Abstract
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant tumors, and a large number of patients are diagnosed and die every year. Due to the lack of appropriate diagnosis, prediction and treatment, early diagnosis rate of CRC is low and the prognosis is poor. Studies have found that abnormally expressed non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) (including microRNAs (miRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs),etc.) play an important regulatory role in the occurrence and development of CRC. Some studies have shown that they are stable in the blood and can be detected repeatedly. They are expected to be non-invasive biomarkers for early diagnosis, prognosis evaluation, and prediction of drug sensitivity of CRC, as well as potential applications in the treatment of CRC.


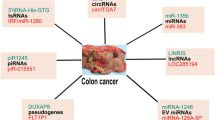
source of circulating ncRNAs in CRC
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- ncRNAs:
-
Non-coding RNAs
- miRNAs:
-
MicroRNAs
- circRNA:
-
Circular RNAs
- lncRNAs:
-
Long non-coding RNAs
- CRAs:
-
Colorectal adenomas
- CEA:
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CA199:
-
Carbohydrate antigen199
- CA125:
-
Carbohydrate antigen125
- WGS:
-
Whole genome sequencing
- tRNAs:
-
Transfer RNAs
- rRNAs:
-
Ribosomal RNAs
- snoRNAs:
-
Small nucleoli RNAs
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristics
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- MVs:
-
Microvesicles
- MPs:
-
Microparticles
- SPRED1:
-
Sprouty related proteins 1
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
- CXCL12:
-
Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12
- AGO:
-
Argonaute
- HDL:
-
High-density lipoprotein
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- CEA:
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristics
- TNM:
-
Tumor Node Metastasis
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- FOLFOX:
-
Fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin
- XELOX:
-
Capecitabine plus oxaliplatin
- NFIX:
-
Nuclear factor I/X
- Bcl-2:
-
B cell lymphoma-2
- MVP:
-
Main vault protein
- ITGA2:
-
Integrin Alpha 2
- ZEB1:
-
Zinc-finger E-box binding homeobox1
- PDCD10:
-
Programmed cell death 10
- RNase:
-
Ribonuclease
- BIDs:
-
Benign intestinal diseases
- HCs:
-
Healthy controls
- FCHSD2:
-
FCH and double SH3 domains protein 2
- siRNA:
-
Small stranded RNA
- H19:
-
The reciprocally imprinted partner of Igf2
- HOTTIP:
-
HOXA distal transcript antisense RNA
- HULC:
-
Highly up-regulated in liver cancer
- CCAT2:
-
Colon cancer-associated transcript 2
- CRNDE-h:
-
Colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed-h
- ZFAS1:
-
Zinc finger antisense 1
- GNAT1-1:
-
G protein subunit α transducin 1
- NATs:
-
Normal appearing tissues
- HIF1A-AS1:
-
HIF 1alpha-antisense RNA 1
- GAS5:
-
Growth arrest-specific transcript 5
- RFS:
-
Relapse-free survival
- RPPH1:
-
RNAse P RNA component H1
- DFS:
-
Disease-free survival
- UCA1:
-
Urothelial carcinoma-associated 1
- XIST:
-
X Inactive Specific Transcript
- MEG3:
-
Maternally expressed gene 3
- Erk:
-
Extracellular regulated protein kinases
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- SNHG11:
-
Small nucleolar host gene 11
- CCAL:
-
Colorectal cancer-associated lncRNA
- HuR:
-
Human antigen R
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- TUBB3:
-
Beta-III tubulin
- MYO6:
-
Myosins of class VI
- ceRNA:
-
Competing endogenous RNAs
- piRNA:
-
PIWI interacting RNA
- snRNA:
-
Small nuclear RNA
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- RNU2-1F:
-
U2 snRNA fragment
- PFS:
-
Progression free survival
- ORs:
-
Odds ratio
- STAT3:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
- PIWIL2:
-
Piwi-like protein 2
- P-SRC:
-
Phosphorylated Src
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factorVEGF
- IGF-1R:
-
Insulin-like growth factor receptorIGF-1R
- MRP2:
-
Multidrug resistance associated protein
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424.
Sun Z, Liu J, Chen C, et al. The biological effect and clinical application of long noncoding RNAs in colorectal cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(2):431–41.
Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Fleshman J, et al. MicroRNAs as potential liquid biopsy biomarkers in colorectal cancer: a systematic review. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018;2:274–82.
