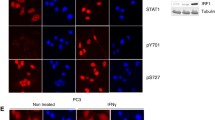
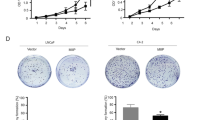
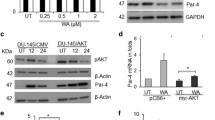
Abstract
Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) is a proto-oncogene overexpressed in prostate cancer (PCa) due to gene amplification and it is involved in the cancer progression of many cancers including PCa. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the role of TPD52 in cancer progression are still under investigation. In this study, we report that the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) by AICAR (5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide) inhibited the LNCaP and VCaP cells growth by silencing TPD52 expression. Activation of AMPK inhibited the proliferation and migration of LNCaP and VCaP cells. Interestingly, AICAR treatment to LNCaP and VCaP cells led to the downregulation of TPD52 via activation of GSK3β by a decrease of inactive phosphorylation at Ser9. Moreover, in AICAR treated LNCaP cells, inhibition of GSK3β by LiCl attenuated downregulation of TPD52 indicating that AICAR acts via GSK3β. Furthermore, we found that TPD52 interacts with serine/threonine kinase 11 or Liver kinase B1 (LKB1) a known tumor suppressor and an upstream kinase for AMPK. The molecular modeling and MD simulations indicates that the interaction between TPD52 and LKB1 leads to inhibition of the kinase activity of LKB1 as its auto-phosphorylation sites were masked in the complex. Consequently, TPD52-LKB1 interaction may lead to inactivation of AMPK. Moreover, overexpression of TPD52 is found to be responsible for the reduction of pLKB1 (Ser428) and pAMPK (Thr172). Therefore, TPD52 may be playing its oncogenic role via suppressing the AMPK activation. Altogether, our results revealed a new mechanism of PCa progression in which TPD52 overexpression inhibits AMPK activation by interacting with LKB1. These results support that the use of AMPK activators and/or small molecules that could disrupt the TPD52-LKB1 interaction might be useful to suppress PCa cell growth.
Graphical abstract

TPD52 interacts LKB1 and interfere with activation of AMPK in PCa cells










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the raw data and material is available with the corresponding author.
References
Beard H, Cholleti A, Pearlman D, Sherman W, Loving KA (2013) Applying physics-based scoring to calculate free energies of binding for single amino acid mutations in protein-protein complexes. PloS One 8(12):e82849. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082849
Byrne JA, Tomasetto C, Garnier JM, Rouyer N, Mattei MG, Bellocq JP, Rio MC, Basset P (1995) A screening method to identify genes commonly overexpressed in carcinomas and the identification of a novel complementary DNA sequence. Can Res 55(13):2896–2903
Byrne JA, Mattei M-G, Basset P (1996) Definition of the tumor protein D52 (TPD52) gene family through cloning of D52Homologues in human (hD53) and mouse (mD52). Genomics 35(3):523–532. https://doi.org/10.1006/geno.1996.0393
Byrne JA, Balleine RL, Fejzo MS, Mercieca J, Chiew YE, Livnat Y, Heaps L, Peters GB, Byth K, Karlan BY, Slamon DJ (2005) Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) is overexpressed and a gene amplification target in ovarian cancer. Int J Can 117(6):1049–1054. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21250
Byrne JA, Frost S, Chen Y, Bright RK (2014) Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) and cancer—oncogene understudy or understudied oncogene? Tumor Biology 35(8):7369–7382. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2006-x
Chen VB, Arendall WB, Headd JJ, Keedy DA, Immormino RM, Kapral GJ, Murray LW, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2010) MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 66(1):12–21. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444909042073
Chen Y, Peng C, Tan W, Yu J, Zayas J, Peng Y, Lou Z, Pei H, Wang L (2022) Tumor protein D52 (TPD52) affects cancer cell metabolism by negatively regulating AMPK. Cancer Med. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.4911
