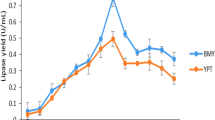
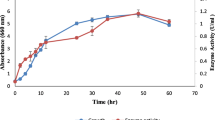
Abstract
Aspergillus terreus produces lipase 7.01 IU/ml in 96 h after optimization by one variable at a time method. Using the significant factors i.e. corn oil (A), sodium nitrate (B), casein (C), agitation rate (D) and incubation period (E) RSM was carried out resulting in 19.65 IU/ml from the combination +1(A), −1(B), −1(C), +1(D) and 0(E). The interactions between sodium nitrate, casein and agitation with corn oil were most significant. Scale up of production from 250 ml shake flask to 30 l bioreactor resulted in increased productivity of 0.52 IU/ml/h as against 0.2 IU/ml/h obtained in shake flasks. This lipase could carryout solvent free synthesis of partial glycerides of oleic acid with 96% efficiency in 12 h.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RSM:
-
Response surface methodology
- FCCCD:
-
Face centered central composite design
- OVAT:
-
One variable at a time
References
Kumar SS, Gupta R (2008) An extracellular lipase from Trichosporon asahii MSR 54: medium optimization and enantioselective deacetylation of phenyl ethyl acetate. Process Biochem 43:1054–1060
Saxena RK, Ghosh PK, Gupta R, Davidson WS, Bradoo S, Gulati R (1999) Microbial lipases: potential biocatalyst for the future industry. Curr Sci 77:101–115
Saxena RK, Agarwal L, Meghwanshi GK (2005) In: Satyanaryana T, Johri BN (eds) Diversity of fungal and yeast lipases: present in future scenario for 21st century. I.K. International Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, pp 796–841
Gupta R, Gupta N, Rathi P (2004) Bacterial lipases: an overview of production, purification and biochemical properties. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:763–781
Treichel H, de Oliveria D, Mazutti MA, Di Luccio M, Oliveria JV (2009) A review on microbial lipases production. Food Bioprocess Technol. doi:10.1007/s11947-009-0202-2
Saxena RK, Davidson WS, Sheoran A, Giri B (2003) Purification and characterization on an alkaline thermostable lipase from Aspergillus carneus. Process Biochem 39:239–247
Kaushik R, Saran S, Isar J, Saxena RK (2006) Statistical optimization of medium components and growth conditions by RSM to enhance lipase production by Aspergillus carneus. J Mol Catal B 40:121–126
Gulati R, Saxena RK, Gupta R (2000) Fermentation and downstream processing on lipase from Aspergillus terreus. Process Biochem 36:149–155
Winkler UK, Stuckman M (1979) Polysaccharide enhancement of exolipase formation by S. marcescens. J Bacteriol 138:663–670
Haaland PD (1989) In: Haaland PD (ed) Experimental design in biotechnology. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 1–8
Elibol M, Ozer D (2002) Response surface analysis of lipase production by freely suspended Rhizopus arrhizus. Process Biochem 38:367–372
Burkert JF, Maureri MF, Rodrigues MI (2004) Optimization of extracellular lipase production by Geotrichum sp. using factorial design. Bioresour Technol 91:77–84
Wang D, Xu Y, Shan T (2008) Effects of oils and oil-related substrates on the synthetic activity of membrane-bound lipase from Rhizopus cihinensis and optimization of the lipase fermentation media. Biochem Eng J 41:30–37
Sharma A, Bardhan D, Patel R (2009) Optimization of physical parameters for lipase production from Arthrobacter sp. BGCC#490. Indian J Biochem Biophys 46:178–183
Bornscheuer VT (1995) Lipase catalyzed synthesis of monoglycerols. Enzym Microb Technol 17:576–586
Kwon SJ, Han JJ, Rhee JS (1995) Production and in situ separation of mono- or diacylglycerol catalyzed by lipases in n-hexane. Enzym Microb Technol 17:700–704
Janssen AEM, Van der Padt A, Van Sonsbeek HM, Van’t Riet K (1993) The effect of organic solvents on the equilibrium position of enzymatic acylglycerol synthesis. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:95–103
Ergan F, Trani M, Andre G (1990) Production of glycerides from glycerol and fatty acid by immobilized lipases in non-aqueous media. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:195–200
Xia YM, Fang Y, Zhang KC, Shi GY, Brown JJ (2003) Enzymatic synthesis of partial glycerol caprate in solvent-free media. J Mol Catal B 23:3–8
Lou F-W, Liu B-K, Wu Q, Lv D-S, Lin X (2008) Candida antarctica lipase B (CAL-B)-catalyzed carbon-sulfur bond addition and controllable selectivity in organic media. Biotechnol Bioeng 80:200–225
Sabeder S, Habulin M, Knez Z (2005) Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of fatty acid fructose esters. J Food Eng 70:880–886
Arcos JA, Otero C, Hill CG (1998) Rapid enzymatic production of acyl glycerols from conjugated linoleic and glycerol in a solvent free system. Biotechnol Lett 20:617–621
Acknowledgment
Authors acknowledge with thanks the help of Ms. Pinki Anand for critically evaluating the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaushik, R., Marwah, R.G., Gupta, P. et al. Optimization of Lipase Production from Aspergillus terreus by Response Surface Methodology and Its Potential for Synthesis of Partial Glycerides Under Solvent Free Conditions. Indian J Microbiol 50, 456–462 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-011-0100-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-011-0100-y