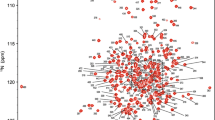
Abstract
Acetohydroxyacid synthase (AHAS) is an enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the branched chain amino acids viz, valine, leucine and isoleucine. The activity of this enzyme is regulated through feedback inhibition by the end products of the pathway. Here we report the backbone and side-chain assignments of ilvN, the 22 kDa dimeric regulatory subunit of E. coli AHAS isoenzyme I, in the valine bound form. Detailed analysis of the structure of ilvN and its interactions with the catalytic subunit of E. coli AHAS I will help in understanding the mechanism of activation and regulation of the branched chain amino acid biosynthesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cavanagh J, Fairbrother WJ, Palmer AG, Rance M, Skelton NJ (2007) Protein NMR spectroscopy, principles and practice, 2nd edn. Elsevier Academic Press, New York
Chipman DM, Duggleby RG, Tittmann K (2005) Mechanisms of acetohydroxyacid synthases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 9:475–481
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Kaplun A, Vyazmensky M, Zherdev Y, Belenky I, Slutzker A, Mendel S, Barak Z, Chipman DM, Shaanan B (2006) Structure of the regulatory subunit of acetohydroxyacid synthase isozyme III from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 357:951–963
Karanth NM, Mitra A, Sarma SP (2009) Solution NMR studies of acetohydroxy acid synthase I: identification of the sites of inter-subunit interactions using multidimensional NMR methods. J Mol Cat B 61:7–13
Kraulis PJ, Domaille PJ, Campbell-Burk T, Van Aken SL, Laue ED (1994) Solution structure and dynamics of ras p21.GDP determined by heteronuclear three- and fourdimensional NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 33:3515–3531
Lawther RP, Wek RC, Lopes JM, Perira R, Taillon BE, Wesley G (1987) The complete nucleotide sequence of the ilvGMEDA operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res 15:2137–2155
Mendel S, Elkayam T, Sella C, Vinogradov V, Vyazmensky M, Chipman DM, Barak Z (2001) Acetohydroxyacid synthase: a proposed structure for regulatory subunits supported by evidence from mutagenesis. J Mol Biol 307:465–477
Mendel S, Vinogradov M, Vyazmensky M, Chipman DM, Barak Z (2003) The N-terminal domain of the regulatory subunit is sufficient for complete activation of acetohydroxyacid synthase III from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 325:275–284
Mitra A, Sarma SP (2008) Escherichia coli ilvN interacts with the FAD binding domain of ilvB and activates the AHAS I enzyme. Biochemistry 47:1518–1531
Muchmore DC, McIntosh LP, Russell CB, Anderson DE, Dahlquist FW (1989) Expression and nitrogen-15 labeling of proteins for proton and nitrogen-15 nuclear magnetic resonance. Methods Enzymol 177:44–73
Pang SS, Duggleby RG, Guddat LW (2002) Crystal structure of yeast acetohydroxyacid synthase: a target for herbicidal inhibitors. J Mol Biol 317:249–262
Squires CH, DeFelice M, Devereux J, Calvo JM (1983) Molecular structure of ilvIH and its evolutionary relationship to ilvG in Escherichia coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res 11:5299–5313
Umbarger HE (1987) Biosynthesis of branched—chain amino acids. In: Neidhardt FC (ed) Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: cellular and molecular biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 352–367
Vinogradov V, Vyazmensky M, Engel S, Belenky I, Kaplun A, Kryukov O, Barak Z, Chipman DM (2006) Acetohydroxyacid synthase isozyme I from Escherichia coli has unique catalytic and regulatory properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:356–363
Vyazmensky M, Zherdev Y, Slutzker A, Belenky I, Kryukov O, Barak Z, Chipman DM (2009) Interactions between large and small subunits of different acetohydroxyacid synthase isozymes of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 48:8731–8737
Wek RC, Hauser CA, Hatfield GW (1985) The nucleotide sequence of the ilvBN operon of Escherichia coli: sequence homologies of the acetohydroxy acid synthase isozymes. Nucleic Acids Res 13:3995–4010
Wishart DS, Sykes BD (1994) The 13C chemical-shift index: a simple method for the identification of protein secondary structure using 13C chemical-shift data. J Biomol NMR 4:171–180
Yamazaki T, Forman-Kay JD, Kay LE (1993) Two-dimensional NMR experiments for correlating 13Cβ and 1Hδ/ε chemical shifts of aromatic residues in 13C-labeled proteins via scalar couplings. J Am Chem Soc 115:11054–11055
Acknowledgments
NMK is a recipient of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research—Senior Research Fellowship from the Government of India. The NMR facility is funded by grants from Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India. SPS acknowledges DBT for research funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karanth, N.M., Sarma, S.P. 1H, 13C, 15N assignments of the dimeric regulatory subunit (ilvN) of the E. coli AHAS I. Biomol NMR Assign 4, 131–133 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-010-9225-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-010-9225-x