Cowan-Jacob SW, Jahnke W, Knapp S (2014) Novel approaches for targeting kinases: allosteric inhibition, allosteric activation and pseudokinases. Future Med Chem 6(5):541–561. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.13.216
Dasari C, Yaghnam DP, Walther R, Ummanni R (2017) Tumor protein D52 (isoform 3) contributes to prostate cancer cell growth via targeting nuclear factor-κB transactivation in LNCaP cells. Tumor Biology 39(5):1010428317698382. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317698382
Dasari C, Reddy K, Natani S, Murthy T, Bhukya S, Ummanni R (2019) Tumor protein D52 (isoform 3) interacts with and promotes peroxidase activity of Peroxiredoxin 1 in prostate cancer cells implicated in cell growth and migration. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Res 1866(8):1298–309
Dauter M, Dauter Z (2011) Deprotonated imidodiphosphate in AMPPNP-containing protein structures. Acta Crystall Sect D Biolog Crystall 67(12):1073–1075. https://doi.org/10.1107/S0907444911046105
El-Masry OS, Al-Sakkaf K, Brown BL, Dobson PR (2015) Differential crosstalk between the AMPK and PI3K/Akt pathways in breast cancer cells of differing genotypes: Leptin inhibits the effectiveness of AMPK activation. Oncol Rep 34(4):1675–1680. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4198
Faubert B, Boily G, Izreig S, Griss T, Samborska B, Dong Z, Dupuy F, Chambers C, Fuerth BJ, Viollet B, Mamer OA (2013) AMPK is a negative regulator of the Warburg effect and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Cell Metab 17(1):113–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.12.001
Fogarty S, Hawley SA, Green KA, Saner N, Mustard KJ, Hardie DG (2010) Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-β activates AMPK without forming a stable complex: synergistic effects of Ca2+ and AMP. Biochem J 426(1):109–118. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20091372
Garner LA, Janda DK (2011) Protein-protein interactions and cancer: targeting the central dogma. Curr Top Med Chem 11(3):258–80. https://doi.org/10.2174/156802611794072614
Gollavilli PN, Kanugula AK, Koyyada R, Karnewar S, Neeli PK, Kotamraju S (2015) AMPK inhibits MTDH expression via GSK 3β and SIRT 1 activation: potential role in triple negative breast cancer cell proliferation. FEBS J 282(20):3971–3985. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13391
Green AS, Chapuis N, Trovati Maciel T, Willems L, Lambert M, Arnoult C, Boyer O, Bardet V, Park S, Foretz M, Viollet B (2010) The LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway has tumor suppressor activity in acute myeloid leukemia through the repression of mTOR-dependent oncogenic mRNA translation. Blood 116(20):4262–4273. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-02-269837
Han D, Li S-J, Zhu Y-T, Liu L, Li M-X (2013) LKB1/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 14(7):4033–4039. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.7.4033
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA (2012) AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(4):251–262. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3311
Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X, Peng J (2020) Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep 47(6):4587–4629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.07.012
Khan AS, Frigo DEA (2017) Spatiotemporal hypothesis for the regulation, role, and targeting of AMPK in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 14(3):164–180. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2016.272
Liang J, Mills GB (2013) AMPK: A Contextual Oncogene or Tumor Suppressor? AMPK Regul Can Metabol Can Res 73(10):2929–2935. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3876
Lizcano JM, Göransson O, Toth R, Deak M, Morrice NA, Boudeau J, Hawley SA, Udd L, Mäkelä TP, Hardie DG, Alessi DR (2004) LKB1 is a master kinase that activates 13 kinases of the AMPK subfamily, including MARK/PAR-1. EMBO J 23(4):833–843. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600110
Luo Z, Zang M, Guo W (2010) AMPK as a metabolic tumor suppressor: control of metabolism and cell growth. Future Oncol 6(3):457–470. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.7.4033