Cheung KWE, Choi S-y R, Lee LTC, et al. The potential of circulating cell free RNA as a biomarker in cancer. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2019;19(7):579–90.
Levin B, Lieberman DA, McFarland B, et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: a joint guideline from the American cancer society, the us multi-society task force on colorectal cancer, and the American college of radiology. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58(3):130–60.
Du M, Liu S, Gu D, et al. Clinical potential role of circulating microRNAs in early diagnosis of colorectal cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35(12):2723–30.
Wei L, Wang X, Lv L, et al. The emerging role of noncoding RNAs in colorectal cancer chemoresistance. Cell Oncol. 2019;42(6):757–68.
Wang L, Duan W, Yan S, et al. Circulating long non-coding RNA colon cancer-associated transcript 2 protected by exosome as a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;113:108758.
Yang F, Liu DY, Guo JT, et al. Circular RNA circ-LDLRAD3 as a biomarker in diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(47):8345–54.
Hang D, Zhou J, Qin N, et al. A novel plasma circular RNA circFARSA is a potential biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2018;7(6):2783–91.
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, et al. Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108(12):5003–8.
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2008;105(30):10513–8.
Han D, Gao X, Wang M, et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 indicates a poor prognosis of colorectal cancer and promotes tumor growth by recruiting and binding to eIF4A3. Oncotarget. 2016;7(16):22159–73.
Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008;18(10):997–1006.
Francavilla A, Turoczi S, Tarallo S, et al. Exosomal microRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as colorectal cancer biomarkers: a review. Mutagenesis. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/mutage/gez038.
Laktionov PP, Tamkovich SN, Rykova EY, et al. Extracellular circulating nucleic acids in human plasma in health and disease. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids. 2004;23(6–7):879–83.
Montero-Hadjadje M, Elias S, Chevalier L, et al. Chromogranin A promotes peptide hormone sorting to mobile granules in constitutively and regulated secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(18):12420–31.
Llobet A, Wu M, Lagnado L. The mouth of a dense-core vesicle opens and closes in a concerted action regulated by calcium and amphiphysin. J Cell Biol. 2008;182(5):1017–28.
Zernecke A, Bidzhekov K, Noels H, et al. Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci Signal. 2009;2(100):ra81–ra81.
Halicka HD, Bedner E, Darzynkiewicz Z. Segregation of RNA and separate packaging of DNA and RNA in apoptotic bodies during apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2000;260(2):248–56.
Zen K, Zhang C-Y. Circulating MicroRNAs: a novel class of biomarkers to diagnose and monitor human cancers. Med Res Rev. 2012;32(2):326–48.
Lawrie CH, Gal S, Dunlop HM, et al. Detection of elevated levels of tumour-associated microRNAs in serum of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2008;141(5):672–5.
Kanaan Z, Rai SN, Eichenberger MR, et al. Plasma miR-21: a potential diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 2012;256(3):544–51.
Liu G-H, Zhou Z-G, Chen R, et al. Serum miR-21 and miR-92a as biomarkers in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Tumor Biol. 2013;34(4):2175–81.
Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, Fleshman J, et al. MicroRNAs as potential liquid biopsy biomarkers in colorectal cancer: a systematic review. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018;1870(2):274–82.
Goel A, Wang Q, Huang Z, et al. Plasma miR-601 and miR-760 are novel biomarkers for the early detection of colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9):e44398.
Huang Z, Huang D, Ni S, et al. Plasma microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(1):118–26.
Zou SL, Chen YL, Ge ZZ, et al. Downregulation of serum exosomal miR-150-5p is associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. 2019;26(1):69–77.
Matsumura T, Sugimachi K, Iinuma H, et al. Exosomal microRNA in serum is a novel biomarker of recurrence in human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;113(2):275–81.
Peng ZY, Gu RH, Yan B. Downregulation of exosome-encapsulated miR-548c-5p is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27291.
Sun Y, Yang B, Lin M, et al. Identification of serum miR-30a-5p as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomarke. 2019;24(3):299–305.
Yuan D, Li K, Zhu K, et al. Plasma miR-183 predicts recurrence and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(2):268–75.
Kou CH, Zhou T, Han XL, et al. Downregulation of mir-23b in plasma is associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 2016;12(6):4838–44.
