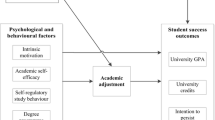
Abstract
Academic failure is one of the most important concerns of teachers, education officials, and families, and is one of the most common problems in the current education system is that it wastes tens of millions of dollars a year from the country’s budget. As a result, the potential forces and assets of society, which are human resources, remain ineffective. Accordingly, the present study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of study skills on self-efficacy, academic eagerness, and academic performance. This research was quasi-experimental having pre-test and post-test design with the unequal control group. The population included all-female high school students of Taybad schools in the academic year of 2017–2018. Using the non-probability (targeted) sampling method, 30 people were selected as a sample and randomly assigned to two experimental and control groups (15 people in each group). For data collection, we used the Academic Self-efficacy scale of Sherer et al. (1982) and the academic engagement of Schaufeli et al. (2002) and academic performance (GPA point). The data were analyzed using covariance analysis (ANCOVA). The experimental group received 8 study skills training sessions during which the control group did not receive any training. The results showed that study skills training significantly increased the academic self-efficacy and its components, including the ability to manage homework, family and school, and academic engagement and its components among the participants in the post-test (p < 0/001). Based on the results, it can be concluded that by implementing study skills training, students’ self-efficacy, academic engagement, and academic performance can be improved.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ames, C., & Archer, J. (1988). Achievement goals in the classroom: Student learning strategies and motivation processes. Journal of Educational Psychology, 80(3), 260–267. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.80.3.260.
Asarta, C. J., & Schmidt, J. R. (2017). Comparing student performance in blended and traditional courses: Does prior academic achievement matter? The Internet and Higher Education, 32(1), 29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.08.002.
Asarta, C. J., & Schmidt, J. R. (2020). The effects of online and blended experience on outcomes in a blended learning environment. The Internet and Higher Education, 44, 100708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2019.100708.
Bahri, L., & Yousefi, F. (2014). Examine the psychometric properties of the questionnaire behavioral and emotional involvement in the academic middle school students. Journal of Teaching and Learning, 66(2), 21–45 [Persian].
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundation of thought and action. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Precentic Hall.
Baugher, D., Varanelli, A., & Weisbord, E. (2003). Student hits in an internet-supported course: How can instructors use them and what do they mean? Decision sciences. Journal of Innovative Education, 1(2), 159–179. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-4609.2003.00016.x.
Biktimirov, E., & Klassen, K. (2008). Relationship between use of online support materials and student performance in an introductory finance course. Journal of Education for Business, 83(3), 153–158. https://doi.org/10.3200/JOEB.83.3.153-158.
Boehler, M. L., Schwind, C. J., & Folse, R. (2001). An evaluation of study habits of third-year medical students in a surgical clerkship. The American Journal of Surgery, 181(3), 268–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0002-9610(01)00569-4.
Brown, S. D., Tramayne, S., Hoxha, D., Telander, K., Fan, X., & Lent, R. W. (2016). Social cognitive predictors of college students’ academic performance and persistence: A meta-analytic path analysis. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 72(3), 298–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2007.09.003.
Bruinsma, M. (2017). Motivation, cognitive processing and achievement in higher education. Journal of Learning and Instruction, 14(6), 549–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2004.09.001.
Buttler, D., & Winne, P. (1995). Feedback and self-regulated learning: A theoretical synthesis. Review of Educational Research, 65(3), 245–281. https://doi.org/10.2307/1170684.
Catalano, A. (2017). Development and Validation of the Metacognitive Strategies for Library Research Skills scale (MS-LRSS). Available: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2017.02.017Get rights and content.
Costa, A., & Faria, L. (2020). The impact of implicit theories on students’ emotional outcomes. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-00750-z.
Côté, S., Van Kleef, G. A., & Sy, T. (2013). The social effects of emotion regulation in organizations. In A. A. Grandey, J. M. Diefendorff, & D. E. Rupp (Eds.), Organization and management. Emotional labor in the 21st century: Diverse perspectives on emotion regulation at work (pp. 79–100). Abingdon: Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group.
Davidson, R. (2009). Relationship of study approach and exam performance. Journal of Education, 20(1), 29–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0748-5751(01)00025-2.
