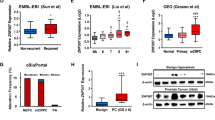
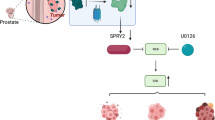
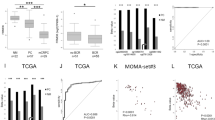
Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) has long been the leading cause of cancer-associated deaths among male worldwide. Our previous studies have shown that Bloom syndrome protein (BLM) plays a vital role in PCa proliferation, yet the underlying molecular mechanism remains largely obscure. Mechanistically, BLM directly interacted with hepatoma-derived growth factor (HDGF). Functionally, BLM and HDGF knockdown resulted in the higher impairment of PC3 proliferation, clonogenicity, migration and invasion than that their counterpart with either BLM or HDGF knockdown exclusively. Of note, HDGF overexpression expedited, whereas its knockdown suppressed, PC3 proliferation, clonogenicity, migration and invasion. Additionally, the potentiation or attenuation was partially antagonized upon BLM depletion or overexpression. In line with the vitro data, the impact of BLM and HDGF on tumor growth was investigated in mouse xenograft models. ChIP-seq, dual-luciferase reporter and western blotting assays were employed to expound the regulatory network in PC3 cells. The results unveiled that HDGF activated KRAS and suppressed RhoA transcription, and that the function of HDGF was mediated, in part, by interaction with BLM. Accordingly, the MAPK/ERK pathway was activated. Moreover, the regulation of HDGF on KRAS and RhoA had a signal crosstalk. To recapitulate, BLM and HDGF may serve as novel prognostic markers and potential therapeutic targets in PCa.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Ahn HK, Lee YH et al (2020) Current status and application of metformin for prostate cancer: a comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci 21(22):8540
Bao C, Wang J et al (2014) HDGF: a novel jack-of-all-trades in cancer. Future Oncol 10(16):2675–2685
Beer TM, Armstrong AJ et al (2014) Enzalutamide in metastatic prostate cancer before chemotherapy. N Engl J Med 371(5):424–433
Chen K, Xu H et al (2019) Bloom syndrome protein activates AKT and PRAS40 in prostate cancer cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:1–19
Chew TW, Liu XJ et al (2014) Crosstalk of Ras and Rho: activation of RhoA abates Kras-induced liver tumorigenesis in transgenic zebrafish models. Oncogene 33(21):2717–2727
Chi KN, Agarwal N et al (2019) Apalutamide for metastatic, castration-sensitive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 381(1):13–24
Clegg NJ, Wongvipat J et al (2012) ARN-509: a novel antiandrogen for prostate cancer treatment. Can Res 72(6):1494–1503
de Sousa Mesquita AP, de Araújo Lopes S et al (2017) Acquisition of anoikis resistance promotes alterations in the Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and matrix remodeling in endothelial cells. Apoptosis 22(9):1116–1137
Der CJ, Krontiris TG et al (1982) Transforming genes of human bladder and lung carcinoma cell lines are homologous to the ras genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79(11):3637–3640
Dreissigacker U, Mueller MS et al (2006) Oncogenic K-Ras down-regulates Rac1 and RhoA activity and enhances migration and invasion of pancreatic carcinoma cells through activation of p38. Cell Signal 18(8):1156–1168
Gu Z, Thomas G et al (2000) Prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA) expression increases with high gleason score, advanced stage and bone metastasis in prostate cancer. Oncogene 19(10):1288–1296
Helenius MA, Savinainen KJ et al (2006) Amplification of the urokinase gene and the sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to urokinase inhibitors. BJU Int 97(2):404–409
Hodge RG, Schaefer A et al (2020) RAS and RHO family GTPase mutations in cancer: twin sons of different mothers? Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 55(4):386–407
Hu T, Huang C et al (2003) Expression of hepatoma-derived growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 98(7):1444–1456
Imperial R, Toor OM et al (2019) Comprehensive pancancer genomic analysis reveals (RTK)-RAS-RAF-MEK as a key dysregulated pathway in cancer: Its clinical implications. Semin Cancer Biol 54:14–28
Kishima Y, Yamamoto H et al (2002) Hepatoma-derived growth factor stimulates cell growth after translocation to the nucleus by nuclear localization signals. J Biol Chem 277(12):10315–22
Lee PY, Costumbrado J et al (2012) Agarose gel electrophoresis for the separation of DNA fragments. J Vis Exp 62:1–5
Morelli AE, Larregina AT et al (2004) Endocytosis, intracellular sorting, and processing of exosomes by dendritic cells. Blood 104(10):3257–3266
Mosedale G, Hickson ID (2013) Encyclopedia of biological chemistry. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 43–49
Mostaghel EA (2014) Abiraterone in the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Manag Res 6:39–51
Nazarenko I, Rana S et al (2010) Cell surface tetraspanin Tspan8 contributes to molecular pathways of exosome-induced endothelial cell activation. Cancer Res 70(4):1668–1678
Pezaro C, Woo HH et al (2014) Prostate cancer: measuring PSA. Intern Med J 44(5):433–440
Qian X, Feng S et al (2017) RecQ helicase BLM regulates prostate cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Oncol Lett 14(4):4206–4212
