Abstract
Purpose
A proportion of patients infected with genotype 2a hepatitis C virus (HCV) cannot achieve a sustained virological response (SVR) to pegylated-interferon plus ribavirin therapy (PEG-IFN/RBV) but the reason remains unclear. The present study aimed to clarify the possible correlation between viral sequence variations and final outcome.
Methods
The pretreatment complete open reading frame (ORF) sequences of genotype 2a HCV were determined by direct sequencing for two independent groups of patients (43 patients as test; group 1 and 35 as validation; group 2), and the correlation with the final outcome was explored.
Results
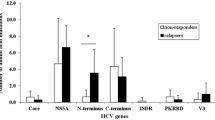
Patients with SVR (n = 58) and with non-SVR (n = 20) differed significantly in pretreatment HCV RNA level (p = 0.002), fibrosis score (p = 0.047), and cumulative RBV dosage (p = 0.003). By comparison of all amino acid positions in the complete HCV ORFs, threonine at amino acid (aa) 110 in the core region was remarkably frequent in SVR (p = 0.01 for group 1, p = 0.004 for group 2, and p = 5E−05 for combined). A sliding window analysis revealed that the total number of amino acid variations within the NS5A aa 2258–2306 region were significantly high in SVR compared to non-SVR patients (p = 0.01 for group 1, p = 0.006 for group 2, and p = 0.0006 for combined). Multivariate analyses revealed that core aa 110 (p = 0.02), NS5A aa 2258–2306 (p = 0.03), and cumulative RBV dosage (p = 0.02) were identified as independent variables associated with the final outcome.
Conclusions
The outcome of PEG-IFN/RBV therapy is significantly influenced by variation in the core and NS5A regions in genotype 2a HCV infection.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EVR:
-
Early virological response
- IFN:
-
Interferon
- IRRDR:
-
Interferon ribavirin resistance determinant region
- ISDR:
-
Interferon sensitivity determinant region
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- PEG-IFN:
-
Pegylated-interferon
- PePHD:
-
PKR-eIF2 phosphorylation homology domain
- PKR-BD:
-
Double-stranded RNA-activated protein Kinase binding domain
- RBV:
-
Ribavirin
- RVR:
-
Rapid virological response
- SVR:
-
Sustained virological response
References
Ghany MG, Strader DB, Thomas DL, Seeff LB. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C: an update. Hepatology 2009;49(4):1335–1374
Di Bisceglie AM, Martin P, Kassianides C, Lisker-Melman M, Murray L, Waggoner J, Goodman Z, Banks SM, Hoofnagle JH. Recombinant interferon alfa therapy for chronic hepatitis C A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med 1989;321(22):1506–1510
Haydon GH, Jarvis LM, Blair CS, Simmonds P, Harrison DJ, Simpson KJ, Hayes PC. Clinical significance of intrahepatic hepatitis C virus levels in patients with chronic HCV infection. Gut 1998;42(4):570–575
Simmonds P. Clinical relevance of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Gut 1997;40(3):291–293
Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P, Ramadori G, Bodenheimer H Jr, Bernstein D, Rizzetto M, Zeuzem S, Pockros PJ, Lin A, Ackrill AM. Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med 2004;140(5):346–355
Manns MP, McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Rustgi VK, Shiffman M, Reindollar R, Goodman ZD, Koury K, Ling M, Albrecht JK. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet 2001;358(9286):958–965
Dalgard O, Bjoro K, Hellum KB, Myrvang B, Ritland S, Skaug K, Raknerud N, Bell H. Treatment with pegylated interferon and ribavarin in HCV infection with genotype 2 or 3 for 14 weeks: a pilot study. Hepatology 2004;40(6):1260–1265
