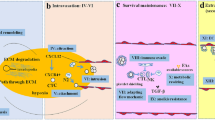
Abstract
Angiogenesis or neovascularization is a complex multi-step physiological process that occurs throughout life both in normal tissues and in disease. It is tightly regulated by the balance between pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors. The angiogenic switch has been identified as the key step during tumor progression in which the balance between pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors leans toward pro-angiogenic stimuli promoting the progression of tumors from dormancy to dysplasia and ultimately malignancy. This event can be described as either the outcome of a genetic event occurring in cancer cells themselves, or the positive and negative cross-talk between tumor-associated endothelial cells and other cellular components of the tumor microenvironment. In recent years, the mechanisms underlying the angiogenic switch have been extensively investigated in particular to identify therapeutic targets that can lead to development of effective therapies. In this review, we will discuss the current findings on the regulatory pathways in endothelial cells that are involved in the angiogenic switch with an emphasis on the role of anti-angiogenic protein, thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) and pro-angiogenic factor, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC, Lawler J (2004) The thrombospondins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:961–968
Almog N (2010) Molecular mechanisms underlying tumor dormancy. Cancer Lett 294:139–146
Baenziger NL, Brodie GN, Majerus PW (1971) A thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 68:240–243
Bocci G, Francia G, Man S, Lawler J, Kerbel RS (2003) Thrombospondin 1, a mediator of the antiangiogenic effects of low-dose metronomic chemotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:12917–12922
Carlson CB, Lawler J, Mosher DF (2008) Structures of thrombospondins. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:672–686
Carmeliet P (2000) Mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. Nat Med 6:389–395
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438:932–936
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Principles and mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:417–427
Chu LY, Ramakrishnan DP, Silverstein RL (2013) Thrombospondin-1 modulates VEGF signaling via CD36 by recruiting SHP-1 to VEGFR2 complex in microvascular endothelial cells. Blood 122:1822–1832
Colombo G, Margosio B, Ragona L, Neves M, Bonifacio S, Annis DS, Stravalaci M, Tomaselli S, Giavazzi R, Rusnati M et al (2010) Non-peptidic thrombospondin-1 mimics as fibroblast growth factor-2 inhibitors: an integrated strategy for the development of new antiangiogenic compounds. J Biol Chem 285:8733–8742
Dawson DW, Volpert OV, Pearce SF, Schneider AJ, Silverstein RL, Henkin J, Bouck NP (1999) Three distinct D-amino acid substitutions confer potent antiangiogenic activity on an inactive peptide derived from a thrombospondin-1 type 1 repeat. Mol Pharmacol 55:332–338
De Bock K, Cauwenberghs S, Carmeliet P (2011) Vessel abnormalization: another hallmark of cancer? Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Genet Dev 21:73–79
Dvorak HF (2002) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol 20:4368–4380
Ebbinghaus S, Hussain M, Tannir N, Gordon M, Desai AA, Knight RA, Humerickhouse RA, Qian J, Gordon GB, Figlin R (2007) Phase 2 study of ABT-510 in patients with previously untreated advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:6689–6695
Eichmann A, Simons M (2012) VEGF signaling inside vascular endothelial cells and beyond. Curr Opin Cell Biol 24:188–193
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8:579–591
Evans EB, Lin SY (2015) New insights into tumor dormancy: Targeting DNA repair pathways. World J Clin Oncol 6:80–88
