Abstract
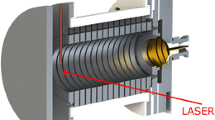
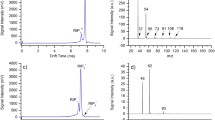
Ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) has been an important tool for decades in the field of trace gas analysis of substances such as explosives, drugs of abuse or chemical warfare agents. In recent years, its application has been extended to more complex set ups. In this paper we present the application of a standard IMS device equipped with a novel pulsed electron gun for ionization in the investigation of the chemical warfare agent simulant dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP). The signal decay times of the reactant ion peak (RIP), the DMMP monomer and dimer have been investigated. Thus, further information could be obtained of the innovative application of different signal decay times in order to filter out signals of contaminants with focus on the decay dependence on the concentration. Additionally, further details regarding the still not fully understood underlying decay mechanisms have been found.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eiceman GA, Karpas Z (2005) Ion mobility spectrometry. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Guharay SK, Dwivedi P, Hill HH Jr (2008) Ion mobility spectrometry: Ion source development and applications in physical and biological sciences. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 36:1458–1470
Chen YH, Siems WF, Hill HH (1996) Fourier transform electrospray ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 334:75–84
Harris GA, Nyadong L, Fernandez FM (2008) Recent developments in ambient ionization techniques for analytical mass spectrometry. Analyst 133:1297–1301
Oberhüttinger C, Langmeier A, Oberpriller H, Kessler M, Goebel J, Müller G (2009) Hydrocarbon detection using laser ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 12:23–32
Sielemann S, Baumbach JI, Schmidt H (2002) IMS with non radioactive ionization sources suitable to detect chemical warfare agent simulation substances. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 5:143–148
Hill C, Thomas P (2002) Pulsed corona discharge: A replacement for 63Ni in ion mobility sources? Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 5:155–160
Gunzer F, Ulrich A, Baether W (2010) A novel non-radioactive electron source for ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 13:9–16
Gunzer F, Zimmermann S, Baether W (2010) Application of a nonradioactive pulsed electron source for ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chem 82:3756–3763
Baether W, Zimmermann S, Gunzer F (2010) Investigation of the influence of voltage parameters on decay times in an ion mobility spectrometer with a pulsed non-radioactive electron source. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 13:95–101
Steiner WE, Klopsch SJ, English WA, Clowers BH, Hill HH (2005) Detection of a chemical warfare simulant in various aerosol matrices by ion mobility tome-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 77:4792–4799
Gushinder K-A, O’Connor G, Aksenov AA, Bocos-Bintintan V, Thomas CLP, Creaser CS (2009) Chemical standards for ion mobility spectrometry: a review. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 12:1–4
Cao L, Harrington PB, Liu J (2005) SIMPLISMA and ALS applied to two-way nonlinear wavelet compressed ion mobility spectra of chemical warfare agent simulants. Anal Chem 77:2575–2586
Ewing RG, Eiceman GA, Harden CS, Stone JA (2006) The kinetics of the decompositions of the proton bound dimers of 1,4-dimethylpyridine and dimethyl methylphosphonate from atmospheric pressure ion mobility spectra. Int J Mass Spectrom 255:76–85
Midey AJ, Miller TM, Viggiano AA (2009) Kinectics of ion-molecule reactions with dimethyl methylphosphonate at 298 K for chemical ionization mass spectrometry detection of GX. J Phys Chem A 113:4982–4989
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gunzer, F., Baether, W. & Zimmermann, S. Investigation of dimethyl methylphosphonate (DMMP) with an Ion mobility spectrometer using a pulsed electron source. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spec. 14, 99–107 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-011-0065-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-011-0065-x