Abstract
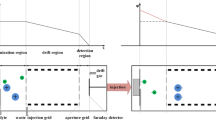
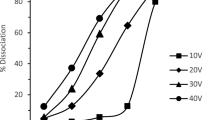
Ion mobility spectrometry (IMS) is a well-known method for detecting hazardous compounds in air. Most ion mobility spectrometers use a radioactive source to provide electrons with high energy (5–50 keV) to ionize analytes in a series of chemical reactions. Instead of a radioactive source, we use a non-radioactive electron gun which can be operated in pulsed mode. Thus a delay time between ionization and ion extraction can be introduced which offers the possibility to use the signal decay characteristic of substances as a further discrimination parameter. The influence of voltages supplied to the reaction region and to the electron gun on signal intensities and decay times will be investigated in order to obtain further insight into the dependence of this signal decay on different experimental parameters and correspondingly into the underlying mechanisms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamagaki T, Sato A (2009) Isomeric oligosaccharides analyses using negative-ion electrospray ionization ion mobility spectrometry combined with collision-induced dissociation MS/MS. Anal Sci 25:985–988
Chen YH, Siems WF, Hill HH (1996) Fourier transform electrospray ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 334:75–84
Harris GA, Nyadong L, Fernandez FM (2008) Recent developments in ambient ionization techniques for analytical mass spectrometry. Analyst 133:1297–1301
Sielemann S, Baumbach JI, Schmidt H (2002) IMS with non radioactive ionization sources suitable to detect chemical warfare agent simulation substances. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 5:143–148
Oberhüttinger C, Langmeier A, Oberpriller H, Kessler M, Goebel J, Müller G (2009) Hydrocarbon detection using laser ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 12:23–32
See e.g. patents in H.R.Döring (2002) US 2002185593; H.R.Döring (2002) US 6429426
Xu J, Whitten WB, Lewis TA, Ramsey JM (2001) A miniature ion mobility spectrometer with a pulsed corona-discharge ion source. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 4:3–6
Hill C, Thomas P (2002) Pulsed corona discharge: A replacement for 63Ni in ion mobility sources? Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 5:155–160
Schmidt H, Baumbach JI, Sielemann S, Wember M, Klockow D (2001) Is partial discharge ion mobility spectrometry an effective tool for the sensitive determination of halogenated hydrocarbons? Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 4:39–42
Guharay SK, Dwivedi P, Hill HH Jr (2008) Ion mobility spectrometry: Ion source development and applications in physical and biological sciences. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci 36:1458–1470
Gunzer F, Ulrich A, Baether W (2010) A novel non-radioactive electron source for ion mobility spectrometry. Int J Ion Mobil Spectrom 13:9–16
Gunzer F, Zimmermann S, Baether W (2010) Application of a nonradioactive pulsed electron source for ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chem 82:3756–3763
Zimmermann S, Barth S, Baether W, Ringer J (2008) Miniaturized low-cost ion mobility spectrometer for fast detection of chemical warfare agents. Anal Chem 80:6671–6676
Barth S, Baether W, Zimmermann S (2009) System design and optimization of a miniaturized ion mobility spectrometer using finite-element analysis. IEEE Sens J 9:337–382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baether, W., Zimmermann, S. & Gunzer, F. Investigation of the influence of voltage parameters on decay times in an ion mobility spectrometer with a pulsed non-radioactive electron source. Int. J. Ion Mobil. Spec. 13, 95–101 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-010-0046-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12127-010-0046-5