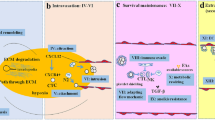
Abstract
Platelet-derived microvesicles (PMVs), the microvesicles with the highest concentration in the bloodstream, play a key role in the regulation of hemostasis, inflammation, and angiogenesis. PMVs have recently been identified as key factors in the link between platelets and cancer. PMVs bind to both cancer cells and nontransformed cells in the microenvironment of the tumor, and then transfer platelet-derived contents to the target cell. These contents have the potential to either stimulate or modulate the target cell's response. PMVs are encased in a lipid bilayer that contains surface proteins and lipids as well as components found inside the PMV. Each of these components participates in known and potential PMV roles in cancer. The complicated roles played by PMVs in the onset, development, and progression of cancer and cancer-related comorbidities are summarized in this study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gurbel PA, Jeong Y-H, Navarese EP, Tantry US. Platelet-mediated thrombosis: from bench to bedside. Circ Res. 2016;118(9):1380–91.
Schwertz H, Rowley JW, Tolley ND, Campbell RA, Weyrich AS. Assessing protein synthesis by platelets. Platelets and Megakaryocytes: Springer; 2012. p. 141–53.
Zaldivia MTK, McFadyen JD, Lim B, Wang X, Peter K. Platelet-derived microvesicles in cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2017;4:74.
Aatonen MT, Öhman T, Nyman TA, Laitinen S, Grönholm M, Siljander PR-M. Isolation and characterization of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles. J Extracell Vesicl. 2014;3(1):24692.
Tafelmeier M, Fischer A, Orso E, Konovalova T, Böttcher A, Liebisch G, et al. Mildly oxidized HDL decrease agonist-induced platelet aggregation and release of pro-coagulant platelet extracellular vesicles. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017;169:176–88.
Liu Q, Peng H, Wang Z-A. Convergence to nonlinear diffusion waves for a hyperbolic-parabolic chemotaxis system modelling vasculogenesis. J Differential Equations. 2022;314:251–86.
Théry C, Witwer KW, Aikawa E, Alcaraz MJ, Anderson JD, Andriantsitohaina R, et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): a position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J Extracellul Vesic. 2018;7(1):1535750.
Żmigrodzka M, Witkowska-Piłaszewicz O, Winnicka A. Platelets extracellular vesicles as regulators of cancer progression—an updated perspective. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):5195.
Lazar S, Goldfinger LE. Platelet microparticles and miRNA transfer in cancer progression: many targets, modes of action, and effects across cancer stages. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018;5:13.
Italiano JE Jr, Mairuhu AT, Flaumenhaft R. Clinical relevance of microparticles from platelets and megakaryocytes. Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(6):578.
Wolf P. The nature and significance of platelet products in human plasma. Br J Haematol. 1967;13(3):269–88.
Warren B, Vales O. The release of vesicles from platelets following adhesion to vessel walls in vitro. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972;53(2):206.
Heijnen HF, Schiel AE, Fijnheer R, Geuze HJ, Sixma JJ. Activated platelets release two types of membrane vesicles: microvesicles by surface shedding and exosomes derived from exocytosis of multivesicular bodies and-granules. Blood J Am Soc Hematol. 1999;94(11):3791–9.
Dovizio M, Alberti S, Sacco A, Guillem-Llobat P, Schiavone S, Maier TJ, et al. Novel insights into the regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression by platelet-cancer cell cross-talk. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015;43(4):707–14.
Antwi-Baffour S, Adjei J, Aryeh C, Kyeremeh R, Kyei F, Seidu MA. Understanding the biosynthesis of platelets-derived extracellular vesicles. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2015;3(3):133–40.
Biró É, Akkerman JWN, Hoek FJ, Gorter G, Pronk LM, Sturk A, et al. The phospholipid composition and cholesterol content of platelet-derived microparticles: a comparison with platelet membrane fractions. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(12):2754–63.
Garcia BA, Smalley DM, Cho H, Shabanowitz J, Ley K, Hunt DF. The platelet microparticle proteome. J Proteome Res. 2005;4(5):1516–21.
