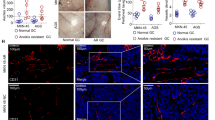
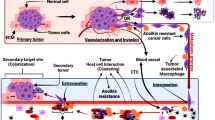
Abstract
Anoikis is a programmed cell death induced upon cell detachment from extracellular matrix. Anoikis resistance is a critical mechanism in tumor metastasis. Cancer cells deregulate and adapt their metabolism to survive in the absence of adhesion, spreading metastases to distant organs. These adaptations include abnormal regulation of growth factor receptors activating prosurvival signaling pathways, such as the Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways, and extracellular matrix remodeling, leading to metastasis by an increase of invasiveness and inhibiting anoikis. This study investigates the possible involvement of ECM components and signaling pathways in the regulation of resistance to anoikis in endothelial cells (EC). Endothelial cells submitted to stressful conditions by blocking adhesion to substrate (anoikis resistance) display an up-regulation of Ras/ERK and PI3k/Akt pathways by high expression of Ras, ERK, PI3K (p110α) and Akt (Thr 308). After ERK and PI3K inhibiting, all EC-derived cell lines studied showed lower growth, a decrease in invasive potential and a higher rate of apoptosis. Furthermore, anoikis-resistant cell lines display a decrease in the expression of fibronectin, collagen IV and hyaluronic acid and an increase in the expression of laminin, perlecan, αv, β3, α5 and β1 integrins subunits, hyaluronidades 1, 2 and 3 and metalloproteinases 2 and 9. These results indicate that the acquisition of anoikis resistance induced remodeling of the extracellular matrix and overexpression of the PI3K/Akt and Ras/ERK pathway components. Acquisition of resistance to anoikis is a potentially crucial step in endothelial cell transformation.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malagobadan S, Nagoor NH (2015) Evaluation of MicroRNAs regulating anoikis pathways and its therapeutic potential. Biomed Res Int 2015:716816. doi:10.1155/2015/716816
Chiarugi P, Giannoni E (2008) Anoikis: a necessary death program for anchorage-dependent cells. Biochem Pharmacol 76(11):1352–1364. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.023
Paoli P, Giannoni E, Chiarugi P (2013) Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1833(12):3481–3498. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.06.026
Simpson CD, Anyiwe K, Schimmer AD (2008) Anoikis resistance and tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett 272(2):177–185. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2008.05.029
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA (2007) Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 7(3):169–181. doi:10.1038/nrc2088
Carneiro BR, Pernambuco Filho PC, Mesquita AP, da Silva DS, Pinhal MA, Nader HB, Lopes CC (2014) Acquisition of anoikis resistance up-regulates syndecan-4 expression in endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 9(12):e116001. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0116001
Nelson CM, Bissell MJ (2006) Of extracellular matrix, scaffolds, and signaling: tissue architecture regulates development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:287–309. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104315
Kim YN, Koo KH, Sung JY, Yun UJ, Kim H (2012) Anoikis resistance: an essential prerequisite for tumor metastasis. Int. J Cell Biol 2012:306879. doi:10.1155/2012/306879
Mendoza MC, Er EE, Blenis J (2011) The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem Sci 36(6):320–328. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2011.03.006
McKay MM, Morrison DK (2007) Integrating signals from RTKs to ERK/MAPK. Oncogene 26(22):3113–3121. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210394
Rozengurt E (2007) Mitogenic signaling pathways induced by G protein-coupled receptors. J Cell Physiol 213(3):589–602. doi:10.1002/jcp.21246
Sengupta S, Peterson TR, Sabatini DM (2010) Regulation of the mTOR complex 1 pathway by nutrients, growth factors, and stress. Mol Cell 40(2):310–322. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.026
Guan X (2015) Cancer metastases: challenges and opportunities. Acta Pharm Sin B 5 (5):402–418. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.005
