Abstract
Background
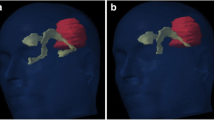
There is growing evidence that the subventricular zone (SVZ) may be involved in both the initiation and progression of glioblastoma (GB). We aimed to assess tumor proximity to the SVZ as a potential prognostic factor in GB.
Method
Retrospective study of 133 patients diagnosed with primary GB who underwent surgery followed by temozolomide-based chemoradiation between 2010 and 2016. All lesions were classified according to their anatomic relation with the SVZ. We determined the effect of tumor contact with the SVZ on progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), type, and patterns of recurrence.
Results
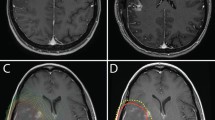
At a median follow-up of 18.6 months (95% CI 15.9–21.2), PFS and OS were 7.5 (95% CI 6.7–8.3) and 13.9 (95% CI 10.9–16.9) months, respectively. On the univariate analyses, initial contact with the SVZ was a factor for poor prognosis for both PFS (6.1 vs. 8.7 months; p = 0.006) and OS (10.6 vs. 17.9 months; p = 0.037). On the multivariate analysis, tumor contact with the SVZ remained statistically significant for PFS, but not OS. Patients with SVZ-contacting tumors presented a higher rate of aggressive clinical progression (30.9% vs. 11.3%; p = 0.007) and contralateral relapse patterns (23.4% vs. 9.1%; p = 0.048).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that glioblastoma contact with the SVZ appears to be an independent prognostic factor for poor PFS. The presence of an SVZ-contacting tumor was associated with more aggressive recurrences and a higher rate of contralateral relapses. These findings suggest that this variable may be a new prognostic factor in glioblastoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Xu J, Kromer C, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, et al. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro-Oncology. 2016;18(suppl_5):v1–v75.
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414(6859):105–11.
Alcantara Llaguno SR, Parada LF. Cell of origin of glioma: biological and clinical implications. Br J Cancer. 2016;115(12):1445–500.
Liu C, Sage JC, Miller MR, Verhaak RGW, Hippenmeyer S, Vogel H, et al. Mosaic analysis with double markers reveals tumor cell of origin in glioma. Cell. 2011;146(2):209–21.
Sanai N, Tramontin AD, Quiñones-Hinojosa A, Barbaro NM, Gupta N, Kunwar S, et al. Unique astrocyte ribbon in adult human brain contains neural stem cells but lacks chain migration. Nature. 2004;427(6976):740–4.
Doetsch F, Garcıa-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A. Cellular composition and three-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zone in the adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci. 1997;17(13):5046–5061. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-13-05046.1997.
Dulken BW, Leeman DS, Boutet SC, Hebestreit K, Brunet A. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis defines heterogeneity and transcriptional dynamics in the adult neural stem cell lineage. Cell Rep. 2017;18(3):777–90.
Lantos PL. The role of the subependymal plate in the origin of gliomas induced by ethylnitrosourea in the rat brain. Experientia. 1977;33(4):521–2.
Vick NA, Lin MJ, Bigner DD. The role of the subependymal plate in glial tumorigenesis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 1977;40(1):63–71.
Zhu Y, Guignard F, Zhao D, Liu L, Burns DK, Mason RP, et al. Early inactivation of p53 tumor suppressor gene cooperating with NF1 loss induces malignant astrocytoma. Cancer Cell. 2005;8(2):119–30.
Alcantara Llaguno S, Chen J, Kwon C-H, Jackson EL, Li Y, Burns DK, et al. Malignant astrocytomas originate from neural stem/progenitor cells in a somatic tumor suppressor mouse model. Cancer Cell. 2009;15(1):45–56.
Piccirillo SG, Spiteri I, Sottoriva A, Touloumis A, Ber S, Price SJ, et al. Contributions to drug resistance in glioblastoma derived from malignant cells in the sub-ependymal zone. Cancer Res. 2015;75(1):194–202.
Chaichana KL, McGirt MJ, Frazier J, Attenello F, Guerrero-Cazares H, Quinones-Hinojosa A. Relationship of glioblastoma multiforme to the lateral ventricles predicts survival following tumor resection. J Neurooncol. 2008;89(2):219–24.
Jafri NF, Clarke JL, Weinberg V, Barani IJ, Cha S. Relationship of glioblastoma multiforme to the subventricular zone is associated with survival. Neuro-Oncology. 2013;15(1):91–6.
Lim DA, Cha S, Mayo MC, Chen M-H, Keles E, VandenBerg S, et al. Relationship of glioblastoma multiforme to neural stem cell regions predicts invasive and multifocal tumor phenotype. Neuro-Oncology. 2007;9(4):424–9.
Young GS, Macklin EA, Setayesh K, Lawson JD, Wen PY, Norden AD, et al. Longitudinal MRI evidence for decreased survival among periventricular glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2011;104(1):261–9.
Adeberg S, König L, Bostel T, Harrabi S, Welzel T, Debus J, et al. Glioblastoma recurrence patterns after radiation therapy with regard to the subventricular zone. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2014;90(4):886–93.