Mancinelli R, Carpino G, Petrungaro S, Mammola CL, Tomaipitinca L, Filippini A, Facchiano A, Ziparo E, Giampietri C (2017) Multifaceted roles of GSK-3 in cancer and autophagy-related diseases. Oxidat Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4629495
Matsumoto S, Iwakawa R, Takahashi K, Kohno T, Nakanishi Y, Matsuno Y, Suzuki K, Nakamoto M, Shimizu E, Minna JD, Yokota J (2007) Prevalence and specificity of LKB1 genetic alterations in lung cancers. Oncogene 26(40):5911–5918. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210418
Mehenni H, Gehrig C, Nezu JI, Oku A, Shimane M, Rossier C, Guex N, Blouin JL, Scott HS, Antonarakis SE (1998) Loss of LKB1 kinase activity in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and evidence for allelic and locus heterogeneity. Am J Human Genet 63(6):1641–1650. https://doi.org/10.1086/302159
Meijer AJ, Dubbelhuis PF (2004) Amino acid signalling and the integration of metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313(2):397–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.07.012
Mirouse V, Billaud M (2011) The LKB1/AMPK polarity pathway. FEBS Lett 585(7):981–985. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2010.12.025
Moritz T, Venz S, Junker H, Kreuz S, Walther R, Zimmermann U (2016) Isoform 1 of TPD52 (PC-1) promotes neuroendocrine transdifferentiation in prostate cancer cells. Tumor Biol 37(8):10435–10446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4925-1
Payton LA, Lewis JD, Byrne JA, Bright RK (2008) Vaccination with metastasis-related tumor associated antigen TPD52 and CpG/ODN induces protective tumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57(6):799–811. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0416-y
Pineda CT, Ramanathan S, Tacer KF, Weon JL, Potts MB, Ou YH, White MA, Potts PR (2015) Degradation of AMPK by a cancer-specific ubiquitin ligase. Cell 160(4):715–728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.034
Rae C, Mairs RJ (2019) AMPK activation by AICAR sensitizes prostate cancer cells to radiotherapy. Oncotarget 10(7):749–759. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.26598
Reddy KR, Dasari C, Duscharla D, Supriya B, Ram NS, Surekha MV, Kumar JM, Ummanni R (2018) Dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase-1 (DDAH1) is frequently upregulated in prostate cancer, and its overexpression conveys tumor growth and angiogenesis by metabolizing asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA). Angiogenesis 21(1):79–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-017-9587-0
Rhodes DR, Barrette TR, Rubin MA, Ghosh D, Chinnaiyan AM (2002) Meta-analysis of microarrays: interstudy validation of gene expression profiles reveals pathway dysregulation in prostate cancer. Can Res 62(15):4427–4433
Ross-Adams H, Lamb AD, Dunning MJ, Halim S, Lindberg J, Massie CM, Egevad LA, Russell R, Ramos-Montoya A, Vowler SL, Sharma NL (2015) Integration of copy number and transcriptomics provides risk stratification in prostate cancer: a discovery and validation cohort study. EBioMed 2(9):1133–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.034
Rubin MA, Varambally S, Beroukhim R, Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Paris PL, Hofer MD, Storz-Schweizer M, Kuefer R, Fletcher JA, Hsi BL (2004) Overexpression, amplification, and androgen regulation of TPD52 in prostate cancer. Can Res 64(11):3814–3822. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3881
Schultze SM, Hemmings BA, Niessen M, Tschopp O (2012) PI3K/AKT, MAPK and AMPK signalling: protein kinases in glucose homeostasis. Exp Rev. Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1462399411002109
Seo Y, Kim J, Park SJ, Park JJ, Cheon JH, Kim WH, Kim TI (2020) Metformin suppresses cancer stem cells through AMPK activation and inhibition of protein prenylation of the mevalonate pathway in colorectal cancer. Cancers 12(9):2554. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092554
Shackelford DB, Shaw RJ (2009) The LKB1–AMPK pathway: metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer 9(8):563–575. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2676
