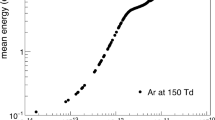
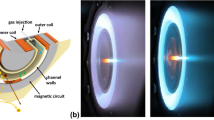
Abstract
A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) software package ANSYS Fluent was employed for simulation of ion transport at atmospheric pressure between a nano-electrospray ionization (nano-ESI) emitter and the mass spectrometer (MS) sampling inlet tube inside an improved air amplifier device incorporating a radiofrequency ion funnel. The flow field, electric field and the ion trajectory calculations were carried out in separate steps. Parallelized user-defined functions were written to accommodate the additional static and transient electric fields and the elastic ion-gas collisions with the Monte Carlo hard-sphere simulation abilities within Fluent’s environment. The ion transmission efficiency from a nano-ESI emitter to the MS sampling inlet was evaluated for different air amplifier and ion funnel operating conditions by tracking 250 sample reserpine ions. Results show that the high velocity gas stream and the external electric field cause a rapid acceleration of the ion beam and its dispersion along the centreline of the air amplifier which leads to reduction of the space-charge effect and the beam divergence. The radiofrequency potential applied to the ion funnel contributed to additional ion focusing.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahadi E, Konermann L (2010) Surface charge of electrosprayed water nanodroplets: a molecular dynamics study. J Am Chem Soc 132:11270–11277. doi:10.1021/ja1041989
Appelhans AD, Dahl DA (2002) Measurement of external ion injection and trapping efficiency in the ion trap mass spectrometer and comparison with a predictive model. Int J Mass Spectrom 216:269–284. doi:10.1016/S1387-3806(02)00627-9
Appelhans AD, Dahl DA (2005) SIMION ion optics simulations at atmospheric pressure. Int J Mass Spectrom 244:1–14. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2005.03.010
Arumugham-Achari AK, Grifoll J, Rosell-Llompart J (2013) Two-way coupled numerical simulation of electrospray with induced gas flow. J Aerosol Sci 65:121–133. doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2013.07.005
Barth TJ, Jespersen DC (1989) The design and application of upwind schemes on unstructured meshes. Paper presented at the AIAA 27th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, Nevada
Dahl DA (2000) SIMION for the personal computer in reflection. Int J Mass Spectrom 200:3–25
Dahl DA, McJunkin TR, Scott JR (2007) Comparison of ion trajectories in vacuum and viscous environments using SIMION: Insights for instrument design. Int J Mass Spectrom 266:156–165. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2007.07.008
Daub CD, Cann NM (2011) How are completely desolvated ions produced in electrospray ionization: insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Anal Chem 83:8372–8376. doi:10.1021/ac202103p
Deng W, Gomez A (2007) Influence of space charge on the scale-up of multiplexed electrosprays. J Aerosol Sci 38:1062–1078. doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2007.08.005
Ding L, Sudakov M, Kumashiro S (2002) A simulation study of the digital ion trap mass spectrometer. Int J Mass Spectrom 221:117–138. doi:10.1016/S1387-3806(02)00921-1
Fenn J, Mann M, Meng C, Wong S, Whitehouse C (1989) Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science 246:64–71. doi:10.1126/science.2675315
FLUENT 6.3 UDF Manual (2006) Fluent Inc
FLUENT 6.3 User’s Guide (2006) Fluent Inc
Forbes MW, Sharifi M, Croley T, Lausevic Z, March RE (1999) Simulation of ion trajectories in a quadrupole ion trap: a comparison of three simulation programs. J Mass Spectrom 34:1219–1239. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-9888(199912)34:12<1219::AID-JMS897>3.0.CO;2-L
Grifoll J, Rosell-Llompart J (2012) Efficient Lagrangian simulation of electrospray droplets dynamics. J Aerosol Sci 47:78–93. doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2012.01.001
Han F et al (2012) Computational fluid dynamics-Monte Carlo method for calculation of the ion trajectories and applications in ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom 309:13–21. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2011.08.017
He L, Lubman DM (1997) Simulation of External ion injection, cooling and extraction processes with SIMION 6.0 for the Ion trap/reflectron time-of-flight mass spectrometer. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 11:1467–1477
