Abstract
Background
Patients with autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) may co-present with features of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) or primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). Using a national transplant registry, the outcomes of patients with these autoimmune liver conditions were compared.
Methods
The UNOS-STAR registry was used to select a study population of AIH, PSC, and PBC liver transplant (LT) patients. Living and multi-organ transplant cases were excluded. Using the UNOS-registered diagnoses, the study population was subdivided into those with nonoverlapping autoimmune liver diseases and those with overlapping forms (e.g., AIH–PBC). Outcomes were compared, using endpoints such as all-cause mortality, graft failure, and organ-system specific causes of death.
Results
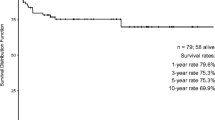
The main analysis featured 2048 entries, with 1927 entries having nonoverlapping AIH, 52 entries having PSC overlap, and 69 entries having PBC overlap. Patients with PBC overlap were more likely to have graft failure (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 3.46 95% CI 1.70–7.05), mortality secondary to respiratory causes (aHR 3.57 95% CI 1.23–10.43), and mortality secondary to recurrent disease (aHR 9.53 95% CI 1.85–49.09). Case incidence rates reflected these findings, expressed in events per 1000 person-years. For patients with PBC overlap and nonoverlapping AIH cases, respectively. Graft failure: 28.87 events vs. 9.42 events, mortality secondary to respiratory causes: 12.83 deaths vs. 3.77 deaths, mortality secondary to recurrent disease: 6.42 deaths vs. 1.26 deaths. Those with AIH–PSC overlap experienced a higher risk of death from graft infection (aHR 10.43 95% CI 1.08–100.37; case-incidence rate: 3.89 vs. 0.31 mortalities per 1000 person-years). Supplementary analysis showed similar findings, in which overlapping autoimmune conditions were associated with higher adverse outcome rates.
Conclusion
Patients with AIH-PBC overlap have higher risk of mortality due to recurrent liver disease and respiratory causes, and patients with AIH-PSC overlap have higher risk of mortality due to graft infection. While further prospective studies are needed to clarify the underlying mechanisms related to these findings, our study characterizes the prognostic implications of AIH overlap on post-LT mortality and graft failure risks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sahebjam F, Vierling JM. Autoimmune hepatitis. Front Med. 2015;9(2):187–219
Sucher E, Sucher R, Gradistanac T, Brandacher G, Schneeberger S, Berg T. Autoimmune hepatitis-immunologically triggered liver pathogenesis-diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. J Immunol Res. 2019;2019:9437043
Dienes HP, Erberich H, Dries V, Schirmacher P, Lohse A. Autoimmune hepatitis and overlap syndromes. Clin Liver Dis. 2002;6(2):349–362
Al-Chalabi T, Portmann BC, Bernal W, Mcfarlane IG, Heneghan MA. Autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndromes: an evaluation of treatment response, long-term outcome and survival. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28(2):209–220
Lüth S, Kanzler S, Frenzel C, et al. Characteristics and long-term prognosis of the autoimmune hepatitis/primary sclerosing cholangitis overlap syndrome. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2009;43(1):75–80
Silveira MG, Lindor KD. Overlap syndromes with autoimmune hepatitis in chronic cholestatic liver diseases. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;1(2):329–340
Kessler WR, Cummings OW, Eckert G, Chalasani N, Lumeng L, Kwo PY. Fulminant hepatic failure as the initial presentation of acute autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;2(7):625–631
Gómez Cabeza de Vaca V, Bernal Bellido C, Álamo Martínez JN, et al. Liver Transplantation Due to Fulminant Hepatic Failure. Transplant Proc. 2012;44(7):2076–2077.
Tang F, Ishwaran H. Random forest missing data algorithms. Stat Anal Data Min. 2017;10(6):363–377
Rigopoulou EI, Zachou K, Gatselis N, Koukoulis GK, Dalekos GN. Autoimmune hepatitis in patients with chronic HBV and HCV infections: patterns of clinical characteristics, disease progression and outcome. Ann Hepatol. 2013;13(1):127–135
Bhanji RA, Mason AL, Girgis S, Montano-Loza AJ. Liver transplantation for overlap syndromes of autoimmune liver diseases. Liver Int. 2013;33(2):210–219
Chayanupatkul M, Fiel MI, Schiano TD. The clinical characteristics, pre‐ and post–liver transplantation outcomes in patients having autoimmune overlap syndromes. Clinical Transplantation. 2020;34(5).