Sakamoto S, Kyprianou N (2010) Targeting anoikis resistance in prostate cancer metastasis. Mol Aspects Med 31(2):205–214. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2010.02.001
Stivarou T, Patsavoudi E (2015) Extracellular molecules involved in cancer cell invasion. Cancers 7 (1):238–265. doi:10.3390/cancers7010238
Hynes RO, Naba A (2012) Overview of the matrisome—an inventory of extracellular matrix constituents and functions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(1):a004903. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a004903
Whittaker CA, Bergeron KF, Whittle J, Brandhorst BP, Burke RD, Hynes RO (2006) The echinoderm adhesome. Dev Biol 300(1):252–266. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.07.044
Yue B (2014) Biology of the extracellular matrix: an overview. J Glaucoma 23(8 Suppl 1):S20-s23. doi:10.1097/IJG.0000000000000108
Lutolf MP, Hubbell JA (2005) Synthetic biomaterials as instructive extracellular microenvironments for morphogenesis in tissue engineering. Nat Biotechnol 23(1):47–55. doi:10.1038/nbt1055
Geiger B, Bershadsky A, Pankov R, Yamada KM (2001) Transmembrane crosstalk between the extracellular matrix-cytoskeleton crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(11):793–805. doi:10.1038/35099066
Desgrosellier JS, Cheresh DA (2010) Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 10(1):9–22. doi:10.1038/nrc2748
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM, Werb Z (2011) Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a005058
Cawston TE, Young DA (2010) Proteinases involved in matrix turnover during cartilage and bone breakdown. Cell Tissue Res 339(1):221–235. doi:10.1007/s00441-009-0887-6
Sternlicht MD, Werb Z (2001) How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:463–516. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.17.1.463
McAtee CO, Barycki JJ, Simpson MA (2014) Emerging roles for hyaluronidase in cancer metastasis and therapy. Adv Cancer Res 123:1–34. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800092-2.00001-0
Buonassisi V, Venter JC (1976) Hormone and neurotransmitter receptors in an established vascular endothelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73(5):1612–1616
Lopes CC, Toma L, Pinhal MA, Porcionatto MA, Sogayar MC, Dietrich CP, Nader HB (2006) EJ-ras oncogene transfection of endothelial cells upregulates the expression of syndecan-4 and downregulates heparan sulfate sulfotransferases and epimerase. Biochimie 88(10):1493–1504. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2006.04.009
Martins JR, Passerotti CC, Maciel RM, Sampaio LO, Dietrich CP, Nader HB (2003) Practical determination of hyaluronan by a new noncompetitive fluorescence-based assay on serum of normal and cirrhotic patients. Anal Biochem 319(1):65–72
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF (1994) A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 269(7):5241–5248
Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, Feeser WS, Van Dyk DE, Pitts WJ, Earl RA, Hobbs F, Copeland RA, Magolda RL, Scherle PA, Trzaskos JM (1998) Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem 273(29):18623–18632
Frisch SM, Francis H (1994) Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 124(4):619–626
Holmstrom TH, Chow SC, Elo I, Coffey ET, Orrenius S, Sistonen L, Eriksson JE (1998) Suppression of Fas/APO-1-mediated apoptosis by mitogen-activated kinase signaling. J Immunol 160(6):2626–2636
Le Gall M, Chambard JC, Breittmayer JP, Grall D, Pouyssegur J, Van Obberghen-Schilling E (2000) The p42/p44 MAP kinase pathway prevents apoptosis induced by anchorage and serum removal. Mol Biol Cell 11(3):1103–1112
McFall A, Ulku A, Lambert QT, Kusa A, Rogers-Graham K, Der CJ (2001) Oncogenic Ras blocks anoikis by activation of a novel effector pathway independent of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol Cell Biol 21(16):5488–5499. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.16.5488-5499.2001
Fukazawa H, Noguchi K, Murakami Y, Uehara Y (2002) Mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase (MEK) inhibitors restore anoikis sensitivity in human breast cancer cell lines with a constitutively activated extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway. Mol Cancer Ther 1(5):303–309
