35, 939–951.
Storage, D., Charlesworth, T. E., Banaji, M. R., & Cimpian, A. (2020). Adults and children implicitly associate brilliance with men more thanwomen. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 90, 104020.
Sun, M. M. (2021). The Relationship between Social support, perseverance and growth thinking in senior primary school students (Master’s thesis, Hebei Normal University)
Tan, C. S., Chin, X. Y., Chng, S. T., Lee, J., & Ooi, C. S. (2022). Perceived Social Support increases Creativity: Experimental evidence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(18), 11841.
Thapa, A., Cohen, J., Guffey, S., & Higgins-D’Alessandro, A. (2013). A review of School Climate Research. Review of Educational Research, 83(3), 357–385.
Tian, H. (2019). Affirming Forward Posture and Maintaining Walking Energy -- The Way of Teacher Professional Development under the guidance of Growth mindset. Journal of Education Institute of Jilin Province, (11), 48–51.
Tong, X. F. (2022). Meaning of life and meaning care of School Education. Contemp. Educ Sci, 6, 9–15.
Toro, J. D., & Wang, M. T. (2021). Longitudinal interrelations between school cultural socialization and school engagement: The mediating role of school climate. Learning and Instruction, 5, 101482.
Tucker-Drob, E. M., Briley, D. A., Engelhardt, L. E., Mann, F. D., & Harden, K. P. (2016). Genetically-mediated associations between measures of childhood character and academic achievement. Journal of personality and social psychology, 111(5), 790–815.
Uchino, & Bert, N. (2004). Social Support and Physical Health: Understanding the Health Consequences of Relationships.New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 21:78–123
Wang, C. K., Hu, Z. F., & Liu, Y. (2001). Reliability and validity of general self-efficacy scale. Applied psychology, 7(1), 4.
Wang, D., Gan, L., & Wang, C. (2021). The effect of growth mindset on reasoning ability in Chinese adolescents and young adults: the moderating role of self-esteem.Current Psychology,1–7.
Wang, M. T., & Degol, J. L. (2016). School Climate: A review of the Construct, Measurement, and impact on Student Outcomes. Educational Psychology Review, 28, 315–352.
Wang, M.-T., & Dishion, T. J. (2012). The Trajectories of Adolescents? Perceptions of School Climate, Deviant Peer Affiliation, and Behavioral Problems During the Middle School Years. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 22(1), 40–53.
Wang, S., Dai, J., Li, J., Wang, X., Chen, T., Yang, X., He, M., Gong, Q. (2018). Neuroanatomical correlates of grit: Growth mindset mediates the association between gray matter structure and trait grit in late adolescence. Human Brain Mapping, 39(4), 1688–1699.
West, M. R., Kraft, M. A., Finn, A. S., Martin, R. E., Duckworth, A. L., Gabrieli, C. F., & Gabrieli, J. D. (2016). Promise and paradox: Measuring students’ non-cognitive skills and the impact of schooling. Educational Evaluation and Policy Analysis, 38, 148–170.
Worrell, F. C., & Hale, R. L. (2001). The relationship of hope in the future and perceived school climate to school completion. School Psychology Quarterly, 16(4), 370.
Wu, L. (2018). Diagnosis and treatment of Chinese youth “hollow disease” from the perspective of modernity.Research of Modern Young People. (1):79–84.
Wu, X. (2021). The influence of parental involvement on primary school students’ academic performance: The Mediating role of growth mindset. Contemporary Education Forum, 02, 75–88.
Yadav, S. (2010). Perceived social support, hope, and quality of life of persons living with aids: A case study from Nepal. Quality of Life Research, 19(2), 157–166.
Yan, Z., King, R. B., & Haw, J. Y. (2021). Formative assessment, growth mindset, and achievement: examining their relations in the East and the West. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 28(5–6),676–702.
Yeager, D. S., & Dweck, C. S. (2012). Mindsets that promote resilience: When students believe that personal characteristics can be developed. Educational psychology, 47, 302–314.
