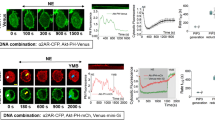
Abstract
CCN1 and CCN2 are matricellular proteins that are transcriptionally induced by various stimuli, including growth factors. CCN proteins act to facilitate signaling events involving extracellular matrix proteins. Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a lipid that activates G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), enhancing proliferation, adhesion, and migration in many types of cancer cells. Our group previously reported that LPA induces production of CCN1 protein in human prostate cancer cell lines within 2–4 h. In these cells, the mitogenic activity of LPA is mediated by LPA Receptor 1 (LPAR1), a GPCR. There are multiple examples of the induction of CCN proteins by LPA, and by the related lipid mediator sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), in various cellular models. The signaling pathways responsible for LPA/S1P-induced CCN1/2 typically involve activation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho and the transcription factor YAP. Inducible CCNs can potentially play roles in downstream signal transduction events required for LPA and S1P-induced responses. Specifically, CCNs secreted into the extracellular space can facilitate the activation of additional receptors and signal transduction pathways, contributing to the biphasic delayed responses typically seen in response to growth factors acting via GPCRs. In some model systems, CCN1 and CCN2 play key roles in LPA/S1P-induced cell migration and proliferation. In this way, an extracellular signal (LPA or S1P) can activate GPCR-mediated intracellular signaling to induce the production of extracellular modulators (CCN1 and CCN2) that in turn initiate another round of intracellular signaling.
Graphical Abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed KA, Hasib TA, Paul SK, Saddam M, Mimi A, Saikat ASM, Faruque HA, Rahman MA, Uddin MJ (2021) Potential role of CCN proteins in breast cancer: therapeutic advances and perspectives. Curr Oncol 28:4972–4985. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol28060417
Balijepalli P, Sitton CC (2021) Meier KE (2021) Lysophosphatidic acid signaling in cancer cells: what makes LPA so special? Cells 10:2059. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10082059
Bruno G, Cencetti F, Pertici I, Japtok L, Bernacchioni C, Donati C, Bruni P (2015) CTGF/CCN2 exerts profibrotic action in myoblasts via the up-regulation of sphingosine kinase-1/S1P3 signaling axis: implications in the action mechanism of TGFβ. Biochim Biophys Acta 1851:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.11.011
Cartier A, Hla T (2019) Sphingosine 1-phosphate: lipid signaling in pathology and therapy. Science 366:eaar5551. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar5551
Cheng JC, Wang EY, Yi Y, Thakur A, Tsai SH, Hoodless PA (2018) S1P stimulates proliferation by upregulating CTGF expression through S1PR2-mediated YAP activation. Mol Cancer Res 16:1543–1555. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-17-0681
Choi JW, Herr DR, Noguchi K, Yung YC, Lee C-W, Mutoh T, Lin M-E, Teo ST, Park KE, Mosley AN, Chun J (2010) LPA receptors: subtypes and biological actions. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:157–186. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.010909.105753
Chou CH, Lai SL, Ho CM, Lin WH, Chen CN, Lee PH, Peng FC, Kuo SH, Wu SY, Lai HS (2015) Lysophosphatidic acid alters the expression profiles of angiogenic factors, cytokines, and chemokines in mouse liver sinusoidal endothelial cells. PloS One 10:e0122060. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122060
Dou Q, Hao F, Sun L, Xu X, Cui MZ (2017) CRE and SRE mediate LPA-induced CCN1 transcription in mouse aortic smooth muscle cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 95:275–280. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2016-0559
Estrada R, Wang L, Jala VR, Lee JF, Lin CY, Gray RD, Haribabu B, Lee MJ (2009) Ligand-induced nuclear translocation of S1P(1) receptors mediates Cyr61 and CTGF transcription in endothelial cells. Histochem Cell Biol 131(2):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0521-9
Fan Q, Cheng Y, Chang HM, Deguchi M, Hsueh AJ, Leung PCK (2017) Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes ovarian cancer cell proliferation by disrupting Hippo signaling. Oncotarget 8:27166–27176. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15677
Fukui H, Teai K, Nakajima H, Chiba A, Fukuhara S, Mochiuki N (2014) S1P-Yap1 signaling regulates endoderm formation required for cardiac precursor cell migration in zebrafish. Dev Cell 31:128–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.08.014
Geraldo LHM, de SampaioSpohr TCL, do Amaral RF, de Fonseca ACC, Garcia C, de Almeida MF, Freitas C, dos Santos MF, Lim FRS (2021) Role of lysophosphatidic acid and its receptor in health and disease: novel therapeutic strategies. Sign Tran Targ Ther 6:45. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00367-5
Hao F, Zhang F, Wu DD, An D, Shi J, Li G, Xu X, Cui MZ (2016) Lysophosphatidic acid-induced vascular neointimal formation in mouse carotid arteries is mediated by the matricellular protein CCN1/Cyr61. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 311:C975–C984. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00227.2016
Ho LTY, Skiba N, Ullmer C, Rao PV (2018) Lysophosphatidic acid induces ECM production via activation of the mechanosensitive YAP/TAZ transcriptional pathway in trabecular meshwork cells. Invest Ophthal vis Sci 59:1969–1984. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.17-23702
Hopkins MM, Liu Z, Meier KE (2016) Positive and negative cross-talk between lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1, free fatty acid receptor 4, and epidermal growth factor receptor in human prostate cancer cells. J Pharm Exp Ther 359:124–133. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.116.233379
Jia Q, Xu B, Zhang Y, Ali A, Liao X (2021) CCN family proteins in cancer: Insight into their structures and coordination role in tumor microenvironment. Front Genet 2021:649387. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.649387