Chen Q, Xia HW, Ge XJ, et al. Serum miR-19a predicts resistance to FOLFOX chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer cases. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(12):7421–6.
Liu C, Eng C, Shen J, et al. Serum exosomal miR-4772-3p is a predictor of tumor recurrence in stage II and III colon cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(46):76250–60.
Hu J, Cai G, Xu Y, et al. The plasma microRNA miR-1914* and -1915 suppresses chemoresistant in colorectal cancer patients by down-regulating NFIX. Curr Mol Med. 2016;16(1):70–82.
Liu T, Zhang X, Du L, et al. Exosome-transmitted miR-128-3p increase chemosensitivity of oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):43.
Gu YY, Yu J, Zhang JF, et al. Suppressing the secretion of exosomal miR-19b by gw4869 could regulate oxaliplatin sensitivity in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma. 2019;66(1):39–45.
Xu Y, Zhu M. Novel exosomal miR-46146 transfer oxaliplatin chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-019-02237-1.
Zaharie F, Muresan MS, Petrushev B, et al. Exosome-carried microRNA-375 inhibits cell progression and dissemination via Bcl-2 blocking in colon cancer. J Gastrointest Liver Dis. 2015;24(4):435–43.
Teng Y, Ren Y, Hu X, et al. MVP-mediated exosomal sorting of miR-193a promotes colon cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14448.
Xu Y, Shen L, Li F, et al. microRNA-16-5p-containing exosomes derived from bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion, while promoting apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating ITGA2. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(11):21380–94.
Liang G, Zhu Y, Ali DJ, et al. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J Nanobiotechnol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-019-0563-2.
Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, et al. Exosomal circRNAs: biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):116.
Memczak S, Papavasileiou P, Peters O, et al. Identification and characterization of circular RNAs as a new class of putative biomarkers in human blood. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(10):e0141214.
Koh W, Pan W, Gawad C, et al. Noninvasive in vivo monitoring of tissue-specific global gene expression in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(20):7361–6.
Li Y, Zheng Q, Bao C, et al. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015;25(8):981–4.
Lin J, Cai D, Li W, et al. Plasma circular RNA panel acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Clin Biochem. 2019;74:60–8.
Pan B, Qin J, Liu X, et al. Identification of serum exosomal hsa-circ-0004771 as a novel diagnostic biomarker of colorectal cancer. Front Genet. 2019;10:1096.
Ye DX, Wang SS, Huang Y, et al. A 3-circular RNA signature as a noninvasive biomarker for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0995-7.
Li XN, Wang ZJ, Ye CX, et al. Circular RNA circVAPA is up-regulated and exerts oncogenic properties by sponging miR-101 in colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108611.
Xu Y, Xia J, Liu S, et al. Endocytosis and membrane receptor internalization: implication of F-BAR protein Carom. Front Biosci. 2017;22:1439–57.
Hon KW, Ab-Mutalib NS, Abdullah NMA, et al. Extracellular vesicle-derived circular RNAs confers chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):16497.
Zhao H, Chen S, Fu Q. Exosomes from CD133(+) cells carrying circ-ABCC1 mediate cell stemness and metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29600.
Gutschner T, Diederichs S. The hallmarks of cancer. RNA Biol. 2014;9(6):703–19.
Luo J, Xiong Y, Fu P-f, et al. Exosomal long non-coding RNAs: biological properties and therapeutic potential in cancer treatment. J Zhejiang Univ-Sci B. 2019;20(6):488–95.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Can Res. 2017;77(15):3965–81.
Oehme F, Krahl S, Gyorffy B, et al. Low level of exosomal long non-coding RNA HOTTIP is a prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. RNA Biol. 2019;16(10):1339–45.
Liu T, Zhang X, Gao S, et al. Exosomal long noncoding RNA CRNDE-h as a novel serum-based biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7(51):85551–63.
Fang C, Zan J, Yue B, et al. Long non-coding ribonucleic acid zinc finger antisense 1 promotes the progression of colonic cancer by modulating ZEB1 expression. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;32(6):1204–11.
Ye C, Shen Z, Wang B, et al. A novel long non-coding RNA lnc-GNAT1-1 is low expressed in colorectal cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor through regulating RKIP-NF-kappaB-Snail circuit. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35(1):187.