Helin Z, Jing L (2012) Molecular dynamics simulation of the behaviour of the charged nanodroplet in electrospray. Micro Nano Lett IET 7:1001–1004. doi:10.1049/mnl.2012.0673
Jung JH, Oh H, Kim SS (2010) Numerical simulation of the deposition pattern in multiple electrohydrodynamic spraying. Powder Technol 198:439–444. doi:10.1016/j.powtec.2009.12.006
Juraschek R, Dülcks T, Karas M (1999) Nanoelectrospray—more than just a minimized-flow electrospray ionization source. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 10:300–308
Jurčíček P, Liu L, Zou H, An Z, Xiao H (2014) Design, simulation and evaluation of improved air amplifier incorporating an ion funnel for nano–ESI MS. Eur J Mass Spectrom 20:143–154
Karas M, Bahr U, Dülcks T (2000) Nano-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: addressing analytical problems beyond routine Fresenius. J Anal Chem 366:669–676. doi:10.1007/s002160051561
Lai H, McJunkin TR, Miller CJ, Scott JR, Almirall JR (2008) The predictive power of SIMION/SDS simulation software for modeling ion mobility spectrometry instruments. Int J Mass Spectrom 276:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijms.2008.06.011
Launder BE, Spalding DB (1972) Lectures in mathematical models of turbulence. Academic, London
Manisali I, Chen DDY, Schneider BB (2006) Electrospray ionization source geometry for mass spectrometry: past, present, and future. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 25:243–256
Meier L, Berchtold C, Schmid S, Zenobi R (2012) Extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry—enhanced sensitivity using an ion funnel. Anal Chem 84:2076–2080
Meier L, Berchtold C, Schmid S, Zenobi R (2012) High mass resolution breath analysis using secondary electrospray ionization mass spectrometry assisted by an ion funnel. J Mass Spectrom 47:1571–1575. doi:10.1002/jms.3118
Meier L, Berchtold C, Schmid S, Zenobi R (2012) Sensitive detection of drug vapors using an ion funnel interface for secondary electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 47:555–559. doi:10.1002/jms.2982
Menter FR (1994) Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA J 32:1598–1605. doi:10.2514/3.12149
Patankar SV (1980) Numerical heat transfer and fluid flow. Hemisphere Publishing Corp, Washington, DC
Steinberg MZ, Breuker K, Elber R, Gerber RB (2007) The dynamics of water evaporation from partially solvated cytochrome c in the gas phase. Phys Chem Chem Phys 9:4690–4697
Wilcox DC (1993) Comparison of two-equation turbulence models for boundary layers with pressure gradient. AIAA J 31:1414–1421. doi:10.2514/3.11790
Wilhelm O, Madler L, Pratsinis SE (2003) Electrospray evaporation and deposition. J Aerosol Sci 34:815–836. doi:10.1016/S0021-8502(03)00034-X
Wilm M (2011) Principles of electrospray ionization. Mol Cell Proteomics. doi:10.1074/mcp.R111.009407
Wilm MS, Mann M (1994) Electrospray and Taylor-Cone theory, Dole’s beam of macromolecules at last? Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Process 136:167–180. doi:10.1016/0168-1176(94)04024-9
Wilm M, Mann M (1996) Analytical properties of the nanoelectrospray ion source. Anal Chem 68:1–8. doi:10.1021/ac9509519
Wu G, Cooks R, Ouyang Z, Yu M, Chappell W, Plass W (2006) Ion trajectory simulation for electrode configurations with arbitrary geometries. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 17:1216–1228. doi:10.1016/j.jasms.2006.05.004
Xu J, Liu Y (2009) Monte Carlo simulation of ion transport in non-linear ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 12:149–156. doi:10.1007/s12127-009-0029-6
Xu J, Whitten W (2008) Monte Carlo simulation of ion transport in ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 11:13–17. doi:10.1007/s12127-008-0001-x
Yang W, Lojewski B, Wei Y, Deng W (2012) Interactions and deposition patterns of multiplexed electrosprays. J Aerosol Sci 46:20–33. doi:10.1016/j.jaerosci.2011.11.004
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51075059).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jurčíček, P., Liu, L. & Zou, H. Numerical simulation of Monte Carlo ion transport at atmospheric pressure within improved air amplifier geometry. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spec. 17, 157–166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-014-0154-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-014-0154-8