Abstract
Objectives
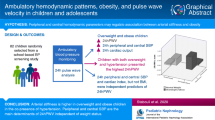
To investigate the pulse wave velocity (PWV) and augmentation index (Alx), measures of arterial stiffness, in relation to hypertension and obesity, the main risk factors for cardiovascular diseases.
Methods
Two groups of pediatric patients, 31 children and adolescents with hypertension and 85 with overweight, were analysed and compared to the control group (50 healthy individuals). Subjects were sampled by opportunity sampling at the Department of Pediatrics, Maribor. In each patient, blood pressure, anthropometrical parameters and PWV measurements using the applanation tonometry technique were performed.
Results
There was a significant correlation between PWV and age (r = 0.461, p = 0.001) in the control group, whereas no correlation was obtained between PWV and body mass index (BMI) or central mean arterial pressure (CMAP). In the hypertensive group, PWV only correlated with CMAP (r = 0.496, p = 0.005). A significant correlation was found in the overweight group between PWV and both age and BMI (r = 0.484, p < 0.001 and r = 0.347, p = 0.001, respectively). Alx results were not taken into consideration.
Conclusions
The results of this pilot study show that overweight and hypertensive children and adolescents are associated with less compliant arteries than their healthy peers, which could be used for screening of patients with expected early cardiovascular risk.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PWV:
-
Pulse wave velocity
- PWA:
-
Pulse wave analysis
- Alx:
-
Augmentation index
- AP:
-
Augmentation pressure
- PP:
-
Pulse pressure
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CMAP:
-
Central mean arterial pressure
References
World Health Organization. Top ten causes of death. Available from URL: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en/index2.html. Accessed 5 Jan 2015.
McGill Jr HC, McMahan CA, Herderick EE, Malcom GT, Tracy RE, Strong JP. Origin of atherosclerosis in childhood and adolescence. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72:1307S–5S.
Raghuveer G Lifetime cardiovascular risk of childhood obesity. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91:1514S–9S.
Avbelj M, Saje-Hribar N, Seher-Zupančič M, et al. Overweight and obesity prevalence among 5 year old children and 15 to 16 year old adolescents in Slovenia. Zdrav Vestn. 2005;74:753–9.
Kudo U, Takahashi I, Matsuzaka M, et al. Influence of obesity on blood pressure and arterial stiffness in the early teens. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2013;7:e211–7.
Lo JC, Chandra M, Sinaiko A, et al. Severe obesity in children: prevalence, persistence and relation to hypertension. Int J Pediatr Endocrinol. 2014;2014:3.
Urbina EM, Williams RV, Alpert BS, et al. Noninvasive assessment of subclinical atherosclerosis in children and adolescents: recommendations for standard assessment for clinical research: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Hypertension. 2009;54:919–50.
London GM, Pannier B. Arterial functions: how to interpret the complex physiology. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25:3815–23.
Fantin F, Mattocks A, Bullpit CJ, Banya W, Rajkumar C. Is augmentation index a good measure of vascular stiffness in the elderly? Age Ageing. 2007;36:43–8.
Haller MJ, Samyn M, Nichols WW, et al. Radial artery tonometry demonstrates arterial stiffness in children with type I diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:2911–7.
Sakuragi S, Abhayaratna K, Gravenmaker KJ, et al. Influence of adiposity and physical activity on arterial stiffness in healthy children: the lifestyle of our kids study. Hypertension. 2009;53:611–6.
Reusz GS, Cseprekal O, Temmar M, et al. Reference values of pulse wave velocity in healthy children and teenagers. Hypertension. 2010;56:217–24.
O’Rourke MF, Adji A. Noninvasive studies of central aortic pressure. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2012;14:8–20.
Benetos A, Weber B, Izzo J, et al. Influence of age, risk factors, and cardiovascular and renal disease on arterial stiffness: clinical applications. Am J Hypertens. 2002;15:1101–8.
Cheung YF, Brogan PA, Pilla CB, Dillon MJ, Redington AN. Arterial distensibility in children and teenagers: normal evolution and the effect of childhood vasculitis. Arch Dis Child. 2002;87:348–50.
Lurbe E, Torro I, Garcia-Vicent C, Alvarez J, Fernández-Fornoso JA, Redon J. Blood pressure and obesity exert independent influences on pulse wave velocity in youth. Hypertension. 2012;60:550–5.
Urbina EM, Kimball TR, Khoury PR, Daniels SR, Dolan LM. Increased arterial stiffness is found in adolescents with obesity or obesity-related type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Hypertens. 2010;28:1692–8.
Riggio S, Mandraffino G, Sardo MA, et al. Pulse wave velocity and augmentation index, but not intima-media thickness, are early indicators of vascular damage in hypercholesterolemic children. Eur J Clin Investig. 2010;40:250–7.
Hughes AD, Park C, Francis D, et al. Limitations of augmentation index in the assessment of wave reflection in normotensive healthy individuals. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e59371.
Keehn L, Milne L, McNeill K, Chowienczyk P, Sinha MD. Measurement of pulse wave velocity in children: comparison of volumetric and tonometric sensors, brachial-femoral and carotid-femoral pathways. J Hypertens. 2014;32:1464–9.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Department of Pediatrics, University Medical Centre Maribor, who supported them throughout this research project, especially to nurses Nina and Valerija, who helped them with the data collection.
Contributions
MM and SN: Planned the study, measured subjects, analysed and interpreted the data, wrote the manuscript; NMV: Planned the study, collected the patients, supervised and guided the study, revised the data analysis and contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. NMV will act as guarantor of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Source of Funding
None.
Additional information
Mirjam Močnik and Sara Nikolić contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Močnik, M., Nikolić, S. & Varda, N.M. Arterial Compliance Measurement in Overweight and Hypertensive Children. Indian J Pediatr 83, 510–516 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1965-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-015-1965-2