Czaja AJ, Carpenter HA. Autoimmune hepatitis overlap syndromes and liver pathology. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2017;46(2):345–364
Freedman BL, Danford CJ, Patwardhan V, Bonder A. Treatment of overlap syndromes in autoimmune liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med Res. 2020;9(5).
Ozaslan E, Efe C, Akbulut S, et al. Therapy response and outcome of overlap syndromes: autoimmune hepatitis and primary biliary cirrhosis compared to autoimmune hepatitis and autoimmune cholangitis. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57(99–100):441–446
Gautam M, Cheruvattath R, Balan V. Recurrence of autoimmune liver disease after liver transplantation: a systematic review. Liver Transpl. 2006;12(12):1813–1824
Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Lindor KD. Recurrence of primary sclerosing cholangitis: what do we learn from several transplant centers? Liver Transpl. 2008;14(2):130–132
Campsen J, Zimmerman MA, Trotter JF, et al. Clinically recurrent primary sclerosing cholangitis following liver transplantation: a time course. Liver Transpl. 2008;14(2):181–185
Hashimoto E, Shimada M, Noguchi S, et al. Disease recurrence after living liver transplantation for primary biliary cirrhosis: a clinical and histological follow-up study. Liver Transpl. 2001;7(7):588–595
Sylvestre PB, Batts KP, Burgart LJ, Poterucha JJ, Wiesner RH. Recurrence of primary biliary cirrhosis after liver transplantation: histologic estimate of incidence and natural history. Liver Transpl. 2003;9(10):1086–1093
Sanchez EQ, Levy MF, Goldstein RM, et al. The changing clinical presentation of recurrent primary biliary cirrhosis after liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2003;76(11):1583–1588
Molmenti EP, Netto GJ, Murray NG, et al. Incidence and recurrence of autoimmune/alloimmune hepatitis in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2002;8(6):519–526
Mottershead M, Neuberger J. Transplantation in autoimmune liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14(21):3388–3395
Futagawa Y, Terasaki PI, Waki K, Cai J, Gjertson DW. No improvement in long-term liver transplant graft survival in the last decade: an analysis of the UNOS data. Am J Transplant. 2006;6(6):1398–1406
Ayata G, Gordon FD, David Lewis W, et al. Liver transplantation for autoimmune hepatitis: A long-term pathologic study. Hepatology. 2000;32(2):185–192
Jeyarajah DR, Netto GJ, Lee SP, et al. Recurrent primary sclerosing cholangitis after orthotopic liver transplantation: is chronic rejection part of the disease process? Transplantation. 1998;66(10):1300–1306
Brandsaeter B, Schrumpf E, Bentdal O, et al. Recurrent primary sclerosing cholangitis after liver transplantation: a magnetic resonance cholangiography study with analyses of predictive factors. Liver Transpl. 2005;11(11):1361–1369
Loftus EV Jr, Harewood GC, Loftus CG, et al. PSC-IBD: a unique form of inflammatory bowel disease associated with primary sclerosing cholangitis. Gut. 2005;54(1):91–96
Li GS, Ye QF, Xia SS, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome after liver transplantation: etiology, prevention and management. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2002;1(3):330–334
Funding
This study was supported by the NIH grant NIDDK T32 DK067872-17 (to David Uihwan Lee MD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
David Uihwan Lee, Reid Ponder, Kijung Lee, Samantha Menegas, Gregory Hongyuan Fan, Harrison Chou, Daniel Jung, Keeseok Lee, David Jeffrey Hastie, Nathalie Helen Urrunaga of this manuscript certify they share no affiliation or involvement with any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.U., Ponder, R., Lee, K. et al. The differences in post-liver transplant outcomes of patients with autoimmune hepatitis who present with overlapping autoimmune liver diseases. Hepatol Int 17, 720–734 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-022-10468-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-022-10468-8