Abstract
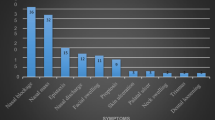
Malignant tumors of sinonasal region are rare and affect less than 1 in 100,000 people per year. They are histologically diverse group and potentially pose significant management problems due to their proximity to the orbit and intracranial cavity. Although squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is most common malignant tumor of paranasal cavity, tumors like adenocarcinoma, olfactory neuroblastoma, malignant melanoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, sarcomas, haemoproliferative tumors, e.g. lymphoma may also occur. Retrospectively study was done in a tertiary care institute from January 2008 to December 2018 in India. Inclusion criteria—all biopsy proven PNS malignancy patients operated by endoscopic approach, irrespective of age and gender. Exclusion criteria- patients diagnosed with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, skin involvement, gross orbital involvement (muscle invasion), metastasis, operated by open approaches. 46 patients who underwent endoscopic tumor removal were reviewed. 36 (78.2%) were males and 10 (4.6%) females. Most common tumor in our study was adenoid cystic carcinoma. Recurrence was seen in 6 patients. Palliative therapy was given to all patients with recurrence. Management of malignant PNS tumor involving anterior skull base is multidisciplinary. R0 resection should be main goal in all malignant PNS malignancy. Tumors invading unresectable areas like cavernous sinus, brain parenchyma, carotids can be left in these places followed by palliation except in cases of squamous cell carcinoma. If R0 cannot be achieved surgically in SCC than patient should be considered inoperable and send for palliation. T1–T3 PNS malignant tumors can be managed by endoscopic approach followed by adjuvant therapy after a period of 6 weeks. Endoscopic excision should be converted to endoscopic assisted open approach in case of T4 tumors. We have tried to give a management protocol for management of malignant PNS tumors.
Level of evidence: II.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson LDR (2006) Sinonasal carcinomas. Curr Diagn Pathol 12:40–53
Grau C, Jakobsen MH, Harbo G et al (2010) Sino-nasal cancer in Denmark 1982–1991—a nation widesurvey. Acta Oncol 40:12–23
Dwivedi M, Singh A, Jain R, Chowdhary A (2014) Non hodkins lymphoma presenting as unilateral nasal mass: A case report. J Evol Med Dent Sci. https://doi.org/10.14260/jemds/2014/3886
Carillo JF, Guemes A, Ramirez-Ortega MC, Onate-Ocana LF (2005) Prognostic factors in maxillary sinus and nasal cavity carcinoma. EJSO 31:1206–1212
Lund V, Stamberger H, Nicolai P et al (2010) European position paper on endoscopic management of tumors of the nose and paranasal sinuses and skull base. Rhinology 22:1–143
Ketcham AS, Wilkins RH, Vanburen JM, Smith RR (1963) A combined intracranial facial approach to the paranasal sinuses. Am J Surg 106:698–703
Nicolai P, Battaglia P, Bignami M et al (2008) Endoscopic surgery for malignant tumors of the sinonasal tract and adjacent skullbase: a 10-year experience. Am J Rhinol 22:308–316
Lund V, Wei W (2015) Endoscopic resection of malignant sinonasal tumors: an eighteen year experience. Rhinology 40:407–411
Nicolai P, Castelnuovo P, Villaret AB (2011) Endoscopic resection of sinonasal malignancies. Curr Oncol Rep 13:138–144
Hanna E, DeMonte F, Ibrhim S et al (2009) Endoscopic resection of sinonasal cancers with and without craniotomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135:1219–1224
Hadad G, Bassagasteguy L, Carrau RL et al (2006) A novel reconstructive technique after endoscopic expanded endonasalapproaches: vascular pedicled nasoseptal flap. Laryngoscope 116:1882–1886
Amit M et al (2013) Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a meta-analysis. J Neurol Surg B 74:118–125
Levine PA, McLean WC, Cantrell RW (1986) Esthesioneuroblastoma: the University of Virginia experience 1960–1985. Laryngoscope 96:742–746
Kumar M, Fallon RJ, Hill JS, Davis MM (2002) Esthesioneuroblastoma in children. J PediatrHematol. Oncol 24:482–487 ([PMID:12218598])
Dulguerov P, Allal AS, Calcaterra TC (2001) Esthesioneuroblastoma: a meta-analysis and review. Lancet Oncol 2:683–690
Kadish S, Goodman M, Wang CC (1976) Olfactory neuroblastoma: a clinical analysis of 17 cases. Cancer 37(3):1571–1576
Weber AL, Strnton AC (1984) Malignant tumors of the paranasal sinuses: radiologic, clinical, and histopathologic evaluation of 200 cases. Head Neck Surg 6:761–776
Lopez JI, Nevado M, Eizaguirre B, Perez A (1990) Intestinal-type adenocarcinoma of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses: a clinicopathologic study of 6 cases. Tumori 76:250–254
Berthelsen A, Andersen AP, Jensen TS, Hansen HS (1984) Melanomas of the mucosa in the oral cavity and the upper respiratory passages. Cancer 54:907–912
Batsakis JG, Regezi JA, Solomon AR, Rice DH (1982) The pathology of head and neck tumors: mucosal melanomas, part 13. Head Neck Surg 4:404–418
Snow GB, van der Waal I (1986) Mucosal melanomas of the head and neck. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 19:537–547
Patel SG, Prasad ML, Escrig M, Singh B, Shaha AR, Kraus DH, Boyle JO, Huvos AG, Busam K, Shah JP (2002) Primary mucosal malignant melanoma of the head and neck. Head Neck 24:247–257
Cheng YF, Lai CC, Ho CY, Shu CH, Lin CZ (2007) Toward a better understanding of sinonasal mucosal melanoma: clinical review of 23 cases. J Chin Med Assoc 70:24–29
Frierson HF, Mills SE, Fechner RE, Taxy JB, Levine PA (1986) Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: an aggressive neoplasm derived from Schneiderian epithelium and distinct from olfactory neuroblastoma. Am J Surg Pathol 10:771–779
Levine PA, Frierson HF, Mills SE, Stewart FM, Fechner RF, Cantrell RW (1987) Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma: A distinctive and highly aggressive neoplasm. Laryngoscope 97:905–908
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Here by all authors of the manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest and no monetary benefits are associated with this article.
Informed consent
Proper informed written consent was taken from all patients of the study.
Human participants and animal rights
This is a retrospective study done in a tertiary care institute on human subjects after informing ethical committee of the institute.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, R., Sankar, R., Singh, A.B. et al. Endoscopic Management of Malignant Tumors of Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity: An Institutional Experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74, 564–574 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-022-03141-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-022-03141-x