Fantin A, Herzog B, Mahmoud M, Yamaji M, Plein A, Denti L, Ruhrberg C, Zachary I (2014) Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) hypomorphism combined with defective VEGF-A binding reveals novel roles for NRP1 in developmental and pathological angiogenesis. Development 141:556–562
Febbraio M, Silverstein RL (2007) CD36: Implications in cardiovascular disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39(11):2012–2030
Febbraio M, Hajjar DP, Silverstein RL (2001) CD36: a class B scavenger receptor involved in angiogenesis, atherosclerosis, inflammation, and lipid metabolism. J Clin Invest 108:785–791
Ferrara N, Henzel WJ (1989) Pituitary follicular cells secrete a novel heparin-binding growth factor specific for vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 161:851–858
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M, Lu L, O'Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ, Moore MW (1996) Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation of the VEGF gene. Nature 380:439–442
Ferrari do Outeiro-Bernstein MA, Nunes SS, Andrade AC, Alves TR, Legrand C, Morandi V (2002) A recombinant NH(2)-terminal heparin-binding domain of the adhesive glycoprotein, thrombospondin-1, promotes endothelial tube formation and cell survival: a possible role for syndecan-4 proteoglycan. Matrix Biol 21:311–324
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Folkman J (1975) Tumor angiogenesis: a possible control point in tumor growth. Ann Intern Med 82:96–100
Gaustad JV, Simonsen TG, Andersen LM, Rofstad EK (2016) Properdistatin inhibits angiogenesis and improves vascular function in human melanoma xenografts with low thrombospondin-1 expression. Oncotarget 7:76806–76815
Gelfand MV, Hagan N, Tata A, Oh WJ, Lacoste B, Kang KT, Kopycinska J, Bischoff J, Wang JH, Gu C (2014) Neuropilin-1 functions as a VEGFR2 co-receptor to guide developmental angiogenesis independent of ligand binding. elife 3:e03720
Githaka JM, Vega AR, Baird MA, Davidson MW, Jaqaman K, Touret N (2016) Ligand-induced growth and compaction of CD36 nanoclusters enriched in Fyn induces Fyn signaling. J Cell Sci 129:4175–4189
Good DJ, Polverini PJ, Rastinejad F, Le Beau MM, Lemons RS, Frazier WA, Bouck NP (1990) A tumor suppressor-dependent inhibitor of angiogenesis is immunologically and functionally indistinguishable from a fragment of thrombospondin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:6624–6628
Greenaway J, Lawler J, Moorehead R, Bornstein P, Lamarre J, Petrik J (2007) Thrombospondin-1 inhibits VEGF levels in the ovary directly by binding and internalization via the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1). J Cell Physiol 210:807–818
Gupta K, Gupta P, Wild R, Ramakrishnan S, Hebbel RP (1999) Binding and displacement of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by thrombospondin: effect on human microvascular endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 3:147–158
Hoeben A, Landuyt B, Highley MS, Wildiers H, Van Oosterom AT, De Bruijn EA (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol Rev 56:549–580
Holmes DI, Zachary I (2005) The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family: angiogenic factors in health and disease. Genome Biol 6:209
Indraccolo S, Stievano L, Minuzzo S, Tosello V, Esposito G, Piovan E, Zamarchi R, Chieco-Bianchi L, Amadori A (2006) Interruption of tumor dormancy by a transient angiogenic burst within the tumor microenvironment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:4216–4221
Iruela-Arispe ML, Lombardo M, Krutzsch HC, Lawler J, Roberts DD (1999) Inhibition of angiogenesis by thrombospondin-1 is mediated by 2 independent regions within the type 1 repeats. Circulation 100:1423–1431
Jimenez B, Volpert OV, Crawford SE, Febbraio M, Silverstein RL, Bouck N (2000) Signals leading to apoptosis-dependent inhibition of neovascularization by thrombospondin-1. Nat Med 6:41–48