Azadeh H, Alizadeh-Navaei R, Rezaiemanesh A, Rajabinejad M. Immune-related adverse events (irAEs) in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients treated with interleukin (IL)-17 inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflammopharmacol. 2022;30(2):435-451
Mobarrez F, Sjövik C, Soop A, Hållström L, Frostell C, Pisetsky DS, et al. CD40L expression in plasma of volunteers following LPS administration: a comparison between assay of CD40L on platelet microvesicles and soluble CD40L. Platelets. 2015;26(5):486–90.
Pan Y, Liang H, Liu H, Li D, Chen X, Li L, et al. Platelet-secreted microRNA-223 promotes endothelial cell apoptosis induced by advanced glycation end products via targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. J Immunol. 2014;192(1):437–46.
Liang H, Yan X, Pan Y, Wang Y, Wang N, Li L, et al. MicroRNA-223 delivered by platelet-derived microvesicles promotes lung cancer cell invasion via targeting tumor suppressor EPB41L3. Mol Cancer. 2015;14(1):1–13.
Boudreau LH, Duchez A-C, Cloutier N, Soulet D, Martin N, Bollinger J, et al. Platelets release mitochondria serving as substrate for bactericidal group IIA-secreted phospholipase A2 to promote inflammation. Blood J Am Soc Hematol. 2014;124(14):2173–83.
Xu S, Tao H, Cao W, Cao L, Lin Y, Zhao S-M, et al. Ketogenic diets inhibit mitochondrial biogenesis and induce cardiac fibrosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):1–13.
Milioli M, Ibáñez-Vea M, Sidoli S, Palmisano G, Careri M, Larsen MR. Quantitative proteomics analysis of platelet-derived microparticles reveals distinct protein signatures when stimulated by different physiological agonists. J Proteomics. 2015;121:56–66.
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Wysoczynski M, Kijowski J, Marquez-Curtis L, Machalinski B, Ratajczak J, et al. Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2005;113(5):752–60.
Qu Y-Y, Zhao R, Zhang H-L, Zhou Q, Xu F-J, Zhang X, et al. Inactivation of the AMPK–GATA3–ECHS1 pathway induces fatty acid synthesis that promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma growth. Can Res. 2020;80(2):319–33.
Duan C, Deng H, Xiao S, Xie J, Li H, Zhao X, et al. Accelerate gas diffusion-weighted MRI for lung morphometry with deep learning. Eur Radiol. 2022;32(1):702–13.
Labelle M, Begum S, Hynes RO. Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2011;20(5):576–90.
Luo K. Signaling cross talk between TGF-β/Smad and other signaling pathways. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9:1.
Guo S-C, Tao S-C, Yin W-J, Qi X, Yuan T, Zhang C-Q. Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma promote the re-epithelization of chronic cutaneous wounds via activation of YAP in a diabetic rat model. Theranostics. 2017;7(1):81.
van Es N, Sturk A, Middeldorp S, Nieuwland R. Effects of cancer on platelets. Semin Oncol. 2014;41(3):311–8.
Mooberry MJ, Key NS. Microparticle analysis in disorders of hemostasis and thrombosis. Cytometry A. 2016;89(2):111–22.
Sinauridze EI, Kireev DA, Popenko NY, Pichugin AV, Panteleev MA, Krymskaya OV, et al. Platelet microparticle membranes have 50-to 100-fold higher specific procoagulant activity than activated platelets. Thromb Haemost. 2007;97(03):425–34.
Hisada Y, Mackman N. Cancer-associated pathways and biomarkers of venous thrombosis. Blood J Am Soc Hematol. 2017;130(13):1499–506.
Geddings JE, Mackman N. Tumor-derived tissue factor–positive microparticles and venous thrombosis in cancer patients. Blood J Am Soc Hematol. 2013;122(11):1873–80.
Liu H, Gao Y, Vafaei S, Gu X, Zhong X. The prognostic value of plasma cell-free DNA concentration in the prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 599602.