Zhan M, Zhao H, Han ZC (2004) Signalling mechanisms of anoikis. Histol Histopathol 19(3):973–983
Jost M, Huggett TM, Kari C, Rodeck U (2001) Matrix-independent survival of human keratinocytes through an EGF receptor/MAPK-kinase-dependent pathway. Mol Biol Cell 12(5):1519–1527
Boerner JL, Demory ML, Silva C, Parsons SJ (2004) Phosphorylation of Y845 on the epidermal growth factor receptor mediates binding to the mitochondrial protein cytochrome c oxidase subunit II. Mol Cell Biol 24(16):7059–7071. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.16.7059-7071.2004
Giannoni E, Buricchi F, Grimaldi G, Parri M, Cialdai F, Taddei ML, Raugei G, Ramponi G, Chiarugi P (2008) Redox regulation of anoikis: reactive oxygen species as essential mediators of cell survival. Cell Death Differ 15(5):867–878. doi:10.1038/cdd.2008.3
Giannoni E, Fiaschi T, Ramponi G, Chiarugi P (2009) Redox regulation of anoikis resistance of metastatic prostate cancer cells: key role for Src and EGFR-mediated pro-survival signals. Oncogene 28(20):2074–2086. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.77
Buchheit CL, Weigel KJ, Schafer ZT (2014) Cancer cell survival during detachment from the ECM: multiple barriers to tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 14(9):632–641. doi:10.1038/nrc3789
Zeng Q, Chen S, You Z, Yang F, Carey TE, Saims D, Wang CY (2002) Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits anoikis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by activation of ERK and Akt signaling independent of NFkappa B. J Biol Chem 277(28):25203–25208. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201598200
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network (2008) Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 455(7216):1061–1068. doi:10.1038/nature07385
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB, Engelman JA (2010) The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol 28(6):1075–1083. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.25.3641
Faes S, Dormond O (2015) PI3K and AKT: unfaithful partners in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 16(9):21138–21152. doi:10.3390/ijms160921138
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M, Tafuri A, Stivala F, Libra M, Basecke J, Evangelisti C, Martelli AM, Franklin RA (2007) Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773(8):1263–1284. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.10.001
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91(2):231–241
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S, Reed JC (1998) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282(5392):1318–1321
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96(6):857–868
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR, Pfeffer LM, Donner DB (1999) NF-kappaB activation by tumour necrosis factor requires the Akt serine-threonine kinase. Nature 401(6748):82–85. doi:10.1038/43466
Kunnimalaiyaan M, Ndiaye M, Chen H (2006) Apoptosis-mediated medullary thyroid cancer growth suppression by the PI3K inhibitor LY294002. Surgery 140 (6):1009–1014. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2006.06.040. (discussion 1014–1005)
Khwaja A, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Wennstrom S, Warne PH, Downward J (1997) Matrix adhesion and Ras transformation both activate a phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and protein kinase B/Akt cellular survival pathway. EMBO J 16(10):2783–2793. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.10.2783
Kodaki T, Woscholski R, Hallberg B, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Downward J, Parker PJ (1994) The activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by Ras. Curr Biol 4(9):798–806
Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne PH, Dhand R, Vanhaesebroeck B, Gout I, Fry MJ, Waterfield MD, Downward J (1994) Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase as a direct target of Ras. Nature 370(6490):527–532. doi:10.1038/370527a0
Suire S, Hawkins P, Stephens L (2002) Activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma by Ras. Curr Biol 12(13):1068–1075