Kaur S, Roberts DD (2011) CD47 applies the brakes to angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Cell Cycle 10:10–12
Kaur S, Martin-Manso G, Pendrak ML, Garfield SH, Isenberg JS, Roberts DD (2010) Thrombospondin-1 inhibits VEGF receptor-2 signaling by disrupting its association with CD47. J Biol Chem 285:38923–38932
Kazerounian S, Yee KO, Lawler J (2008) Thrombospondins: from structure to therapeutics : Thrombospondins in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:700–712
Kazerounian S, Duquette M, Reyes MA, Lawler JT, Song K, Perruzzi C, Primo L, Khosravi-Far R, Bussolino F, Rabinovitz I, Lawler J (2011) Priming of the vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway by thrombospondin-1, CD36, and spleen tyrosine kinase. Blood 117:4658–4666
Kliche S, Waltenberger J (2001) VEGF receptor signaling and endothelial function. IUBMB Life 52:61–66
Koch M, Hussein F, Woeste A, Grundker C, Frontzek K, Emons G, Hawighorst T (2011) CD36-mediated activation of endothelial cell apoptosis by an N-terminal recombinant fragment of thrombospondin-2 inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis in vivo. Breast Cancer Res Treat 128:337–346
Kosfeld MD, Pavlopoulos TV, Frazier WA (1991) Cell attachment activity of the carboxyl-terminal domain of human thrombospondin expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 266:24257–24259
Lawler J, Detmar M (2004) Tumor progression: the effects of thrombospondin-1 and -2. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:1038–1045
Lawler PR, Lawler J (2012) Molecular basis for the regulation of angiogenesis by thrombospondin-1 and -2. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2:a006627
Lawler JW, Slayter HS, Coligan JE (1978) Isolation and characterization of a high molecular weight glycoprotein from human blood platelets. J Biol Chem 253:8609–8616
Lawler J, Miao WM, Duquette M, Bouck N, Bronson RT, Hynes RO (2001) Thrombospondin-1 gene expression affects survival and tumor spectrum of p53-deficient mice. Am J Pathol 159:1949–1956
Leung DW, Cachianes G, Kuang WJ, Goeddel DV, Ferrara N (1989) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science 246:1306–1309
Lopez-Dee ZP, Chittur SV, Patel B, Stanton R, Wakeley M, Lippert B, Menaker A, Eiche B, Terry R, Gutierrez LS (2012) Thrombospondin-1 type 1 repeats in a model of inflammatory bowel disease: transcript profile and therapeutic effects. PLoS One 7:e34590
Lopez-Ramirez MA, Fonseca G, Zeineddine HA, Girard R, Moore T, Pham A, Cao Y, Shenkar R, de Kreuk BJ, Lagarrigue F, et al (2017) Thrombospondin1 (TSP1) replacement prevents cerebral cavernous malformations. J Exp Med 214:3331–3346 (in press)
Margosio B, Rusnati M, Bonezzi K, Cordes BL, Annis DS, Urbinati C, Giavazzi R, Presta M, Ribatti D, Mosher DF, Taraboletti G (2008) Fibroblast growth factor-2 binding to the thrombospondin-1 type III repeats, a novel antiangiogenic domain. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40:700–709
Mosher DF (1990) Physiology of thrombospondin. Annu Rev Med 41:85–97
Mpekris F, Baish JW, Stylianopoulos T, Jain RK (2017) Role of vascular normalization in benefit from metronomic chemotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:1994–1999
Nagy JA, Dvorak AM, Dvorak HF (2007) VEGF-A and the induction of pathological angiogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol 2:251–275
Naumov GN, Bender E, Zurakowski D, Kang SY, Sampson D, Flynn E, Watnick RS, Straume O, Akslen LA, Folkman J, Almog N (2006) A model of human tumor dormancy: an angiogenic switch from the nonangiogenic phenotype. J Natl Cancer Inst 98:316–325
Oganesian A, Armstrong LC, Migliorini MM, Strickland DK, Bornstein P (2008) Thrombospondins use the VLDL receptor and a nonapoptotic pathway to inhibit cell division in microvascular endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 19:563–571