Derossis, A. M., Rosa, D. D., Schwartz, A., Hauge, L. S., & Bordage, G. (2004). Study habits of surgery residents and performance on American Board of Surgery in-Training examinations. The American Journal of Surgery, 188(3), 230–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.06.001.
Diseth, A. (2011). Self-efficacy, goal orientations and learning strategies as mediators between preceding and subsequent academic achievement, 3rd world conference on educational science. Learning and Individual Differences, 21(2), 191–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2011.01.003.
Duff, A. (2014). The relationship between personality, approach to learning and academic performance. Journal of Personality and Individual Differences., 36(8), 1907–1920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2003.08.020.
Godellas, C. V., Hauge, L. S., & Huang, R. (2000). Factors affecting improvement on the American Board of Surgery in-Training Examination (ABSITE). Surgery Resources, 91(1), 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1006/jsre.2000.5852.
Goli, Z., Omidi, A., & Momeni, J. (2016). Effect of metacognitive skills training on metacognitive awareness, self-efficacy and academic achievement of university students. International Archives of Health Sciences, 3(4), 171–177 http://oldiahs.kaums.ac.ir/article-1-120-en.html.
Gurat, M. G., & Medula Jr., C. T. (2016). Metacognitive strategy knowledge use through mathematical problem solving amongst pre-service teachers. American Journal of Educational Research, 4(2), 170–189. https://doi.org/10.12691/education-4-2-5.
Hunter, M. S., & Linder, C. V. (2015). How to study. Journal of Experimental Psychology, 130(2), 224–237.
Javidan, S. H., Hossein Khanzadeh, A. A., & Abolghasemi, A. (2018). Effectiveness of meta-cognitive skills training on self-handicapping and self-efficacy of students. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal, 16(1), 69–76. https://doi.org/10.29252/NRIP.IRJ.16.1.69.
Johnson, M. D. (2005). Academic performance of transfer versus “native” students in natural resources & sciences. College Student Journal, 39(3), 570–579.
Jones, C. T., Kouliavtsev, M. S., & Ethridge, J. R. (2013). Lower level prerequisites and student performance in intermediate business courses: Does it matter where students take their principles courses? Journal of Education for Business, 88(4), 238–245. https://doi.org/10.1080/08832323.2012.688777.
Kirk, S., Gallagher, G., & Coleman, M. R. (2015). Educating Exceptional Children (14th Ed). Prilnted in the United States of America: Cengage Learning.
Kokkinos, C. M., & Vlavianou, E. (2018). The moderating role of emotional intelligence in the association between parenting practices and academic achievement among adolescents. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-019-00343-5.
Lee, J., & Shute, V. J. (2015). Personal and social- contextual factor in K-12 academic performance: An integrative perspective on student learning. Educational Psychologist, 45(3), 185–202. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2010.493471.
Li, R., Liu, H., Chen, Y., & Yao, M. (2019). Teacher engagement and self-efficacy: The mediating role of continuing professional development and moderating role of teaching experience. Current Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-019-00575-5.
Maslach, C., Schaufeli, W. B., & Leiter, M. P. (2001). Job burnout. Annual Review of Psychology, 52(1), 397–422. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.52.1.397.
Mayer, J. D. (2001). A field guide to emotional intelligence. In J. Ciarrochi, J. P. Forgas, & J. D. Mayer (Eds.), Emotional intelligence in everyday life: A scientific inquiry (pp. 3–24). New York: Psychology Press.
Nakhostin Goldoost, A., Ghazanfari, A., Sharifi, T., & Chorami, M. (2019). The effect of metacognitive skills training on academic self-efficacy and academic eagerness of 10th grade male students in Ardabil. Journal of school psychology, 8(2), 131–155. https://doi.org/10.22098/jsp.2019.817.
Naseri, M., Kazemi, M., & Effati Motlag, M. (2017). The effectiveness of metacognitive skills training on increasing academic achievement. Iranian journal of educational Sociology, 1(3), 83–88.
Nijhuis, J., Segers, M., & Gijselaers, W. (2008). The extent of variability in learning strategies and students’ perceptions of the learning environment. Learning and Instruction, 18(2), 121–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2007.01.009.
