Abstract
Background
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is associated with poor prognosis in cirrhosis. Gut-derived nitrogenous substances play a role in pathogenesis of HE. The present study was conducted to assess small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) and prolonged orocecal transit time (OCTT) in cirrhosis and low-grade HE.
Methods
In cross-sectional prospective study, 75 patients were divided into 3 groups: group 1 (no HE, n = 31), group 2 (minimal HE, n = 29), and group 3 (early/grade 1 HE, n = 15). Minimal HE (MHE) was diagnosed when psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES) was ≤5. Early HE was diagnosed, according to West Haven criteria. All patients underwent glucose hydrogen breath test (GHBT) for SIBO and lactulose hydrogen breath test (LHBT) for OCTT.
Results
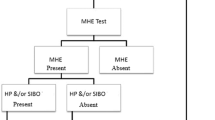
A total of 29 patients (38.67 %) had MHE and 15 (20 %) had early HE. Prevalence of MHE in Child–Turcotte–Pugh (CTP) class A, B, and C was 33.3, 38.71, and 45 %, respectively, while SIBO was detected in 26 (34.67 %). Prevalence of SIBO was 12.5 % in CTP class A, 41.94 % in CTP class B, and 50 % in CTP class C. Five (16.13 %) patients in no HE group had SIBO as compared to 14 (48.28 %) in MHE group and 7 (46.67 %) in early HE group (p = 0.018). OCTT was 111.13 ± 13.95 min in patients with no HE as compared to 137.59 ± 14.80 min in patients with MHE and 150 ± 15.12 min in patients with early HE (p < 0.001). OCTT was significantly prolonged in patients with SIBO (145 ± 17.49 min) than in those without SIBO (120.71 ± 18.3 min) (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
SIBO and delayed OCTT are more common with MHE and early HE in patients with cirrhosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferenci P, Lockwood A, Mullen K et al. Hepatic encephalopathy—definition, nomenclature, diagnosis and quantification: final report of the working party at the 11th world congress of gastroenterology, Vienna 1998. Hepatology 2002;35:716–721
Dhiman RK, Saraswat VA, Sharma BK et al. Minimal hepatic encephalopathy: consensus statement of a working party of the Indian National Association for study of the liver. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;25(6):1029–1041
Bustamante J, Rimola A, Ventura PJ et al. Prognostic significance of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. J Hepatol 1999;30:890–895
Poordad FF. The burden of hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2007;25(Suppl 1):3–9
Butterworth RF. Hepatic encephalopathy: a central neuroinflammatory disorder? Hepatology 2011;53(4):1372–1376
Butterworth RF. Pathogenesis and treatment of portal-systemic encephalopathy: an update. Dig Dis Sci 1992;37:321–327
Liu Q, Duan ZP, Ha DK et al. Symbiotic modulation of gut flora: effect on MHE in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004;39:1441–1449
Bauer TM, Schwacha H, Steinbrückner et al. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in human cirrhosis is associated with systemic endotoxemia. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97(9):2364–2370
Gupta A, Dhiman RK, Kumari S et al. Role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and delayed gastrointestinal transit time in cirrhotic patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J Hepatol 2010;53(5):849–855
Nagasako CK, de Oliveira Figueiredo MJ, de Souza Almeida JR et al. Investigation of autonomic function and orocecal transit time in patients with nonalcoholic cirrhosis and the potential influence of these factors on disease outcome. J Clin Gastroenterol 2009;43(9):884–889
Mittal VV, Sharma BC, Sharma P et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing lactulose, probiotics, and l-ornithine l-aspartate in treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;23(8):725–732
Dhiman RK, Kurmi R, Thumburu KK et al. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis of liver. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:2381–2390
Kircheis G, Wettstein M, Timmermann L et al. Critical flicker frequency for quantification of low-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2002;35:357–366
Romero-Gómez M, Córdoba J, Jover R et al. Value of critical flicker frequency in patients with minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 2007;45(4):879–885
Kerlin P, Wong L. Breath hydrogen testing in bacterial overgrowth of small intestine. Gastroenterology 1988;95:982–988
Sarno S, Erasmas LP, Haslbeck M et al. Orocaecal transit, bacterial overgrowth and hydrogen production in diabetes mellitus. Ital J Gastroenterol 1993;25:490–496
Lakshmi CP, Ghoshal UC, Kumar S et al. Frequency and factors associated with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and extra hepatic portal venous obstruction. Dig Dis Sci 2010;55:1142–1148
Gunnarsdottir SA, Sadik R, Shev S et al. Small intestinal motility disturbances and bacterial overgrowth in patients with liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98:1362–1370
Pande C, Kumar A, Sarin SK. Small-intestinal bacterial overgrowth in cirrhosis is related to the severity of liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2009;29:1273–1281
Casafont Morencos F, de las Heras Castaño G, Martín Ramos L et al. Small bowel bacterial overgrowth in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. Dig Dis Sci 1996;41:552–556
Savarino V, Mela GS, Zentilin P et al. Evaluation of 24-hour gastric acidity in patients with hepatic cirrhosis. Hepatology 1996;25(2):152–157
Rimola A, Soto R, Bory F et al. Reticuloendothelial system phagocytic activity in cirrhosis and its relation to bacterial infections and prognosis. Hepatology 1984;4(1):53–58
Van Thiel DH, Fagiuoli S, Wright HI et al. Gastrointestinal transit in cirrhotic patients: effect of hepatic encephalopathy and its treatment. Hepatology 1994;19:67–71
Fleckenstein JF, Frank S, Thuluvath PJ. Presence of autonomic neuropathy is a poor prognostic indicator in patients with advanced liver disease. Hepatology 1996;23:471–475
Thuluvath PJ, Triger DR. Autonomic neuropathy and chronic liver disease. Q J Med 1989;72:737–747
Shukla S, Shukla A, Mehboob S et al. Meta-analysis: the effects of gut flora modulation using prebiotics, probiotics and synbiotics on minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2011;33(6):662–671
Bajaj JS, Saeian K, Christensen KM et al. Probiotic yogurt for the treatment of minimal hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Gastroenterol 2008;103:1707–1715
Madrid AM, Hurtado C, Venegas M et al. Long-term treatment with cisapride and antibiotics in liver cirrhosis: effect on small intestinal motility, bacterial overgrowth, and liver function. Am J Gastroenterol 2001;96:1251–1255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lunia, M.K., Sharma, B.C. & Sachdeva, S. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and delayed orocecal transit time in patients with cirrhosis and low-grade hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatol Int 7, 268–273 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-012-9360-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-012-9360-9