Abstract
The essential steps implicated in carcinogenesis are acquisition of autonomous proliferative signaling; inhibition of growth inhibitory signals; evasion of apoptosis; immortalization; angiogenesis; tissue invasion and metastasis. A considerable progress in understanding the process of carcinogenesis has further stimulated the high throughput translational methods and systems biology approach to revolutionize this field of cancer biology. The era of molecular targeted therapy has dawned and would soon replace the more ‘toxic’ classical ‘broad-spectrum’ cancer chemotherapy. This review summarises the steps of carcinogenesis and the concepts involved in translational methods, systems-biology and molecular targeted therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hahn WC, Counter CM, Lundberg AS, Beijerbergen RL, Brooks MW, Weinberg RA (1999) Creation of human tumour cells with defined genetic elements. Nature 400:464–468
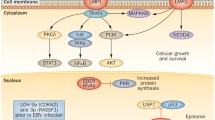
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Sauter ER, Ridge JA, Gordon J et al (1992) p53 overexpression correlates with increased survival in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue base. Am J Surg 164:651–653
Furata Y, Takasu T, Asai T et al (1992) Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor gene in squamous cell carcinomas of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses. Cancer 69:358–362
Maurizi M, Scambia G, Benedetti Panici P Ferrandina G, Almadori G et al (1992) EGF receptor expression in primary laryngeal cancer: Corelation with clinico-pathological features and prognostic significance. Int J Cancer 52:862–866
Grandis JR, Tweardy D (1993) Elevated levels of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor messenger RNA are early markers of carcinogenesis in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 53:3579–3584
Grandis JR, Melhem MF, Gooding WE, Day R, Holst VA, Wagener MM, et al (1998) Levels of TGF-alpha and EGFR protein in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma and patient survival. Journal of National Cancer Institute 90(11):824–832
Dasonville O, Formento JL, Francoual M, Ramaioli A, Santini J, Schneider M et al (1993) Expression of epidermal growth factor receptor survival in upper aerodigestive tract cancer. J Clin Oncol 11:1873–1878
Formento JL, Francoual M, RAmaioli A, Dassonville O, Santini J, Demard F et al (1994) EGF receptor: a prognostic factor in epidermoid cancers of the upper aerodigestive tracts. Bull Cancer 81:610–615
Maxwell SA, Sacks PG, Gutterman JU, Gallick GE (1989) Epidermal growth factor receptor protein-tyrosine kinase activity in human cell lines established from squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck. Cancer Res 49:1130–1137
Pornchai O-charoenrat, Helmount Modjtahedi, Peter Rhysevans, William J Court, Gary M Box, Suzanne A (2000) Eccles epidermal growth factor like ligands differentially up regulate MMP 9 in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 60:1121–1128
Shibata T, Kawano T, Nagayasu H, Okumura K, Arisue M, Hamada J, et al (1996) Enhancing effects of epidermal growth factor on human squamous cell carcinoma motility and matrix degradation but not growth. Tumour biology 17(3):168–175
Kastan MB, Onyekere O, Sidransky D Vogelstein B, Craig RW (1991) Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res 51:6304–6311
Yin Y, Tainsky MA, Bischoff FZ Strong LC, Wahl GM (1992) Wild type p53 restores cell cycle control and inhibits gene amplification in cells with mutant p53 alleles. Cell 170:937–948
Yonish-Rouach E, Resnitzky D, Lotem J Sachs L, Kimchi A, Oren M (1991) Wild type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukemic cells that are inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature 352:345–347
Somers KD, Merrick MA, Lopez ME Incognito LS, Schechter GL, Casey G (1992) Frequent p53 mutations in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 52:5997–6000
Shin DM, Charuruks N, Lippman SM, Lee JJ, Ro JY, Hong WK, et al (2001) p53 protein accumulation and genomic instability in head and neck multistep Tumorigenesis. [Journal Article] Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 10(6):603–609
Syrjanen SM, Syrjanen KJ (1999) New concepts on the role of Human papilloma virus in cell cycle regulation. Annals of Medicine 31(3):175–187
Oliner JD et al (1993) Oncoprotein MDM2 conceals the activation domain of tumour suppressor p53. Nature 362:857–860
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M (1997) Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature 387:296–299