Chen L, Chaichana KL, Kleinberg L, Ye X, Quinones-Hinojosa A, Redmond K. Glioblastoma recurrence patterns near neural stem cell regions. Radiother Oncol. 2015;116(2):294–300.
Adeberg S, Bostel T, König L, Welzel T, Debus J, Combs SE. A comparison of long-term survivors and short-term survivors with glioblastoma, subventricular zone involvement: a predictive factor for survival? Radiat Oncol. 2014;9(1):95.
Khalifa J, Tensaouti F, Lusque A, Plas B, Lotterie J-A, Benouaich-Amiel A, et al. Subventricular zones: new key targets for glioblastoma treatment. Radiat Oncol [Internet]. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-017-0791-2(cited 2017 Sep 15).
Barani IJ, Cuttino LW, Benedict SH, Todor D, Bump EA, Wu Y, et al. Neural stem cell-preserving external-beam radiotherapy of central nervous system malignancies. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2007;68(4):978–85.
Stupp R, Mason WP, Van Den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–96.
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–66.
Roa W, Brasher PMA, Bauman G, Anthes M, Bruera E, Chan A, et al. Abbreviated course of radiation therapy in older patients with glioblastoma multiforme: a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22(9):1583–8.
Kusumawidjaja G, Gan PZ, Ong WS, Teyateeti A, Dankulchai P, Tan YD, Chua ET, Chua KL, Tham CK, Wong FY, Chua M. Dose-escalated intensity-modulated radiotherapy and irradiation of subventricular zones in relation to tumor control outcomes of patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Onco Targets Ther. 2016;9:1115–1122. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S96509.
Mistry AM, Hale AT, Chambless LB, Weaver KD, Thompson RC, Ihrie RA. Influence of glioblastoma contact with the lateral ventricle on survival: a meta-analysis. J Neurooncol. 2017;131(1):125–33.
Mistry AM, Dewan MC, White-Dzuro GA, Brinson PR, Weaver KD, Thompson RC, et al. Decreased survival in glioblastomas is specific to contact with the ventricular–subventricular zone, not subgranular zone or corpus callosum. J Neurooncol. 2017;132(2):341–9.
Kappadakunnel M, Eskin A, Dong J, Nelson SF, Mischel PS, Liau LM, et al. Stem cell associated gene expression in glioblastoma multiforme: relationship to survival and the subventricular zone. J Neurooncol. 2010;96(3):359–67.
Liang TH-K, Kuo S-H, Wang C-W, Chen W-Y, Hsu C-Y, Lai S-F, et al. Adverse prognosis and distinct progression patterns after concurrent chemoradiotherapy for glioblastoma with synchronous subventricular zone and corpus callosum invasion. Radiother Oncol. 2016;118(1):16–23.
Lee SW, Fraass BA, Marsh LH, Herbort K, Gebarski SS, Martel MK, et al. Patterns of failure following high-dose 3-D conformal radiotherapy for high-grade astrocytomas: a quantitative dosimetric study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;43(1):79–88.
Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Franceschi E, Sotti G, Frezza G, Amistà P, et al. Recurrence pattern after temozolomide concomitant with and adjuvant to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma: correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1275–9.
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC, Cairncross JG. Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8(7):1277–80.
Sherriff J, Tamangani J, Senthil L, Cruickshank G, Spooner D, Jones B, et al. Patterns of relapse in glioblastoma multiforme following concomitant chemoradiotherapy with temozolomide. Br J Radiol. 2013;86(1022):20120414.
Oh J, Sahgal A, Sanghera P, Tsao MN, Davey P, Lam K, et al. Glioblastoma: patterns of recurrence and efficacy of salvage treatments. Can J Neurol Sci. 2011;38(4):621–5.
Chamberlain MC. Radiographic patterns of relapse in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 2011;101(2):319–23.
Baldock AL, Rockne RC, Boone AD, et al. From patient-specific mathematical neuro-oncology to precision medicine. Front Oncol. 2013;3:62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2013.00062(published 2013 Apr 2).
Wick W, Stupp R, Beule AC, et al. A novel tool to analyze MRI recurrence patterns in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2008;10(6):1019–24. https://doi.org/10.1215/15228517-2008-058.
Han S, Li X, Qiu B, Jiang T, Wu A. Can lateral ventricle contact predict the ontogeny and prognosis of glioblastoma? J Neurooncol. 2015;124(1):45–55.
Batista KMP, Vega IF, de Eulate-Beramendi SA, Morales JCG, Kurbanov A, Asnel D, et al. Original article prognostic significance of the markers IDH1 and YKL40 related to the subventricular zone. Folia Neuropathol. 2015;1:52–9.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Bradley Londres for professional English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests related to the present study or manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comas, S., Luguera, E., Molero, J. et al. Influence of glioblastoma contact with the subventricular zone on survival and recurrence patterns. Clin Transl Oncol 23, 554–564 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02448-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-020-02448-x