Shahheydari H, Frost S, Smith BJ, Groblewski GE, Chen Y, Byrne JA (2014) Identification of PLP2 and RAB5C as novel TPD52 binding partners through yeast two-hybrid screening. Mol Biol Rep 41(7):4565–4572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3327-y
Sun L, Cao J, Chen K, Cheng L, Zhou C, Yan B, Qian W, Li J, Duan W, Ma J, Qi D (2019) Betulinic acid inhibits stemness and EMT of pancreatic cancer cells via activation of AMPK signaling. Int J Oncol 54(1):98–110. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4604
Tennstedt P, Bölch C, Strobel G, Minner S, Burkhardt L, Grob T, Masser S, Sauter G, Schlomm T, Simon R (2014) Patterns of TPD52 overexpression in multiple human solid tumor types analyzed by quantitative PCR. Int J Oncol 44(2):609–615. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2013.2200
Ummanni R, Teller S, Junker H, Zimmermann U, Venz S, Scharf C, Giebel J, Walther R (2008) Altered expression of tumor protein D52 regulates apoptosis and migration of prostate cancer cells. FEBS J 275(22):5703–5713. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06697.x
Wang R, Xu J, Saramäki O, Visakorpi T, Sutherland WM, Zhou J, Sen B, Lim SD, Mabjeesh N, Amin M, Dong JT (2004) PrLZ, a novel prostate-specific and androgen-responsive gene of the TPD52 family, amplified in chromosome 8q21.1 and overexpressed in human prostate cancer. Cancer research 64(5):1589–1594. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3331
William WN, Kim JS, Liu DD, Solis L, Behrens C, Lee JJ, Lippman SM, Kim ES, Hong WK, Wistuba II, Lee HY (2012) The impact of phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase expression on lung cancer survival. Ann Oncol 23(1):78–85. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdr036
Woods A, Johnstone SR, Dickerson K, Leiper FC, Fryer LG, Neumann D, Schlattner U, Wallimann T, Carlson M, Carling D (2003) LKB1 is the upstream kinase in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. Curr Biol 13(22):2004–2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2003.10.031
Xiang X, Saha AK, Wen R, Ruderman NB, Luo Z (2004) AMP-activated protein kinase activators can inhibit the growth of prostate cancer cells by multiple mechanisms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321(1):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.06.133
Yu SY, Chan DW, Liu VW, Ngan HY (2009) Inhibition of cervical cancer cell growth through activation of upstream kinases of AMP-activated protein kinase. Tumor Biol 30(2):80–85. https://doi.org/10.1159/000216843
Zeng J, Liu W, Fan YZ, He DL, Li L (2018) PrLZ increases prostate cancer docetaxel resistance by inhibiting LKB1/AMPK-mediated autophagy. Theranostics 8(1):109. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.20356
Zeqiraj E, Filippi BM, Deak M, Alessi DR, Van Aalten DM (2009) Structure of the LKB1-STRAD-MO25 complex reveals an allosteric mechanism of kinase activation. Science 326(5960):1707–1711. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1178377
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the HCP-040 project funded by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR). PK acknowledges CSIR for graduate student fellowship. CSIR-IICT manuscript communication no: IICT/Pubs./2022/241.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RU and PK: Study design and planning of experiments. PK, SK, AP, SN and SSJ: Experimentations, data acquisition, data analysis. RU and PK: Manuscript writing, review and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Consent for publication
All the authors reviewed the data, read the manuscript and consented to publication of the article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khilar, P., Sruthi, K.K., Parveen, S.M.A. et al. AMPK targets a proto-oncogene TPD52 (isoform 3) expression and its interaction with LKB1 suppress AMPK-GSK3β signaling axis in prostate cancer. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 957–974 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00745-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00745-y