Yeager, D. S., Hanselman, P., Walton, G. M., Murray, J. S., Crosnoe, R., Muller, C., & Dweck, C. S. (2019). A national experiment reveals where a growth mindset improves achievement. Nature, 573(7774), 364–369.
Yuan, W. P., Li, X. Q., & Ma, L. (2021). The relationship between positive psychological quality and subjective well-being of higher vocational students: Understanding the chain mediating role of social support and school belonging. Chinese Journal of Health Psychology, 04, 615–619.
Yu, J., Kreijkes, P., & Salmela-Aro, K. (2022). Students’ growth mindset: Relation to teacher beliefs, teaching practices, and school climate. Learning and Instruction, 80.
Zander, L., Brouwer, J., Jansen, E., Crayen, C., & Hannover, B. (2018). Academic self-efficacy, growth mindsets, and university students’ integration in academic and social support networks. Learning and Individual Differences, 62, 98–107.
Zarrinabadi, N., Lou, N. M., & Shirzad, M. (2021). Autonomy support predicts language mindsets: Implications for developing communicative competence and willingness to communicate in EFL classrooms. Learning and Individual Differences, 86, 101981.
Zeng, G., Chen, X., & Cheung, H. Y., Peng, K. (2019). Teachers’ growth mindset and work engagement in the chinese educational context: Well-being and perseverance of effort as mediators. Frontiers in Psychology, 10, 839.
Zhang, L. C. (2018). Study on the Relationship and Intervention between Troubled Children’s Emotional Intelligence, Social Support. and Post-Stress Growth. [Unpublished Doctoral dissertation ]. Guangxi Normal University.
Zhang, P. P., Li, L. Y. & Xin, T. (2011). Cross-cultural comparison of the influence of school climate on students' Mathematics Achievement: Based on the results of a multilevel analysis. Psychological Development and Education, 27(6), 625–632.
Zhao, C., Xu, H., Lai, X., Yang, X., Tu, X., Ding, N., Lv, Y., & Zhang, G. (2021). Effects of online social support and perceived social support on the relationship between perceived stress and problematic smartphone usage among chinese undergraduates. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 14, 529–539.
Zhao, H., Zhang, M., Li, Y., & Wang, Z. (2023). The Relationship between a Growth Mindset and Junior High School Students’ Meaning in Life: A Serial Mediation Model. Behavioral Sciences, 13(2), 189.
Zhao, Q., Wichman, A., & Frishberg, E. (2019). Self-doubt effects depend on beliefs about ability: Experimental evidence. The Journal of General Psychology, 146(3), 299–324.
Zhao, Y. F., Zhai, X. P., Zhang, G. X., Liang, X., & Xin, S. F. (2022). The relationship between growth mindset and persistence: Future time perception and multiple mediators of achievement motivation. Psychological Development and Education, (02), 216–222.
Zhao, Y., Niu, G., Hou, H., Zeng, G., Xu, L., Peng, K., & Yu, F. (2018). From growth mindset to grit in chinese schools: The mediating roles of learning motivations. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1–7.
Zhou, H., & Long, L. R. (2004). Statistical tests and control methods for common method deviations. Advances in psychological Science, 12(6), 942–950.
Zullig, K. J., Huebner, E. S., & Patton, J. M. (2010). Relationships among school climate domains and school satisfaction. Psychology in the Schools, 48(2), 133–145.
Acknowledgements
Thanks for the following funding support Northwest Normal University under Grant [No. 2018SKGG06] and Northwest Normal University under Grant [No. NWNU-LKQN-18-36].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Li Chen was mainly responsible for the conception and design of the whole experiment and the writing of articles, ying Tang and Ying Zhang was responsible for the implementation of the experiment, the collection of data and Proofreading of article format.On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval
All human subjects involved in the design of this study received moral and ethical approval from the School of Psychology at Northwest Normal University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, L., Zhang, Y. & Tang, Y. The relationship between school climate and growth mindset of junior middle school students: a mediating model of perceived social support and positive personality. Curr Psychol 43, 4142–4154 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04570-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-023-04570-9