Mangia A, Santoro R, Minerva N, Ricci GL, Carretta V, Persico M, Vinelli F, Scotto G, Bacca D, Annese M, Romano M, Zechini F, Sogari F, Spirito F, Andriulli A. Peginterferon alfa-2b and ribavirin for 12 vs 24 weeks in HCV genotype 2 or 3. N Engl J Med 2005;352(25):2609–2617
Enomoto N, Sakuma I, Asahina Y, Kurosaki M, Murakami T, Yamamoto C, Ogura Y, Izumi N, Marumo F, Sato C. Mutations in the nonstructural protein 5A gene and response to interferon in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus 1b infection. N Engl J Med 1996;334(2):77–81
El-Shamy A, Nagano-Fujii M, Sasase N, Imoto S, Kim SR, Hotta H. Sequence variation in hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A predicts clinical outcome of pegylated interferon/ribavirin combination therapy. Hepatology 2008;48(1):38–47
Hamano K, Sakamoto N, Enomoto N, Izumi N, Asahina Y, Kurosaki M, Ueda E, Tanabe Y, Maekawa S, Itakura J, Watanabe H, Kakinuma S, Watanabe M. Mutations in the NS5B region of the hepatitis C virus genome correlate with clinical outcomes of interferon-alpha plus ribavirin combination therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005;20(9):1401–1409
Chayama K, Suzuki F, Tsubota A, Kobayashi M, Arase Y, Saitoh S, Suzuki Y, Murashima N, Ikeda K, Takahashi N, Kinoshita M, Kumada H. Association of amino acid sequence in the PKR-eIF2 phosphorylation homology domain and response to interferon therapy. Hepatology 2000;32(5):1138–1144
Akuta N, Suzuki F, Sezaki H, Suzuki Y, Hosaka T, Someya T, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S, Watahiki S, Sato J, Matsuda M, Arase Y, Ikeda K, Kumada H. Association of amino acid substitution pattern in core protein of hepatitis C virus genotype 1b high viral load and non-virological response to interferon–ribavirin combination therapy. Intervirology 2005;48(6):372–380
Toyoda H, Kumada T, Tada T, Arakawa T, Hayashi K, Honda T, Katano Y, Goto H. Association between HCV amino acid substitutions and outcome of peginterferon and ribavirin combination therapy in HCV genotype 1b and high viral load. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2010;25(6):1072–1078
Donlin MJ, Cannon NA, Aurora R, Li J, Wahed AS, Di Bisceglie AM, Tavis JE. Contribution of genome-wide HCV genetic differences to outcome of interferon-based therapy in Caucasian American and African American patients. PLoS One 2010;5(2):e9032
Donlin MJ, Cannon NA, Yao E, Li J, Wahed A, Taylor MW, Belle SH, Di Bisceglie AM, Aurora R, Tavis JE. Pretreatment sequence diversity differences in the full-length hepatitis C virus open reading frame correlate with early response to therapy. J Virol 2007;81(15):8211–8224
Murakami T, Enomoto N, Kurosaki M, Izumi N, Marumo F, Sato C. Mutations in nonstructural protein 5A gene and response to interferon in hepatitis C virus genotype 2 infection. Hepatology 1999;30(4):1045–1053
Hayashi K, Katano Y, Honda T, Ishigami M, Itoh A, Hirooka Y, Nakano I, Urano F, Yoshioka K, Toyoda H, Kumada T, Goto H. Mutations in the interferon sensitivity-determining region of hepatitis C virus genotype 2a correlate with response to pegylated-interferon-alpha 2a monotherapy. J Med Virol 2009;81(3):459–466
Kobayashi M, Watanabe K, Ishigami M, Murase K, Ito H, Ukai K, Yano M, Takagi K, Hattori M, Kakumu S, Yoshioka K. Amino acid substitutions in the nonstructural region 5A of hepatitis C virus genotypes 2a and 2b and its relation to viral load and response to interferon. Am J Gastroenterol 2002;97(4):988–998