Yang JY, Zong CS, Xia W, Yamaguchi H, Ding Q, Xie X, Lang JY, Lai CC, Chang CJ, Huang WC, Huang H, Kuo HP, Lee DF, Li LY, Lien HC, Cheng X, Chang KJ, Hsiao CD, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Sahin AA, Muller WJ, Mills GB, Yu D, Hortobagyi GN, Hung MC (2008) ERK promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting FOXO3a via MDM2-mediated degradation. Nat Cell Biol 10(2):138–148. doi:10.1038/ncb1676
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129(7):1261–1274. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.009
Abrahamsen I, Lorens JB (2013) Evaluating extracellular matrix influence on adherent cell signaling by cold trypsin phosphorylation-specific flow cytometry. BMC Cell Biol 14:36. doi:10.1186/1471-2121-14-36
Lopez-Otin C, Matrisian LM (2007) Emerging roles of proteases in tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer 7(10):800–808. doi:10.1038/nrc2228
Lokeshwar VB, Gomez P, Kramer M, Knapp J, McCornack MA, Lopez LE, Fregien N, Dhir N, Scherer S, Klumpp DJ, Manoharan M, Soloway MS, Lokeshwar BL (2008) Epigenetic regulation of HYAL-1 hyaluronidase expression. identification of HYAL-1 promoter. J Biol Chem 283(43):29215–29227. doi:10.1074/jbc.M801101200
Stern R (2008) Hyaluronidases in cancer biology. Semin Cancer Biol 18(4):275–280. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.03.017
Gu J, Fujibayashi A, Yamada KM, Sekiguchi K (2002) Laminin-10/11 and fibronectin differentially prevent apoptosis induced by serum removal via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt- and MEK1/ERK-dependent pathways. J Biol Chem 277(22):19922–19928. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200383200
Skyldberg B, Salo S, Eriksson E, Aspenblad U, Moberger B, Tryggvason K, Auer G (1999) Laminin-5 as a marker of invasiveness in cervical lesions. J Natl Cancer Inst 91(21):1882–1887
Xue LY, Zou SM, Zheng S, Liu XY, Wen P, Yuan YL, Lin DM, Lu N (2011) Expressions of the gamma2 chain of laminin-5 and secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and their relation to prognosis. Chin J Cancer 30(1):69–78
Yamamoto H, Itoh F, Iku S, Hosokawa M, Imai K (2001) Expression of the gamma(2) chain of laminin-5 at the invasive front is associated with recurrence and poor prognosis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 7(4):896–900
Miyazaki T, Shen M, Fujikura D, Tosa N, Kim HR, Kon S, Uede T, Reed JC (2004) Functional role of death-associated protein 3 (DAP3) in anoikis. J Biol Chem 279(43):44667–44672. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408101200
Ikeda K, Iyama K, Ishikawa N, Egami H, Nakao M, Sado Y, Ninomiya Y, Baba H (2006) Loss of expression of type IV collagen alpha5 and alpha6 chains in colorectal cancer associated with the hypermethylation of their promoter region. Am J Pathol 168(3):856–865
Tanjore H, Kalluri R (2006) The role of type IV collagen and basement membranes in cancer progression and metastasis. Am J Pathol 168(3):715–717. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2006.051321
Zeng ZS, Cohen AM, Guillem JG (1999) Loss of basement membrane type IV collagen is associated with increased expression of metalloproteinases 2 and 9 (MMP-2 and MMP-9) during human colorectal tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis 20(5):749–755
O’Brien V, Frisch SM, Juliano RL (1996) Expression of the integrin alpha 5 subunit in HT29 colon carcinoma cells suppresses apoptosis triggered by serum deprivation. Exp Cell Res 224(1):208–213. doi:10.1006/excr.1996.0130
Zhang Z, Morla A, Vuori K, Bauer J, Juliano R, Ruoslahti E (1993) The alpha v beta 1 integrin functions as a fibronectin receptor but does not support fibronectin matrix assembly and cell migration on fibronectin. J Cell Biol 122:235–242
Jia Y, Zeng ZZ, Markwart SM, Rockwood KF, Ignatoski KM, Ethier SP, Livant DL (2004) Integrin fibronectin receptors in matrix metalloproteinase-1-dependent invasion by breast cancer and mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 64(23):8674–8681. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0069
Morozevich G, Kozlova N, Cheglakov I, Ushakova N, Berman A (2009) Integrin alpha5beta1 controls invasion of human breast carcinoma cells by direct and indirect modulation of MMP-2 collagenase activity. Cell cycle 8(14):2219–2225. doi:10.4161/cc.8.14.8980
