Abstract
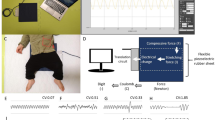
A new nasal sensor has been designed using Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film using its piezoelectric property to measure nasal patency. The aim of this study is to determine the intra- and intersession reliability of the new PVDF nasal sensor measurement of unilateral and combined nasal parameters in a group of healthy subjects. Two identical nasal sensors: for right nostril (RN) and left nostril (LN) were designed using piezoelectric natured PVDF films. Twenty subjects were studied. To evaluate the repeatability, total three sets of PVDF sensor measurements were recorded, two sets were taken 5 min apart during same session without repositioning the PVDF nasal sensors and two more sets were taken during 1 h apart successively, by repositioning the PVDF nasal sensor. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) of PVDF sensor measurements for intra- and intersession showed a high and greater repeatability over time for all the combined (mean) and unilateral (RN and LN) values. In both healthy and patients, ICC values for both intra- and intersession measurements were ≥ 0.80 confirming strong reliability and also almost all of the coefficients of variation for the same parameters were low (below 10%). PVDF sensor measurements showed good intra- and intersession repeatability and can be recommended for the objective monitoring of nasal patency during diagnosis and follow-up of conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scadding G, Hellings P, Alobid I, Bachert C, Fokkens W, van Wijk RG et al (2011) Diagnostic tools in Rhinology EAACI position paper. Clin Transl Allergy 1:2
Hilberg O, Jackson AC, Swift DL, Pedersen OF (1989) Acoustic rhinometry: evaluation of nasal cavity geometry by acoustic reflection. J Appl Physiol 66(1):295–303
Kern EB (1981) Committee report on standardization of rhinomanometry. Rinology 19(4):231–236
Fairley JW, Durham LH, Ell SR (1993) Correlation of subjective sensation of nasal patency with nasal peak flow rate. Clin Otolaringol 18(1):19–22
Chaaban M, Jacquelynne PC (2011) Assessing nasal air flow: options and utility. Proc Am Thorac Soc 8:70–78
Pallanch JF, Mccaffrey TV, Kern EB (1993) Evaluation of nasal breathing function. In: Cummings CW, Fredrickson JM, Harher LA, Krause CJ, Shuller DE (eds) Otolaryngology—head and neck surgery, 2nd edn. Mosby-Year Book, St Louis, pp 1–59
Corey JP, Gungor A, Nelson R, Fredberg J, Lai V (1997) A comparison of the nasal cross-sectional areas and volumes obtained with acoustic rhinometry and magnetic resonance imaging. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 117(4):349–354
Silkoff PE, Chakravorty S, Chapnik J, Cole P, Zamel N (1999) Reproducibility of acoustic rhinometry and rhinomanometry in normal subjects. Am J Rhinol 13(2):131–135
Cheung EJ, Citardi MJ, Fakhri S, Cain J, Batra PS, Luong A (2010) Com-parison of optical rhinometry to acoustic rhinometry using nasal provocation testing with Dermatophagoides farinae. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 143(2):290–293
Al Ahmari MD, Wedzicha JA, Hurst JR (2012) Intersession repeatability of acoustic rhinometry measurements in healthy volunteers. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 5(3):156–160
Kawai H (1969) The piezoelectric of polyvinylidene fluoride. Jpn J Appl Phys 8(7):975–976
Manjunatha RG, Rajanna K, Mahapatra DR, Prakash S (2014) Evaluation of polyvinylidene fluoride nasal sensor to assess deviated nasal septum in comparison with peak nasal inspiratory flow measurements. Am J Rhinol Allergy 28(1):e62–e67
Manjunatha RG, Rajanna K, Mahapatra DR, Nayak MM, Krishnaswamy UM, Srinivasa R (2013) Polyvinylidene fluoride film based nasal sensor to monitor human respiration pattern: an initial clinical study. J Clin Monit Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-013-9486-x
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174
Starling-Schwanz R, Peake HL, Salome CM, Toelle BG, Ng KW, Marks GB, Lean ML, Rimmer SJ (2005) Repeatability of peak nasal inspiratory flow measurements and utility for assessing the severity of rhinitis. Allergy 60(6):795–800
Acknowledgements
Authors also thank Prof. NS Murthy and Ms. Radhika, Department of Biostatistics, M. S. Ramaiah Medical College, Bangalore, India for their valuable inputs and contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RGM carried out the design and coordinated the study, participated in most of the experiments and prepared the manuscript. SP provided assistance for clinical data and expertise. All authors have read and approved the content of the manuscript. KR provided expertise in the design of the study, coordinated all the experiments and participated in manuscript preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjunatha, R.G., Prakash, S. & Rajanna, K. The Reliability of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Sensor for Intra- and Intersession Measurements. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 3), 1935–1939 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1349-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1349-9