Ren H, Tang X et al (2004) Expression of hepatoma-derived growth factor is a strong prognostic predictor for patients with early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 22(16):3230–3237
Rezazadeh S (2013) On BLM helicase in recombination-mediated telomere maintenance. Mol Biol Rep 40(4):3049–3064
Rothermundt C, Hayoz S et al (2014) Metformin in chemotherapy-naive castration-resistant prostate cancer: a multicenter phase 2 trial (SAKK 08/09). Eur Urol 66(3):468–474
Ruan Y, Xu H et al (2021) BLM interaction with EZH2 regulates MDM2 expression and is a poor prognostic biomarker for prostate cancer. Am J Cancer Res 11(4):1347–1368
Schroder FH, Hugosson J et al (2009) Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. N Engl J Med 360(13):1320–1328
Shariat SF, Karam JA et al (2008) Improved prediction of disease relapse after radical prostatectomy through a panel of preoperative blood-based biomarkers. Clin Cancer Res 14(12):3785–3791
Shen N, Li L et al (2019) A missense variant in PTPN12 associated with the risk of colorectal cancer by modifying Ras/MEK/ERK signaling. Cancer Epidemiol 59:109–114
Shetty A, Dasari S et al (2016) Hepatoma-derived growth factor: a survival-related protein in prostate oncogenesis and a potential target for vitamin K2. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig 34(11):483.e1-483.e8
Sohn E (2015) Screening: diagnostic dilemma. Nature 528(7582):S120–S122
Spratt DE (2018) Ki-67 remains solely a prognostic biomarker in localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 101(3):513–515
Stec I, Nagl SB et al (2000) The PWWP domain: a potential protein-protein interaction domain in nuclear proteins influencing differentiation? FEBS Lett 473(1):1–5
Sung H, Ferlay J et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Taftachi R, Ayhan A et al (2005) Proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) as an independent prognostic marker in patients after prostatectomy: a comparison of PCNA and Ki-67. BJU Int 95(4):650–654
Tang L, Dai F et al (2018) RhoA/ROCK signaling regulates smooth muscle phenotypic modulation and vascular remodeling via the JNK pathway and vimentin cytoskeleton. Pharmacol Res 133:201–212
Thakkar MK, Lee J et al (2022) RecQ Helicase Somatic alterations in Cancer. Front Mol Biosci 9:887758
Tomayko MM, Reynolds CP (1989) Determination of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 24(3):148–154
Tsai HE, Liu GS et al (2013) Downregulation of hepatoma-derived growth factor contributes to retarded lung metastasis via inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition by systemic POMC gene delivery in melanoma. Mol Cancer Ther 12(6):1016–1025
Tsujino T, Komura K et al (2021) CRISPR screen contributes to novel target discovery in prostate cancer. Int J Mol Sci 22(23):12777
Uyama H, Tomita Y et al (2006) Hepatoma-derived growth factor Is a novel prognostic factor for patients with pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12(20):6043–6048
Wang Q, Lv H et al (2015) Genome-wide haplotype association study identifies BLM as a risk gene for prostate cancer in Chinese population. Tumor Biol 36(4):2703–2707
Weeks SE, Metge BJ et al (2019) The nucleolus: a central response hub for the stressors that drive cancer progression. Cell Mol Life Sci 76(22):4511–4524
Wilkins AC, Gusterson B et al (2018) Ki67 is an independent predictor of recurrence in the largest randomized trial of 3 radiation fractionation schedules in localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 101(2):309–315
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y et al (2006) Expression of hepatoma-derived growth factor is correlated with lymph node metastasis and prognosis of gastric carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12(1):117–122
Yang Y, Ma Y et al (2021) A novel HDGF-ALCAM axis promotes the metastasis of Ewing sarcoma via regulating the GTPases signaling pathway. Oncogene 40(4):731–745
Zeng C, Zeng B et al (2020) Rho-ROCK signaling mediates entotic cell death in tumor. Cell Death Discov 6(1):1–3
Zhao Z, Liu J et al (2009) Prostate stem cell antigen mRNA expression in preoperatively negative biopsy specimens predicts subsequent cancer after transurethral resection of the prostate for benign prostatic hyperplasia. Prostate 69(12):1292–1302
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support received from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers 31860242).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y Ruan conceived the project. M Huang prepared all the materials. Y Guo carried out the in vitro and in vitro experiments. All authors participated in the discussion and evaluation of experimental results. Y Guo completed the first draft and drew the schematic figures. H Xu finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
All animal experimental procedures were approved by the Laboratory Animal Ethics Committee of Guizhou University (License Number: EAE-GZU-2022-P001).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, Y., Xu, H., Huang, M. et al. BLM promotes malignancy in PCa by inducing KRAS expression and RhoA suppression via its interaction with HDGF and activation of MAPK/ERK pathway. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 17, 757–772 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00717-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-022-00717-8