Abstract
Objective
To synthesize the evidence for incidence, pathophysiology, etiology, and protocol-based management of hyperammonemia in lung transplant patients.
Background
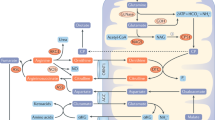
Elevated ammonia levels are toxic to the brain, and hyperammonemia results in a potentially fatal complication for lung transplant recipients. The hallmark of this condition is ammonia production being way out of proportion to the degree of liver derangement. While there are many hypotheses, the cause remains obscure.
Methods
A retrospective review of patients with hyperammonemia following lung transplantation was done to understand the pathophysiology, various treatment modalities, and its impact on patient mortality and morbidity. Studies in the English literature were identified through an electronic database search from PubMed/MEDLINE, Ovid Embase, Google Scholar, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Scopus, Web of Science, and ClinicalTrials.gov until June 2020. No restriction of dates were used, and the search was up until June 2020.
Discussion
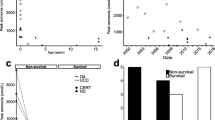
Mortality among patients with hyperammonemia following lung transplantation is high. Multi-modal treatment approaches include avoiding nephrotoxic drugs, use of bowel decontamination, nitrogen scavengers, branched-chain amino acids, adjustment of immunosuppression, antibiotics like fluoroquinolones or azithromycin, and renal replacement therapy. However, there remains a scarcity of preoperative screening protocol for patients at risk of hyperammonemia as well evidence-based post-operative management guidelines. Intermittent hemodialysis, compared to continuous venovenous hemodialysis, provides better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Early detection of patients at risk by appropriate screening, along with maintaining a high degree of suspicion for hyperammonemia and multi-modal treatment approach, is the key to successful patient outcomes. Further prospective observational studies would facilitate development of protocol-based treatment of this potentially fatal condition.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambers DC, Cherikh WS, Harhay MO, et al. The International Thoracic Organ Transplant Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-sixth adult lung and heart–lung transplantation Report—2019; Focus theme: Donor and recipient size match. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2019;38:1042–55.
NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Database. Ammonia, CID=222. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ammonia
Hawkes ND, Thomas GA, Jurewicz A, et al. Non-hepatic hyperammonaemia: an important, potentially reversible cause of encephalopathy. Postgrad Med J. 2001;77:717–22. https://doi.org/10.1136/pmj.77.913.717.
Machado MCC, da Silva FP. Hyperammonemia due to urea cycle disorders: a potentially fatal condition in the intensive care setting. 2014; 2: 22.
Häberle J. Clinical and biochemical aspects of primary and secondary hyperammonemic disorders. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013;536:101–8.
Batshaw ML. Hyperammonemia. Curr Probl Pediatr. 1984;14:1-69.
Group TUCDC. Consensus statement from a conference for the management of patients with urea cycle disorders. J Pediatr. 2001;138:S1–5.
Clay AS, Hainline BE. Hyperammonemia in the ICU. Chest. 2007;132:1368–78.
U-King-Im JM, Yu E, Bartlett E, Soobrah R, Kucharczyk W. Acute hyperammonemic encephalopathy in adults: imaging findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011;32:413–8. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A2290.
Chen C, Bain KB, Iuppa JA, et al. Hyperammonemia syndrome after lung transplantation: a single center experience. Transplantation. 2016;100:678–84.
Lichtenstein GR, Yang YX, Nunes FA, et al. Fatal hyperammonemia after orthotopic lung transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 2000;132:283–7.
Ryder KW, Olson JF, Kahnoski RJ, Karn RC, Oei TO. Hyperammonemia after transurethral resection of the prostate: a report of 2 cases. J Urol. 1984;132:995–7.
Hoekstra PT, Kahnoski R, McCamish MA, Bergen W, Heetderks DR. Transurethral prostatic resection syndrome—a new perspective: encephalopathy with associated hyperammonemia. J Urol. 1983;130:704–7.
Frere P, Canivet JL, Gennigens C, Rebeix JP, Fillet G, Beguin Y. Hyperammonemia after high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;26:343–5.
Liu B, Yu M, Song Y-x, et al. Surgery for gastric cancer in a patient with non-cirrhotic hyperammonemia: a case report. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:1–4.