Öz, H. (2016). Metacognitive awareness and academic motivation: A cross- sectional study in teacher education context of Turkey. International Conference on Teaching and Learning English as an Additional Language. Turkey: Antalya.
Partovi, T., & Razavi, M. R. (2019). The effect of game-based learning on academic achievement motivation of elementary school students. Learning and Motivation, 68, 101592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lmot.2019.101592.
Pellas, N. (2014). The influence of computer self-efficacy, metacognitive self-regulation and self-esteem on student engagement in online learning programs: Evidence from the virtual world of second life. Journal of Computers in Human Behavior, 35, 157–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.02.048.
Pintrich, P. R., & de Groot, E. V. (1990). Motivational and self-regulated learning components of classroom academic performance. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82(1), 33–40. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.82.1.33.
Razavi, M. R. (2013). Conditions influencing faculty Members’ stages of concern and levels of implementation of online learning technology at E-learning centers in Iranian universities. University Putra Malaysia.
Razavi, M. R. (2018). Gender differences in the effect of virtual social networks use on students’ academic performance. Current Psychology, 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-018-9991-7.
Riffell, S., & Sibley, D. (2005). Using web-based instruction to improve large undergraduate biology courses: An evaluation of a hybrid course format. Computers & Education, 44(3), 217–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2004.01.005.
Schaufeli, W. B., Salanova, M., Gonzalez-Roma, V., & Baker, A. B. (2002). The measurement of engagement and burnout. Journal of Happiness Studies, 3(1), 71–92. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015630930326.
Schmidt, D., & Wartick, M. (2014). Performance in upper-level accounting courses: The case of transfer students. Advances in Accounting Education, 14, 171–192. https://doi.org/10.1108/S1085-4622(2013)0000014014.
Schneider, W. (2015). Metacognitive Development: Educational Implications. In Metacognitive. Development: Educational Implications, Available. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-097086-8.92011-7.
Schwarzer, R., & Fuchs, R. (2006). Self-efficacy and health behaviors. In M. Conner & P. Norman (Eds.), Predicting health behavior: Research and practice with social cognition models. UK: Open University press.
Sherer, M., Maddux, J. E., Mercandente, B., Prentice-Dunn, S., Jacobs, B. M., & Rogers, R. W. (1982). The self-efficacy scale: Construction and validation. Psychological Reports, 51(2), 663–671. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.1982.51.2.663.
Wisneski, J. E., Ozogul, G., & Bichelmeyer, B. A. (2017). Investigating the impact of learning environments on undergraduate students' academic performance in a prerequisite and post-requisite course sequence. Internet and Higher Education, 32, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2016.08.003.
Yip, M., & Chung, O. (2002). Relation of study strategies to the academic performance of Hong Kong University students. Psychological Reports, 90(1), 338–340. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.2002.90.1.338.
You, J. W. (2016). Identifying significant indicators using LMS data to predict course achievement in online learning. Internet and Higher Education, 29, 23–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.11.003.
Zimmerman, B. J., & Schunk, D. H. (2016). Handbook of self-regulation of learning and performance. New York: Routledge Taylor & Francis.
Zimmerman, B. J., Schunk, D. H., & DiBenedetto, M. K. (2017). The role of self-efficacy and related beliefs in self-regulation of learning and performance. In A. J. Elliot, C. S. Dweck, & D. S. Yeager (Eds.), Handbook of competence and motivation: Theory and application (pp. 313–333). New York: The Guilford Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Current Themes of Research
Metacognitive Skills; Educational Psychology, Educational Technology, Academic Engagement and Performance.
Most Relevant Publications
- The effect of game-based learning on academic achievement motivation of elementary school students.
- Gender differences in the effect of virtual social networks use on students’ academic performance.
- Conditions Influencing Faculty Members’ Stages of Concern and Levels of Implementation of Online Learning Technology at E-learning Centers in Iranian Universities.
- Digital Education.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taghani, A., Razavi, M.R. The effect of metacognitive skills training of study strategies on academic self-efficacy and academic engagement and performance of female students in Taybad. Curr Psychol 41, 8784–8792 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-01278-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-020-01278-y