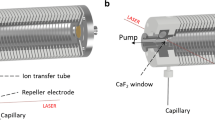
Abstract
Infrared matrix-assisted laser dispersion and ionization (IR-MALDI) in combination with ion mobility (IM) spectrometry enables the direct analysis of biomolecules in aqueous solution. The release of ions directly from an aqueous solution is based on a phase explosion, induced by the absorption of an IR laser pulse, which disperses the liquid as vapor, nano- and micro-droplets. The ionization process is characterized initially by a broad spatial distribution of the ions, which is a result of complex fluid dynamics and desolvation kinetics. These processes have a profound effect on the shape and width of the peaks in the IM spectra. In this work, the transport of ions by the phase explosion-induced shockwave could be studied independently from the transport by the electric field. The shockwave-induced mean velocities of the ions at different time scales were determined through IM spectrometry and shadowgraphy. The results show a deceleration of the ions from 118 m∙s−1 at a distance of 400 μm from the liquid surface to 7.1 m∙s−1 at a distance of 10 mm, which is caused by a pile-up effect. Furthermore, the desolvation kinetics were investigated and a first-order desolvation constant of 325 ± 50 s−1 was obtained. In the second part, the IR-MALDI-IM spectrometer is used as an HPLC detector for the two-dimensional separation of a pesticide mixture.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koomen JM, Ruotolo BT, Gillig KJ et al (2002) Oligonucleotide analysis with MALDI-ion-mobility-TOFMS. Anal Bioanal Chem 373:612–617
von Helden G, Wyttenbach T, Bowers MT (1995) Inclusion of a MALDI ion source in the ion chromatography technique: conformational information on polymer and biomolecular ions. Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Process 146–147:349–364
Tong H, Sze N, Thomson B et al (2002) Solid phase microextraction with matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization introduction to mass spectrometry and ion mobility spectrometry. Analyst 127:1207–1210
Steiner WE, Clowers BH, English WA, Hill HH (2004) Atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with analysis by ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 18:882–888
Charvat A, Abel B (2007) How to make big molecules fly out of liquid water: applications, features and physics of laser assisted liquid phase dispersion mass spectrometry. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9:3335–3360
Charvat A, Lugovoj E, Faubel M, Abel B (2004) New design for a time-of-flight mass spectrometer with a liquid beam laser desorption ion source for the analysis of biomolecules. Rev Sci Instrum 75:1209
Kleinefort W, Avdiev J, Brutschy B (1996) A new method of laser desorption mass spectrometry for the study of biological macromolecules. Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Process 152:135–142
Morgner N, Barth H-D, Brutschy B (2006) A new way to detect noncovalently bonded complexes of biomolecules from liquid micro-droplets by laser mass spectrometry. Aust J Chem 59:109
Laiko VV, Taranenko NI, Berkout VD et al (2002) Desorption/ionization of biomolecules from aqueous solutions at atmospheric pressure using an infrared laser at 3 μm. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 13:354–361
Rapp E, Charvát A, Beinsen A et al (2009) Atmospheric pressure free liquid infrared MALDI mass spectrometry: toward a combined ESI/ MALDI-liquid chromatography interface. Anal Chem 81:443–452
Hoffmann J, Schmidt TL, Heckel A, Brutschy B (2009) Probing the limits of liquid droplet laser desorption mass spectrometry in the analysis of oligonucleotides and nucleic acids. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 23:2176–2180
Villatoro J, Zühlke M, Riebe D, Riedel J, Beitz T, Löhmannsröben H-G (2016) IR-MALDI ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem. doi:10.1007/s00216-016-9739-x
Chen Z, Vertes A (2008) Early plume expansion in atmospheric pressure midinfrared laser ablation of water-rich targets. Phys Rev E 77:036316
Charvat A, Stasicki B, Abel B (2006) Product screening of fast reactions in IR-laser-heated liquid water filaments in a vacuum by mass spectrometry. J Phys Chem A 110:3297–3306
Apitz I, Vogel A (2005) Material ejection in nanosecond Er:YAG laser ablation of water, liver, and skin. Appl Phys A 81:329–338
Wiederschein F, Vöhringer-Martinez E, Beinsen A et al (2015) Charge separation and isolation in strong water droplet impacts. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17:6858–6864
Berkenkamp S, Menzel C, Hillenkamp F, Dreisewerd K (2002) Measurements of mean initial velocities of analyte and matrix ions in infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 13:209–220
Leisner A, Rohlfing A, Röhling U et al (2005) Time-resolved imaging of the plume dynamics in infrared matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with a glycerol matrix. J Phys Chem B 109:11661–11666
Rohlfing A, Menzel C, Kukreja LM et al (2003) Photoacoustic analysis of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization processes with pulsed infrared lasers. J Phys Chem B 107:12275–12286
Zühlke M, Riebe D, Beitz T et al (2015) An electrospray ionization-ion mobility spectrometer as detector for high- performance liquid chromatography. Eur J Mass Spectrom 21:391–402
Mason EA, McDaniel EW (1988) Transport properties of ions in gases. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim
Michalik-Onichimowska A, Beitz T, Panne U, Löhmannsröben H-G, Riedel J (2016) Microsecond mid-infrared laser pulses for atmospheric pressure laser ablation/ionization of liquid samples. Sensors Actuators B. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.155
Sturm M, Bertsch A, Gröpl C et al (2008) OpenMS—an open-source software framework for mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinf 9:163
Acknowledgments
For financial support the authors would like to thank the German Excellence Initiative (DFG – Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft), the School of Analytical Sciences Adlershof (SALSA) and the Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und—prüfung (BAM). Furthermore, we would also like to thank Ales Charvat (IOM Leipzig) for providing the microbeam nozzle mount and accompanying our first steps in IR-MALDI, as well as Sandro Andreotti (FU Berlin) for the support in OpenMS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Villatoro, J., Zühlke, M., Riebe, D. et al. IR-MALDI ion mobility spectrometry: physical source characterization and application as HPLC detector. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spec. 19, 197–207 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-016-0208-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-016-0208-1