Hernández C, Orbe J, Roncal C, Alvarez-Hernandez M, de Lizarrondo SM, Alves MT, et al. Tissue factor expressed by microparticles is associated with mortality but not with thrombosis in cancer patients. Thromb Haemost. 2013;110(09):598–608.
Zwicker JI, Lacroix R, Dignat-George F, Furie BC, Furie B. Measurement of platelet microparticles. Platelets and Megakaryocytes: Springer; 2012. p. 127–39.
Levi M. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in cancer patients. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2009;22(1):129–36.
Tabib A, Khorgami MR, Meraji M, Omidi N, Mirmesdagh Y. Accuracy of Doppler-derived indices in predicting pulmonary vascular resistance in children with pulmonary hypertension secondary to congenital heart disease with left-to-right shunting. Pediatr Cardiol. 2014;35(3):521–9.
Levi M, editor Disseminated intravascular coagulation in cancer: an update. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2019 ;45(4):342-347
Zhang X, Liu L, Chen WC, Wang F, Cheng YR, Liu YM, et al. Gestational Leucylation Suppresses Embryonic T‐Box Transcription Factor 5 Signal and Causes Congenital Heart Disease. Adv Sci. 2022; 9(15): 2201034.
Khorgami MR, Moradian M, Omidi N, Moghadam MYA. Management of cardiovascular disorders in patients with Noonan Syndrome: a case report. J Tehr Univ Heart Center. 2017;12(4):184.
Kim AS, Khorana AA, McCrae KR. Mechanisms and biomarkers of cancer-associated thrombosis. Transl Res. 2020;225:33-53.
Yamanaka Y, Sawai Y, Nomura S. Platelet-derived microparticles are an important biomarker in patients with cancer-associated thrombosis. Int J Gen Med. 2019;12:491.
Algra AM, Rothwell PM. Effects of regular aspirin on long-term cancer incidence and metastasis: a systematic comparison of evidence from observational studies versus randomised trials. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(5):518–27.
Gay LJ, Felding-Habermann B. Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11(2):123–34.
Goubran HA, Kotb RR, Stakiw J, Emara ME, Burnouf T. Regulation of tumor growth and metastasis: the role of tumor microenvironment. Cancer Growth Metast. 2014;7:11285.
Montoro-García S, Shantsila E, Hernández-Romero D, Jover E, Valdés M, Marín F, et al. Small-size platelet microparticles trigger platelet and monocyte functionality and modulate thrombogenesis via P-selectin. Br J Haematol. 2014;166(4):571–80.
Domanska UM, Kruizinga RC, Nagengast WB, Timmer-Bosscha H, Huls G, de Vries EG, et al. A review on CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in oncology: no place to hide. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(1):219–30.
Hao P, Li H, Zhou L, Sun H, Han J, Zhang Z. Serum metal ion-induced cross-linking of photoelectrochemical peptides and circulating proteins for evaluating cardiac ischemia/reperfusion. ACS Sens. 2022;7(3):775–83.
Wang D, Wang F, Shi K-H, Tao H, Li Y, Zhao R, et al. Lower circulating folate induced by a fidgetin intronic variant is associated with reduced congenital heart disease susceptibility. Circulation. 2017;135(18):1733–48.
Manoochehrabadi T, Sharifi Z, Yari F. Role of platelet-derived microparticles in transfer of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 to CXCR4-negative cells. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2019;33:55.
Dashevsky O, Varon D, Brill A. Platelet-derived microparticles promote invasiveness of prostate cancer cells via upregulation of MMP-2 production. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(8):1773–7.
Milasan A, Tessandier N, Tan S, Brisson A, Boilard E, Martel C. Extracellular vesicles are present in mouse lymph and their level differs in atherosclerosis. J Extracell Vesicl. 2016;5(1):31427.
Hayon Y, Dashevsky O, Shai E, Brill A, Varon D, Leker R, R,. Platelet microparticles induce angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2012;9(3):185–92.
Gawaz M, Langer H, May AE. Platelets in inflammation and atherogenesis. J Clin Investig. 2005;115(12):3378–84.