Gong W, Tian M, Qiu H, et al. Elevated serum level of lncRNA-HIF1A-AS1 as a novel diagnostic predictor for worse prognosis in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2017;20(4):417–24.
Liu L, Meng T, Yang XH, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of long non-coding RNA GAS5 and mircoRNA-221 in colorectal cancer and their effects on colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Cancer Biomark. 2018;22(2):283–99.
Gao T, Liu X, He B, et al. Exosomal lncRNA 91H is associated with poor development in colorectal cancer by modifying HNRNPK expression. Cancer Cell Int. 2018;18:11.
Liang ZX, Liu HS, Wang FW, et al. LncRNA RPPH1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by interacting with TUBB3 and by promoting exosomes-mediated macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(11):829.
Yang YN, Zhang R, Du JW, et al. Predictive role of UCA1-containing exosomes in cetuximab-resistant colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2018;18:164.
Xiao Y, Yurievich UA, Yosypovych SV. Long noncoding RNA XIST is a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer and inhibits 5-fluorouracil-induced cell cytotoxicity through promoting thymidylate synthase expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8(47):83171–82.
Li L, Shang J, Zhang Y, et al. MEG3 is a prognostic factor for CRC and promotes chemosensitivity by enhancing oxaliplatin-induced cell apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 2017;38(3):1383–92.
Li Y, Huang S, Li Y, et al. Decreased expression of LncRNA SLC25A25-AS1 promotes proliferation, chemoresistance, and EMT in colorectal cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(10):14205–15.
Xu W, Zhou G, Wang HZ, et al. Circulating lncRNA SNHG11 as a novel biomarker for early diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.32747.
Deng X, Ruan H, Zhang X, et al. Long noncoding RNA CCAL transferred from fibroblasts by exosomes promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 2020;146(6):1700–16.
Luan Y, Li X, Luan Y, et al. Circulating lncRNA UCA1 promotes malignancy of colorectal cancer via the miR-143/MYO6 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;19:790–803.
Ling H, Spizzo R, Atlasi Y, et al. CCAT2, a novel noncoding RNA mapping to 8q24, underlies metastatic progression and chromosomal instability in colon cancer. Genome Res. 2013;23(9):1446–61.
Lin Y, Zheng J, Lin D. PIWI-interacting RNAs in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.08.012.
Ge L, Zhang N, Li D, et al. Circulating exosomal small RNAs are promising non-invasive diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16077.
Mai D, Ding P, Tan L, et al. PIWI-interacting RNA-54265 is oncogenic and a potential therapeutic target in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Theranostics. 2018;8(19):5213–30.
Qu A, Wang W, Yang Y, et al. A serum piRNA signature as promising non-invasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:3703–20.
Vychytilova-Faltejskova P, Stitkovcova K, Radova L, et al. Circulating PIWI-interacting RNAs piR-5937 and piR-28876 are promising diagnostic biomarkers of colon cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2018;27(9):1019–28.
Wang Z, Yang H, Ma D, et al. Serum PIWI-Interacting RNAs piR-020619 and piR-020450 are promising novel biomarkers for early detection of colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2020;29(5):990–8.
Mai D, Zheng Y, Guo H, et al. Serum piRNA-54265 is a New Biomarker for early detection and clinical surveillance of Human Colorectal Cancer. Theranostics. 2020;10(19):8468–78.
Baraniskin A, Nopel-Dunnebacke S, Ahrens M, et al. Circulating U2 small nuclear RNA fragments as a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(2):E48–57.
Aghamiri S, Jafarpour A, Malekshahi ZV, et al. Targeting siRNA in colorectal cancer therapy: nanotechnology comes into view. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(9):14818–27.
Yin Y, Cao LY, Wu WQ, et al. Blocking effects of siRNA on VEGF expression in human colorectal cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(9):1086–92.
Shen K, Cui D, Sun L, et al. Inhibition of IGF-IR increases chemosensitivity in human colorectal cancer cells through MRP-2 promoter suppression. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(6):2086–97.
Li P, Chen W, Wang Y, et al. Effects of ephrinB2 gene siRNA on the biological behavior of human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2015;33(2):758–66.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Ningbo (No.2016A610121).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Zhang, X. & Hu, G. Circulating non-coding RNAs as new biomarkers and novel therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 2220–2236 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02639-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-021-02639-0