Abstract
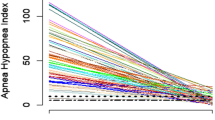
Snoring & obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) is a globally prevalent problem which is on the rise in recent times. The treatment modalities include medical appliances and surgery. It is mandatory to have a rational approach in the management of OSAS, by meticulously analyzing both anatomical and physiological parameters causing the disorder. To define a rational approach for the management of OSAS, by devising a comprehensive protocol with assessment of anatomical level of obstruction by dynamic MRI and physiological factors by Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS) and Polysomnography. A prospective study in 110 patients was conducted over a period of 2 years, at our institute. All patients in the study group were evaluated with dynamic MRI and ESS and Polysomnography. As per the management protocols defined in the study, surgery was advocated in 46 patients (Group 1) with severe compromise in airway, while another group of 64 patients (Group 2) were provided continuous positive airway pressure support (CPAP). Successful outcomes among these 110 patients were analyzed at the end of the study period. A few patients required multimodal therapy which included surgery and CPAP support. Among 46 patients, surgical treatment proved successful in 41 patients in whom AHI reduced from 46.96 to 12.88 (improved by 62%) and ESS improved by almost ten points. Among 64 patients in CPAP group, AHI reduced from 54.2 to 11.3 (improved by 79%) and ESS improved by 11 points in all the patients, but six of them had poor compliance. Five patients among the surgical group had persistence of symptoms. Inferences derived from the above results proved the success of formulating a rational approach in the management of OSAS. Critical analysis of the anatomical and physiological factors inducing obstructive episodes and an appropriate treatment plan is vital, to produce successful outcomes in patients with OSAS. Failure of surgical procedures, are often due to improper case selection. A small group of patients may require multimodal therapy with surgery and CPAP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guilleminault C, Eldridge FL, Dement WC (1973) Insomnia with sleep apnea: a new syndrome. Science 181:856–858
Suto Y, Matsuda E, Inoue Y, Suzuki T, Ohta Y (1996) Sleep apnea syndrome. Comparison of MR imaging of the oropharynx with physiologic indexes. Radiology 201:393–398
Sher JW, Schechtman KB, Piccirillo JF (1996) The efficacy of surgical modifications of the upper airway in adults with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep 19:156–177
Kamani Y (1994) Outpatient treatment of sleep apnea syndrome with Co2 laser: laser assisted uppp. J Otolaryngol 24:395–398
Walker RP, Garrity T, Gopalasami C (1999) Early polysomnographic findings and long term subjective results in sleep apnea patients treated with LAUP. Laryngoscope 109:1438–1444
Mickelson SA, Ahuja (1999) Short term objective and long term subjective results of LAUP for obstructive sleep apnea. Laryngoscope 109:362–367
Kim ST, Choi JH, Jeon HG, Cha He, Kim DY, Chung Ys (2004) Polysomnographic effects of nasal surgery for snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea. Acta Oto Laryngol 124:297–300
Johnson NT, Chin J (1994) Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty and inferior sagittal mandibular osteotomy with genioglossus advancement for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 105:278
Riley R, Powell N, Guilleminault C (1993) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: a review of 306 consecutively treated surgical patients. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 108:117
Li KK, Riley RW, Powell NB et al (1999) Overview of phase II surgery for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Ear Nose Throat J 78:851–857
Thatcher GW, Maisel RH (2003) The long term evaluation of tracheostoma in the management of obstructive sleep apnoea. Laryngoscope 113:201–204
Campanini A, De Vito A, Frassineti S, Vieini C (2003) Temporary tracheostomy in the surgical treatment of obstructive sleep apoea syndrome: personal experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngological Italic 23:474–478
Engelman Hm, kingshott R, Wraith PK, Mackay TW, Deary IJ, Douglas NJ (1999) Randomized placebo-controlled crossover trial of continuous positive airway pressure for mild sleep apnea/hypoapnea syndrome. Am J Respire Crit Care Med 159:461–467
Ballester E, Badia Jr, Hernandez L, Carrasco E, De Pablo J, Fornas C et al (1999) Evidence of the effectiveness of CPAP in the treatment of sleep apnea/hypoapnea syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:495–501
Lee Nr, Givens CD Jr, Wilson J et al (1999) Staged surgical treatment of obstructive sleep apnea syndromy: a review of 35 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57:382–385
Bettega G, Pepin J, Veale D et al (2000) Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: fifty one consecutive patients treated by maxillofacial surgery. Am J Respire Crit Care Med 162:641–649
Loube DI, Gay PC, Strohl KP et al (1999) Indications for positive airway pressure treatment of adult obstructive sleep apnea patients: a consensus statement. Chest 15(3):863–866
Baltzan Ma, Kassissia I, Elkholi O et al (2006) Prevalence of persistent sleep apnea in patients treated with continuous positive airway pressure. Sleep 29(4):557–563
Patel SR, White DP, Malhotra A et al (2003) Continuous positive airway pressure therapy for treating sleepiness in a diverse population with obstructive sleep apnea: results of a metaanalysis. Arch Intern Med 163(5):565–571
Ramirez SG, Loube Di (1996) Inferior sagittal osteotomy with hyoid bone suspension for obese patients with sleep apnea. Arch Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surg 122:953
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vijaya Krishnan, P., Raghunandhan, S., Anand Kumar, R.S. et al. A Rational Approach to the Management of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 66 (Suppl 1), 138–146 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0381-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-011-0381-9