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J, Claesson-Welsh L (2006) VEGF receptor signalling - in control of vascular function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:359–371
Pagano K, Torella R, Foglieni C, Bugatti A, Tomaselli S, Zetta L, Presta M, Rusnati M, Taraboletti G, Colombo G, Ragona L (2012) Direct and allosteric inhibition of the FGF2/HSPGs/FGFR1 ternary complex formation by an antiangiogenic, thrombospondin-1-mimic small molecule. PLoS One 7:e36990
Park JE, Keller GA, Ferrara N (1993) The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) isoforms: differential deposition into the subepithelial extracellular matrix and bioactivity of extracellular matrix-bound VEGF. Mol Biol Cell 4:1317–1326
Primo L, Ferrandi C, Roca C, Marchio S, di Blasio L, Alessio M, Bussolino F (2005) Identification of CD36 molecular features required for its in vitro angiostatic activity. FASEB J 19:1713–1715
Qin L, Zhao D, Xu J, Ren X, Terwilliger EF, Parangi S, Lawler J, Dvorak HF, Zeng H (2013) The vascular permeabilizing factors histamine and serotonin induce angiogenesis through TR3/Nur77 and subsequently truncate it through thrombospondin-1. Blood 121:2154–2164
Quail DF, Joyce JA (2013) Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med 19:1423–1437
Quesada AJ, Nelius T, Yap R, Zaichuk TA, Alfranca A, Filleur S, Volpert OV, Redondo JM (2005) In vivo upregulation of CD95 and CD95L causes synergistic inhibition of angiogenesis by TSP1 peptide and metronomic doxorubicin treatment. Cell Death Differ 12:649–658
Rahimi N (2006) VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2: two non-identical twins with a unique physiognomy. Front Biosci 11:818–829
Ren B, Song K, Parangi S, Jin T, Ye M, Humphreys R, Duquette M, Zhang X, Benhaga N, Lawler J, Khosravi-Far R (2009) A double hit to kill tumor and endothelial cells by TRAIL and antiangiogenic 3TSR. Cancer Res 69:3856–3865
Roberts DD (1996) Regulation of tumor growth and metastasis by thrombospondin-1. FASEB J 10:1183–1191
Roberts DD, Miller TW, Rogers NM, Yao M, Isenberg JS (2012) The matricellular protein thrombospondin-1 globally regulates cardiovascular function and responses to stress via CD47. Matrix Biol 31:162–169
Rodriguez-Manzaneque JC, Lane TF, Ortega MA, Hynes RO, Lawler J, Iruela-Arispe ML (2001) Thrombospondin-1 suppresses spontaneous tumor growth and inhibits activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and mobilization of vascular endothelial growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:12485–12490
Russell S, Duquette M, Liu J, Drapkin R, Lawler J, Petrik J (2015) Combined therapy with thrombospondin-1 type I repeats (3TSR) and chemotherapy induces regression and significantly improves survival in a preclinical model of advanced stage epithelial ovarian cancer. FASEB J 29:576–588
Sakurai Y, Ohgimoto K, Kataoka Y, Yoshida N, Shibuya M (2005) Essential role of Flk-1 (VEGF receptor 2) tyrosine residue 1173 in vasculogenesis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:1076–1081
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF (1983) Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science 219:983–985
Senger DR, Perruzzi CA, Feder J, Dvorak HF (1986) A highly conserved vascular permeability factor secreted by a variety of human and rodent tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 46:5629–5632
Short SM, Derrien A, Narsimhan RP, Lawler J, Ingber DE, Zetter BR (2005) Inhibition of endothelial cell migration by thrombospondin-1 type-1 repeats is mediated by beta1 integrins. J Cell Biol 168:643–653
Silverstein RL, Febbraio M (2009) CD36, a scavenger receptor involved in immunity, metabolism, angiogenesis, and behavior. Sci Signal, 2:re3