Jun J-I, Lau LF (2011) Taking aim at the extracellular matrix: CCN proteins as emerging therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:945–963. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3599
Kim H, Son S (2018) Shin I (2018) Role of the CCN protein family in cancer. BMB Rep 51:486–292. https://doi.org/10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.10.192
Kim YM, Lim C, Han CY, Kay HY, Cho IJ, Ki SH, Lee MY, Dwon HM, Lee CH, Kim G (2011) G∝12/13 induction of CYR61 in association with arteriocloerotic intimal hyperplasia. Effect of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Arterio Thromb Vasc Biol 31:861–869. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.218552
Koo JH, Plouffe SW, Meng Z, Lee DH, Yang D, Lim DS, Wang CY, Guan KL (2022) Induction of AP-1 by YAP/TAZ contributes to cell proliferation and organ growth. Genes Devel 34:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.331546.119
Lau LF (2016) Cell surface receptors for CCN proteins. J Cell Comm Signal 10:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-016-0324-z
Leask A (2020) Conjunction junction, what’s the function? CCN proteins as targets in fibrosis and cancers. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 318:C1046–C1054. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00028.2020
Li J, Ye L, Owen S, Weeks HP, Zhang Z, Jiang WG (2015) Emerging role of CCN family proteins in tumorigenesis and cancer metastasis. Int J Mol Med 36:1451–1463. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2015.2390
Liu Z, Hopkins MM, Zhang Z, Quisenberry CR, Fix L, Galvan BM, Meier KE (2015) Omega-3 fatty acids and other FFA4 agonists inhibit growth factor signaling in human prostate cancer cells. J Pharm Exp Ther 352:380–394. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.114.218974
Markiewicz M, Nakerakanti SS, Kapanadze B, Ghatnekar A, Trojanowska M (1994) Connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) mediates angiogenic effect of S1P in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Microcirc NY 18(1):1–11
Nivison MP, Meier KE (2018) The role of CCN4/WISP-1 in the cancerous phenotype. Cancer Manag Res 27(10):2893–2903. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S133915
Perbal B (2018) The concept of the CCN protein family revisited: a centralized coordination network. J Cell Commun Signal 12:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-018-0455-5
Riquelme-Guzman C, Contreras O, Branan E (2018) Expression of CTGF/CCN2 in response to LPA is stimulated by fibrotic extracellular matrix via the integrin/FAK axis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 314:C415–C427. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00013.2017
Sakamoto S, Yokoyama M, Zhang X, Prakash K, Nagao K, Hatanaka T, Getzenberg RH, Kakehi Y (2004) Increased expression of CYR61, an extracellular matrix signaling protein, in human benign prostatic hyperplasia and its regulation by lysophosphatidic acid. Endocrinology 145:2929–2940. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2003-1350
Stortelers C, Kerkhoven R, Moolenaar WH (2008) Multiple actions of lysophosphatidic acid on fibroblasts revealed by transcriptional profiling. BMC Genomics 9:387. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-387
Walsh CT, Radeff-Huang J, Matteo R, Hsiao A, Subramaniam S, Stupack D, Brown JH (2008) Thrombin receptor and RhoA mediate cell proliferation through integrin and cysteine-rich protein 61. FASEB J 22:4011–4021. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.08-113266
Wu DD, Zhang F, Hao F, Chun J, Xu X, Cui MZ (2014) Matricellular protein Cyr61 bridges lysophosphatidic acid and integrin pathways leading to cell migration. J Biol Chem 289:5774–5783. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.533042
Young N, Van Brocklyn JR (2007) Roles of phingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptors in malignant behavior of glioma cells. Differential effect of S1P2 on cell migration and invasiveness. Exp Cell Res 313:1615–1627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2007.02.009
Young N, Pearl DK, Van Brocklyn JR (2009) Sphingosine-1-phosphate regulates glioblastoma cell invasiveness through the urokinase plasminogen activator system and CCN1/Cyr61. Mol Canc Res 7:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0061
Yu FX, Zhao B, Panupinthu N, Jewell JL, Wang LH, Zhao J, Yuan H, Tumarneng K, Fu XD, Mills GB, Guan KL (2012) Regulation of the Hippo-YAP pathway by G-protein-coupled receptor signaling. Cell 150:780–791. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2450
Yu OM, Miyamoto S, Brown JH (2015) Myocardin-related transcription factor A and Yes-associated protein exert dual control in G protein-coupled receptor- and RhoA-mediated transcriptional regulation and cell proliferation. Mol Cell Biol 36:714–716. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00772-15
Yu ZL, Li DQ, Huang ZY, Xing X, Yu RQ, Li Z, Li ZB (2016) Lysophosphatidic acid upregulates connective tissue growth factor expression in osteoblasts through the GPCR/PKC and PKA pathways. Int J Mol Med 37:468–474. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2016.2450
Zhao X, Ding EY, Yu OM, Xiang SY, Tan-Sah VP, Yung BS, Hedgpeth J, Neubig RR, Lau LF, Brown JH, Miyamoto S (2014) Induction of the matricellular protein CCN1 through RhoA and MRTF-A contributes to ischemic cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol 75:152–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2014.07.017
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the ASPET David Lehr Award (K.E.M.) and by the Washington State University College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
The authors have no financial or non-financial competing interests that are directly or indirectly related to the work submitted for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Balijepalli, P., Meier, K.E. From outside to inside and back again: the lysophosphatidic acid-CCN axis in signal transduction. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 845–849 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00728-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-023-00728-z