Shibata K, Kikkawa F, Nawa A, Suganuma N, Hamaguchi M (1997) Fibronectin secretion from human peritoneal tissue induces Mr 92,000 type IV collagenase expression and invasion in ovarian cancer cell lines. Cancer Res 57(23):5416–5420
Brassard DL, Maxwell E, Malkowski M, Nagabhushan TL, Kumar CC, Armstrong L (1999) Integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-mediated activation of apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 251(1):33–45. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4559
Montgomery AM, Reisfeld RA, Cheresh DA (1994) Integrin alpha v beta 3 rescues melanoma cells from apoptosis in three-dimensional dermal collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(19):8856–8860
Petitclerc E, Stromblad S, von Schalscha TL, Mitjans F, Piulats J, Montgomery AM, Cheresh DA, Brooks PC (1999) Integrin alpha(v)beta3 promotes M21 melanoma growth in human skin by regulating tumor cell survival. Cancer Res 59(11):2724–2730
Laplante P, Raymond MA, Labelle A, Abe J, Iozzo RV, Hebert MJ (2006) Perlecan proteolysis induces an alpha2beta1 integrin- and Src family kinase-dependent anti-apoptotic pathway in fibroblasts in the absence of focal adhesion kinase activation. J Biol Chem 281(41):30383–30392. doi:10.1074/jbc.M606412200
Farach-Carson MC, Carson DD (2007) Perlecan—a multifunctional extracellular proteoglycan scaffold. Glycobiology 17(9):897–905. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwm043
Oba-Shinjo SM, Correa M, Ricca TI, Molognoni F, Pinhal MA, Neves IA, Marie SK, Sampaio LO, Nader HB, Chammas R, Jasiulionis MG (2006) Melanocyte transformation associated with substrate adhesion impediment. Neoplasia 8(3):231–241. doi:10.1593/neo.05781
Segev A, Nili N, Strauss BH (2004) The role of perlecan in arterial injury and angiogenesis. Cardiovasc Res 63(4):603–610. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2004.03.028
Chen WY, Abatangelo G (1999) Functions of hyaluronan in wound repair. Wound Repair Regen 7(2):79–89
Solis MA, Chen YH, Wong TY, Bittencourt VZ, Lin YC, Huang LL (2012) Hyaluronan regulates cell behavior: a potential niche matrix for stem cells. Biochem Res Int 2012:346972. doi:10.1155/2012/346972
Park JB, Kwak HJ, Lee SH (2008) Role of hyaluronan in glioma invasion. Cell Adh Migr 2(3):202–207
Afratis N, Gialeli C, Nikitovic D, Tsegenidis T, Karousou E, Theocharis AD, Pavao MS, Tzanakakis GN, Karamanos NK (2012) Glycosaminoglycans: key players in cancer cell biology and treatment. FEBS J 279(7):1177–1197. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08529.x
Sa VK, Rocha TP, Moreira A, Soares FA, Takagaki T, Carvalho L, Nicholson AG, Capelozzi VL (2015) Hyaluronidases and hyaluronan synthases expression is inversely correlated with malignancy in lung/bronchial pre-neoplastic and neoplastic lesions, affecting prognosis. Braz J Med Biol Res 48(11):1039–1047. doi:10.1590/1414-431X20154693
Cao Y, Liu X, Lu W, Chen Y, Wu X, Li M, Wang XA, Zhang F, Jiang L, Zhang Y, Hu Y, Xiang S, Shu Y, Bao R, Li H, Wu W, Weng H, Yen Y, Liu Y (2015) Fibronectin promotes cell proliferation and invasion through mTOR signaling pathway activation in gallbladder cancer. Cancer Lett 360(2):141–150. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.01.041
Rundhaug JE (2005) Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 9(2):267–285
Kim D, Kim S, Koh H, Yoon SO, Chung AS, Cho KS, Chung J (2001) Akt/PKB promotes cancer cell invasion via increased motility and metalloproteinase production. FASEB J 15(11):1953–1962. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0198com
Acknowledgements
Supported by grants from Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP); Equipamentos Multiusuário (EMU—FAPESP); Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnológico (CNPq); Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal do Ensino Superior (CAPES) and Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (FINEP), Brazil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Sousa Mesquita, A.P., de Araújo Lopes, S., Pernambuco Filho, P.C. et al. Acquisition of anoikis resistance promotes alterations in the Ras/ERK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways and matrix remodeling in endothelial cells. Apoptosis 22, 1116–1137 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1392-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-017-1392-0