Simons M, Gordon E, Claesson-Welsh L (2016) Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17:611–625
Sosa MS, Bragado P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA (2014) Mechanisms of disseminated cancer cell dormancy: an awakening field. Nat Rev Cancer 14:611–622
Stenina-Adognravi O (2013) Thrombospondins: old players, new games. Curr Opin Lipidol 24:401–409
Stenina-Adognravi O (2014) Invoking the Power of Thrombospondins: Regulation of Thrombospondins Expression. Matrix Biol 37:69–82
Streit M, Velasco P, Riccardi L, Spencer L, Brown LF, Janes L, Lange-Asschenfeldt B, Yano K, Hawighorst T, Iruela-Arispe L, Detmar M (2000) Thrombospondin-1 suppresses wound healing and granulation tissue formation in the skin of transgenic mice. EMBO J 19:3272–3282
Sun J, Hopkins BD, Tsujikawa K, Perruzzi C, Adini I, Swerlick R, Bornstein P, Lawler J, Benjamin LE (2009) Thrombospondin-1 modulates VEGF-A-mediated Akt signaling and capillary survival in the developing retina. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296:H1344–H1351
Sweetwyne MT, Murphy-Ullrich JE (2012) Thrombospondin1 in tissue repair and fibrosis: TGF-beta-dependent and independent mechanisms. Matrix Biol 31:178–186
Takahashi K, Sumarriva K, Kim R, Jiang R, Brantley-Sieders DM, Chen J, Mernaugh RL, Takahashi T (2016) Determination of the CD148-Interacting Region in Thrombospondin-1. PLoS One 11:e0154916
Tan K, Duquette M, Liu JH, Dong Y, Zhang R, Joachimiak A, Lawler J, Wang JH (2002) Crystal structure of the TSP-1 type 1 repeats: a novel layered fold and its biological implication. J Cell Biol 159:373–382
Taraboletti G, Roberts D, Liotta LA, Giavazzi R (1990) Platelet thrombospondin modulates endothelial cell adhesion, motility, and growth: a potential angiogenesis regulatory factor. J Cell Biol 111:765–772
Volpert OV, Zaichuk T, Zhou W, Reiher F, Ferguson TA, Stuart PM, Amin M, Bouck NP (2002) Inducer-stimulated Fas targets activated endothelium for destruction by anti-angiogenic thrombospondin-1 and pigment epithelium-derived factor. Nat Med 8(4):349–357
Wang S, Blois A, El Rayes T, Liu JF, Hirsch MS, Gravdal K, Palakurthi S, Bielenberg DR, Akslen LA, Drapkin R et al (2016) Development of a prosaposin-derived therapeutic cyclic peptide that targets ovarian cancer via the tumor microenvironment. Sci Transl Med 8:329ra334
Westphal JR (2004) Technology evaluation: ABT-510, Abbott. Curr Opin Mol Ther 6:451–457
Yamauchi M, Imajoh-Ohmi S, Shibuya M (2007) Novel antiangiogenic pathway of thrombospondin-1 mediated by suppression of the cell cycle. Cancer Sci 98(9):1491–1497
Yano K, Brown LF, Lawler J, Miyakawa T, Detmar M (2003) Thrombospondin-1 plays a critical role in the induction of hair follicle involution and vascular regression during the catagen phase. J Invest Dermatol 120:14–19
Zhang X, Lawler J (2007) Thrombospondin-based antiangiogenic therapy. Microvasc Res 74:90–99
Zhang X, Galardi E, Duquette M, Delic M, Lawler J, Parangi S (2005a) Antiangiogenic treatment with the three thrombospondin-1 type 1 repeats recombinant protein in an orthotopic human pancreatic cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 11:2337–2344
Zhang X, Galardi E, Duquette M, Lawler J, Parangi S (2005b) Antiangiogenic treatment with three thrombospondin-1 type 1 repeats versus gemcitabine in an orthotopic human pancreatic cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 11:5622–5630
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the assistance of Sami Lawler in editing the manuscript. This work was supported by a CAO Pilot grant from the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazerounian, S., Lawler, J. Integration of pro- and anti-angiogenic signals by endothelial cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 12, 171–179 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-017-0433-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-017-0433-3