Samimi Z, Kardideh B, Zafari P, Bahrehmand F, Roghani SA, Taghadosi M. The impaired gene expression of adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase (AMPK), a key metabolic enzyme in leukocytes of newly diagnosed rheumatoid arthritis patients. Mol Biol Rep. 2019;46(6):6353–60.
Servais L, Wéra O, DibatoEpoh J, Delierneux C, Bouznad N, Rahmouni S, et al. Platelets contribute to the initiation of colitis-associated cancer by promoting immunosuppression. J Thromb Haemost. 2018;16(4):762–77.
Muralidharan-Chari V, Clancy JW, Sedgwick A, D’Souza-Schorey C. Microvesicles: mediators of extracellular communication during cancer progression. J Cell Sci. 2010;123(10):1603–11.
Gao Y, Chen S, Vafaei S, Zhong X. Tumor-infiltrating immune cell signature predicts the prognosis and chemosensitivity of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10: 557638.
Boilard E, Nigrovic PA, Larabee K, Watts GF, Coblyn JS, Weinblatt ME, et al. Platelets amplify inflammation in arthritis via collagen-dependent microparticle production. Science. 2010;327(5965):580–3.
Iranshahi N, Assar S, Amiri SM, Zafari P, Fekri A, Taghadosi M. Decreased gene expression of Epstein-Barr Virus-Induced Gene 3 (EBI-3) may contribute to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol Invest. 2019;48(4):367–77.
McGregor L, Martin J, McGregor JL. Platelet-leukocyte aggregates and derived microparticles in inflammation, vascular remodelling and thrombosis. Front Biosci Landmark. 2006;11(1):830–7.
Zafari P, Yari K, Mostafaei S, Iranshahi N, Assar S, Fekri A, et al. Analysis of Helios gene expression and Foxp3 TSDR methylation in the newly diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis patients. Immunol Invest. 2018;47(6):632–42.
Sadallah S, Eken C, Martin PJ, Schifferli JA. Microparticles (ectosomes) shed by stored human platelets downregulate macrophages and modify the development of dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2011;186(11):6543–52.
Kim H, Song K, Park Y, Kang Y, Lee Y, Lee K, et al. Elevated levels of circulating platelet microparticles, VEGF, IL-6 and RANTES in patients with gastric cancer: possible role of a metastasis predictor. Eur J Cancer. 2003;39(2):184–91.
Mege D, Panicot-Dubois L, Ouaissi M, Robert S, Sielezneff I, Sastre B, et al. The origin and concentration of circulating microparticles differ according to cancer type and evolution: a prospective single-center study. Int J Cancer. 2016;138(4):939–48.
Wang C-C, Tseng C-C, Chang H-C, Huang K-T, Fang W-F, Chen Y-M, et al. Circulating microparticles are prognostic biomarkers in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. Oncotarget. 2017;8(44):75952.
Edelstein LC. The role of platelet microvesicles in intercellular communication. Platelets. 2017;28(3):222–7.
Ambrose AR, Alsahli MA, Kurmani SA, Goodall AH. Comparison of the release of microRNAs and extracellular vesicles from platelets in response to different agonists. Platelets. 2018;29(5):446–54.
Rajabinejad M, Asadi G, Ranjbar S, Varmaziar FR, Karimi M, Salari F, et al. The MALAT1-H19/miR-19b-3p axis can be a fingerprint for diabetic neuropathy. Immunol Lett. 2022;245:69–78.
Zhang Y, Zhang W, Zha C, Liu Y. Platelets activated by the anti-β2GPI/β2GPI complex release microRNAs to inhibit migration and tube formation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018;23(1):1–10.
Michael JV, Wurtzel JG, Mao GF, Rao AK, Kolpakov MA, Sabri A, et al. Platelet microparticles infiltrating solid tumors transfer miRNAs that suppress tumor growth. Blood J Am Soc Hematol. 2017;130(5):567–80.
