Abstract
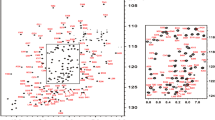
Retinoblastoma-binding protein 1 (RBBP1), also known as AT-rich interaction domain 4A (ARID4A), is a tumour suppressor involved in the regulation of the epigenetic programming in leukemia and Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes. The ARID domain of RBBP1 binds to DNA non-specifically and has gene suppression activity. However, no structural data has been obtained for the human RBBP1 ARID domain so far. Here we report the near-complete 1H, 13C, 15N backbone and side-chain NMR assignment of a 27 kDa tandem PWWP-ARID domain construct that spans residues 171–414 with the removal of a short disordered region between the two domains. The predicted secondary structure based on the assigned chemical shifts is consistent with the structures of the isolated PWWP domain of human RBBP1 previously solved and the homologous ARID domains of other proteins.



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 October 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-021-10051-6
References
Binda O, Roy JS, Branton PE (2006) RBP1 family proteins exhibit SUMOylation-dependent transcriptional repression and induce cell growth inhibition reminiscent of senescence. Mol Cell Biol 26:1917–1931
Binda O, Nassif C, Branton PE (2008) SIRT1 negatively regulates HDAC1-dependent transcriptional repression by the RBP1 family of proteins. Oncogene 27:3384–3392
Delaglio F et al (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Gong W et al (2012) Structural insight into recognition of methylated histone tails by retinoblastoma-binding protein 1. J Biol Chem 287:8531–8540
Gong W, Wang J, Perrett S, Feng Y (2014) Retinoblastoma-binding protein 1 has an interdigitated double Tudor domain with DNA binding activity. J Biol Chem 289:4882–4895
Hurst DR et al (2008) Alterations of BRMS1-ARID4A interaction modify gene expression but still suppress metastasis in human breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283:7438–7444
Iwahara J, Iwahara M, Daughdrill GW, Ford J, Clubb RT (2002) The structure of the Dead ringer-DNA complex reveals how AT-rich interaction domains (ARIDs) recognize DNA. EMBO J 21:1197–1209
Johnson BA, Blevins RA (1994) NMRView: a computer program for visualization and analysis of NMR data. J Biomol NMR 4:603–614
Lai A et al (1999a) RBP1 recruits both histone deacetylase-dependent and -independent repression activities to retinoblastoma family proteins. Mol Cell Biol 19:6632–6641
Lai A, Marcellus RC, Corbeil HB, Branton PE (1999b) RBP1 induces growth arrest by repression of E2F-dependent transcription. Oncogene 18:2091–2100
Lai A et al (2001) RBP1 recruits the mSIN3-histone deacetylase complex to the pocket of retinoblastoma tumor suppressor family proteins found in limited discrete regions of the nucleus at growth arrest. Mol Cell Biol 21:2918–2932
Malovannaya A et al (2010) Streamlined analysis schema for high-throughput identification of endogenous protein complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:2431–2436
Patsialou A, Wilsker D, Moran E (2005) DNA-binding properties of ARID family proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 33:66–80
Shen Y, Bax A (2013) Protein backbone and sidechain torsion angles predicted from NMR chemical shifts using artificial neural networks. J Biomol NMR 56:227–241
Tu S et al (2008) The ARID domain of the H3K4 demethylase RBP2 binds to a DNA CCGCCC motif. Nat Struct Mol Biol 15:419–421
Winter SF, Lukes L, Walker RC, Welch DR, Hunter KW (2012) Allelic variation and differential expression of the mSIN3A histone deacetylase complex gene Arid4b promote mammary tumor growth and metastasis. PLoS Genet 8:e1002735
Wu MY, Tsai TF, Beaudet AL (2006) Deficiency of Rbbp1/Arid4a and Rbbp1l1/Arid4b alters epigenetic modifications and suppresses an imprinting defect in the PWS/AS domain. Genes Dev 20:2859–2870
Wu MY, Eldin KW, Beaudet AL (2008) Identification of chromatin remodeling genes Arid4a and Arid4b as leukemia suppressor genes. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:1247–1259
Wu RC, Jiang M, Beaudet AL, Wu MY (2013) ARID4A and ARID4B regulate male fertility, a functional link to the AR and RB pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:4616–4621
Wu RC, Zeng Y, Chen YF, Lanz RB, Wu MY (2017) Temporal-spatial establishment of initial niche for the primary spermatogonial stem cell formation is determined by an ARID4B regulatory network. Stem Cells 35:1554–1565
Acknowledgements
This work was support by a National Key R&D Program of China Grant 2017YFA0504000 to SP; National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants 31470747 to WG, 31670735 and 31661143023 to YF; a Beijing Natural Science Foundation Grant 5172026 to WG; and the CAS Center for Excellence in Biomacromolecules.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, W., Yao, X., Liang, Q. et al. Resonance assignments for the tandem PWWP-ARID domains of human RBBP1. Biomol NMR Assign 13, 177–181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-019-09873-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-019-09873-2