Ganly I, Soutar DS, Brown R, Kaye SB (2000) p53 alterations in recurrent squamous cell cancer of the head and neck refractory to radiotherapy. British J Cancer 82(2):392–398
Serrano M, Hannon GJ, Beach D (1993) A new motif in cell cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature 366:704–707
Reed AL, Califano J, Cairns P, Westra WH, Jones RM, Koch W, et al (1996) high frequency of p16 (CDKN2/MTS-1/ INK4A) inactivation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 56:3630–3633
Papadimitrakopoulou V, Izzo J, Lippman SM, Lee JS, Fan YH, Clayman GL et al (1997) frequent inactivation of p16 (INK4A) in oral premalignant lesions. Oncogene 14:1799–1803
El-Naggar A, lai S, Clayman GL, Zhou JH, Tucker SA, Myers JN (1999) Expression of p16, Rb and cyclin D1gene products in oral and laryngeal squamous carcinoma: biological and clinical implications. Hum Pathol 30:1013–1018
Mao L, Lee JS, Fan YH, Ro JY, Batsakis JG, Lippman SM et al (1996) Frequent microsattelite alterations in chromosomes 9p21 and 3p14 in oral premalignant lesions and their value in cancer risk assessment. Nature 2:682–685
Bartkova J, Lukas J, Muller H Strauss M, Guterson B, Bartek J (1995) Abnormal patterns of D typecyclin expression and G1 regulation in human head and neck cancer. Cancer Res 55:949–956
Bova RJ, Quinn DI, Nankervis JS, Cole IE, Sheridan BF, Jensen MJ et al (1999) Cyclin D1 and p16INK4A expression predict reduced survival in carcinoma of the anterior tongue. Clin Cancer Res 5:2810–2819
Mineta H, Miura K, Takebayashi S, Ueda Y, Misawa K, Harada H, et al (2000) Cyclin D1 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in patients with toungue squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncology 36(2):194–198
Michalides RJ, van Veelen NM, Kristel PM Hart AA, Loftus BM, Hilgers FJ et al (1997) Overexpression of cyclin D1 indicates a poor prognosis in squamous cell carcinoma on the head and neck. Arch otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 123:497–502
Nakashima T, Clayman GL (2000) Antisense inhibition of cyclin D1 in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Archives Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126(8):957–961
Pena JC, Thompson CB, Recant W, Vokes EE, Rudin CM (1999) Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer 85(1):164–170
Gallo O, Chiarelli I, Boddi V, Bocciolini C, Bruschini L, Porfirio B (1999) Cumulative prognostic value of p53 mutations and Bcl-2 protein expression in head and neck cancer treated by radiotherapy. Int J Cancer 84(6):573–579
Baldwin AS (2001) Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor nf-kappa-B. J Clin Investigation 107(3):241–246
Webster G, Perkins N (1999) Transcriptional cross-talk between nf-kappa-B and p53. Mol. Cell Biol 19:3485–3495
Duffey DC, Crowl-Bancroft CV, Chen Z, Ondrey FG, Nejad-Sattari M, Dong G, et al (2000) Inhibition of transcription factor nf-kappa-B by mutant inhibitor-kappa-B-alpha attenuates resistance of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma to TNF-alpha caspase mediated cell death. British J Cancer 83(10):1367–1374
Riedel F, Gotte K, Bergler W, Rojas W, Horman K (2000) Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor protein and its downregulation by interferons in head and neck cancer. Head & Neck, 22:183–189
Bancroft CC, Chen Z, Dong G Sunwoo JB, Yeh N, Park C et al (2001) Co-expression of pro-angiogenic factors IL-8 & VEGF by human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma involves coactivation by MEK-MAPK & IKK-nf-kappa-B signal pathways. Clin Cancer Res 7:435–442
O-charoenrat P, Rhys-Evans P, Eccles SA (2001) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor family members in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma correlates with lymph node metastasis. Cancer 92:556–568
Carter RL, Burman JF, Barr L Gusterson BA (1985) Immunohistochemical localization of basement membrane type IV collagen in invasive and metastatic squamous carcinomas of head and neck. J Pathol 147:159–164
Visser R, Beek JMH, Havenith MG Cleutiens JP, Bosman FT (1986) Immunocytochemical detection of basement membrane antigens in the histopathological evaluation of laryngeal dysplasia and noeplasia. Histopathology 10:171–180
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, A., Pandey, A. & Nong, X. Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer: Biology (II) and Translational Methods. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck S 59, 245–251 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-007-0071-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-007-0071-9