Tran JQ, Pedersen OH, Larsen ML, Grove EL, Kristensen SD, Hvas A-M, et al. Platelet microRNA expression and association with platelet maturity and function in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Platelets. 2020;31(3):365–72.
Lai W-F. Development of hydrogels with self-healing properties for delivery of bioactive agents. Mol Pharm. 2021;18(5):1833–41.
Lai W-F, Wong W-T. Property-tuneable microgels fabricated by using flow-focusing microfluidic geometry for bioactive agent delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(6):787.
Boilard E. Extracellular vesicles and their content in bioactive lipid mediators: more than a sack of microRNA. J Lipid Res. 2018;59(11):2037–46.
Tan AS, Baty JW, Dong L-F, Bezawork-Geleta A, Endaya B, Goodwin J, et al. Mitochondrial genome acquisition restores respiratory function and tumorigenic potential of cancer cells without mitochondrial DNA. Cell Metab. 2015;21(1):81–94.
Li Y, Yao C-F, Xu F-J, Qu Y-Y, Li J-T, Lin Y, et al. APC/CCDH1 synchronizes ribose-5-phosphate levels and DNA synthesis to cell cycle progression. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1–16.
Wang D, Zhao R, Qu Y-Y, Mei X-Y, Zhang X, Zhou Q, et al. Colonic lysine homocysteinylation induced by high-fat diet suppresses DNA damage repair. Cell Rep. 2018;25(2):398–412.
Yao B, Qu S, Hu R, Gao W, Jin S, Ju J, et al. Delivery of platelet TPM3 mRNA into breast cancer cells via microvesicles enhances metastasis. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(12):2159–69.
Yang W, Liu W, Li X, Yan J, He W (2022). Turning chiral peptides into a racemic supraparticle to induce the self-degradation of MDM2. J Adv Res
Denis MM, Tolley ND, Bunting M, Schwertz H, Jiang H, Lindemann S, et al. Escaping the nuclear confines: signal-dependent pre-mRNA splicing in anucleate platelets. Cell. 2005;122(3):379–91.
Simon LM, Edelstein LC, Nagalla S, Woodley AB, Chen ES, Kong X, et al. Human platelet microRNA-mRNA networks associated with age and gender revealed by integrated plateletomics. Blood J Am Soc Hematol. 2014;123(16):e37–45.
Lopez E, Srivastava AK, Burchfield J, Wang Y-W, Cardenas JC, Togarrati PP, et al. Platelet-derived-extracellular vesicles promote hemostasis and prevent the development of hemorrhagic shock. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):1–10.
Agrahari V, Agrahari V, Burnouf PA, Chew CH, Burnouf T. Extracellular microvesicles as new industrial therapeutic frontiers. Trends Biotechnol. 2019;37(7):707–29.
Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G, Théry C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(1):9–17.
Kong L, Li K, Gao L, Yin A, Zhou L, Teng G, et al. Mediating effects of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles on PM(2.5)-induced vascular endothelial injury. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2020;198:110652.
Burnouf T, Goubran HA, Chou ML, Devos D, Radosevic M. Platelet microparticles: detection and assessment of their paradoxical functional roles in disease and regenerative medicine. Blood Rev. 2014;28(4):155–66.
Ponomareva A, Nevzorova T, Mordakhanova E, Andrianova I, Rauova L, Litvinov R, et al. Intracellular origin and ultrastructure of platelet-derived microparticles. J Thromb Haemost. 2017;15(8):1655–67.
Lopez E, Srivastava AK, Pati S, Holcomb JB, Wade CE. Platelet-derived microvesicles: a potential therapy for trauma-induced coagulopathy. Shock. 2018;49(3):243–8.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LGF22H080009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.P, Zh.L, and Y.H., contributed to the idea design and literature search. Yi.W., M.H., and Ya.W, wrote parts of the manuscript. Sh.X., and F.J. contributed to designing the figure.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
It is not applicable.
Informed consent
It is not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Platelet-derived microvesicles (PMVs) in cancer progression and clinical applications. Clin Transl Oncol 25, 873–881 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03014-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-022-03014-3