Akuta N, Suzuki F, Hirakawa M, Kawamura Y, Yatsuji H, Sezaki H, Suzuki Y, Hosaka T, Kobayashi M, Saitoh S, Arase Y, Ikeda K, Kumada H. Association of amino acid substitution pattern in core protein of hepatitis C virus genotype 2a high viral load and virological response to interferon–ribavirin combination therapy. Intervirology 2009;52(6):301–309
Saito T, Ito T, Ishiko H, Yonaha M, Morikawa K, Miyokawa A, Mitamura K. Sequence analysis of PePHD within HCV E2 region and correlation with resistance of interferon therapy in Japanese patients infected with HCV genotypes 2a and 2b. Am J Gastroenterol 2003;98(6):1377–1383
Watanabe H, Nagayama K, Enomoto N, Itakura J, Tanabe Y, Sato C, Izumi N, Watanabe M. Amino acid substitutions in PKR-eIF2 phosphorylation homology domain (PePHD) of hepatitis C virus E2 protein in genotype 2a/2b and 1b in Japan and interferon efficacy. Hepatol Res 2003;26(4):268–274
Gale M Jr, Blakely CM, Kwieciszewski B, Tan SL, Dossett M, Tang NM, Korth MJ, Polyak SJ, Gretch DR, Katze MG. Control of PKR protein kinase by hepatitis C virus nonstructural 5A protein: molecular mechanisms of kinase regulation. Mol Cell Biol 1998;18(9):5208–5218
Hiramatsu N, Oze T, Yakushijin T, Inoue Y, Igura T, Mochizuki K, Imanaka K, Kaneko A, Oshita M, Hagiwara H, Mita E, Nagase T, Ito T, Inui Y, Hijioka T, Katayama K, Tamura S, Yoshihara H, Imai Y, Kato M, Yoshida Y, Tatsumi T, Ohkawa K, Kiso S, Kanto T, Kasahara A, Takehara T, Hayashi N. Ribavirin dose reduction raises relapse rate dose-dependently in genotype 1 patients with hepatitis C responding to pegylated interferon alpha-2b plus ribavirin. J Viral Hepat 2009;16(8):586–594
Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, Simon JS, Shianna KV, Urban TJ, Heinzen EL, Qiu P, Bertelsen AH, Muir AJ, Sulkowski M, McHutchison JG, Goldstein DB. Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature 2009;461(7262):399–401
Tanaka Y, Nishida N, Sugiyama M, Kurosaki M, Matsuura K, Sakamoto N, Nakagawa M, Korenaga M, Hino K, Hige S, Ito Y, Mita E, Tanaka E, Mochida S, Murawaki Y, Honda M, Sakai A, Hiasa Y, Nishiguchi S, Koike A, Sakaida I, Imamura M, Ito K, Yano K, Masaki N, Sugauchi F, Izumi N, Tokunaga K, Mizokami M. Genome-wide association of IL28B with response to pegylated interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy for chronic hepatitis C. Nat Genet 2009;41(10):1105–1109
Rauch A, Kutalik Z, Descombes P, Cai T, di Iulio J, Mueller T, Bochud M, Battegay M, Bernasconi E, Borovicka J, Colombo S, Cerny A, Dufour JF, Furrer H, Gunthard HF, Heim M, Hirschel B, Malinverni R, Moradpour D, Mullhaupt B, Witteck A, Beckmann JS, Berg T, Bergmann S, Negro F, Telenti A, Bochud PY. Genetic variation in IL28B is associated with chronic hepatitis C and treatment failure—a genome-wide association study. Gastroenterology 2010 Jan 7
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a grant-in-aid scientific research fund of the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture number 20390206 and in part by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan (H19-kanen-002). We are grateful to Yamanashi Pegintron Ribavirin Study Group and Ochanomizu Liver Conference Group for their cooperation and advices. Especially, we thank Asuka Kanayama and Takako Ohmori for their technical assistance, and Takatoshi Kitamura and Shunichi Okada for their cooperation and advices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kadokura, M., Maekawa, S., Sueki, R. et al. Analysis of the complete open reading frame of hepatitis C virus in genotype 2a infection reveals critical sites influencing the response to peginterferon and ribavirin therapy. Hepatol Int 5, 789–799 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-011-9267-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12072-011-9267-x