Chiu CG, Zaghiyan KN, Silberman AW. Hyperammonemic encephalopathy associated with GI stromal tumor. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:e51-3. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.48.9302
Yoshida E, Ostrow D, Erb S, Fradet G. Hyperammonemia after heart-lung transplantation. Gastroenterology (New York, NY. 1943) 1997; 112.
Hocker S, Rabinstein AA, Wijdicks EFM. Pearls & oy-sters: status epilepticus from hyperammonemia after lung transplant. Neurology. 2011;77:e54–6.
Lichtenstein GR, Kaiser LR, Tuchman M, et al. Fatal hyperammonemia following orthotopic lung transplantation. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:236–40.
Richeldi L, Kolb M, Azuma A, et al. FVC decline over 1 year predicts mortality but not subsequent FVC decline in patients with IPF. Eur Respir J. 2017;50: PA 4892.
Nagarur A, Fenves AZ. Late presentation of fatal hyperammonemic encephalopathy after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. In Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings. Taylor & Francis 2017; 41–43.
Anwar S, Gupta D, Ashraf MA, et al. Symptomatic hyperammonemia after lung transplantation: lessons learnt. Hemodial Int. 2014;18:185–91.
Berry GT, Bridges ND, Nathanson KL, et al. Successful use of alternate waste nitrogen agents and hemodialysis in a patient with hyperammonemic coma after heart-lung transplantation. Arch Neurol. 1999;56:481–4.
Tuchman M, Lichtenstein GR, Rajagopal BS, et al. Hepatic glutamine synthetase deficiency in fatal hyperammonemia after lung transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 1997;127:446–9. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-127-6-199709150-00005.
Trivedi M, Zafar S, Spalding MJ, Jonnalagadda S. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency unmasked because of gastrointestinal bleeding. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2001;32:340–3. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004836-200104000-00013.
Bharat A, Cunningham SA, Budinger GS, et al. Disseminated ureaplasma infection as a cause of fatal hyperammonemia in humans. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7:284re283-284re283.
Smith DG, Russell WC, Ingledew WJ, Thirkell D. Hydrolysis of urea by Ureaplasma urealyticum generates a transmembrane potential with resultant ATP synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:3253–8. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.175.11.3253-3258.1993.
Fernandez R, Chi M, Ison MG, et al. Sequelae of donor-derived mollicutes transmission in lung recipients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195:687–9.
Hopkins PM, Winlaw DS, Chhajed PN, et al. Mycoplasma hominis infection in heart and lung transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2002;21:1225–9.
Spiller OB. Emerging pathogenic respiratory Mycoplasma hominis infections in lung transplant patients: time to reassesses it’s role as a pathogen? EBioMedicine. 2017;19:8–9.
Wylam ME, Kennedy CC, Hernandez NM, et al. Fatal hyperammonaemia caused by Mycoplasma hominis. Lancet. 2013;382:1956. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62115-7.
Palmer SM, Alexander BD, Sanders LL, et al. Significance of blood stream infection after lung transplantation: analysis in 176 consecutive patients. Transplantation. 2000;69:2360–6.
De Santo LS, Romano G, Amarelli C, et al. Implications of acute kidney injury after heart transplantation: what a surgeon should know. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011;40:1355–61.
Krishnappa V, Gupta M, Manu G, Kwatra S, Owusu O-T, Raina R. Acute kidney injury in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a review. Int J Nephrol 2016;2016:5163789. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5163789.
Fidalgo P, Ahmed M, Meyer SR, et al. Incidence and outcomes of acute kidney injury following orthotopic lung transplantation: a population-based cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2014;29:1702–9.
Devasahayam JVM, John SG, Assar S, et al. Hyperammonemia as an adverse effect in parenteral nutrition. In Rajendram R, Preedy VR, Patel VB (eds): Diet and Nutrition in Critical Care. New York, NY: Springer New York 2014; 1–15.
Shigemura N, Sclabassi RJ, Bhama JK, et al. Early major neurologic complications after lung transplantation: incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Transplantation. 2013;95:866–71.
Krutsinger D, Pezzulo A, Blevins AE, Reed RM, Voigt MD, Eberlein M. Idiopathic hyperammonemia after solid organ transplantation: primarily a lung problem? A single-center experience and systematic review. Clin Transplant. 2017;31. https://doi.org/10.1111/ctr.12957.
Fernandez R, Ratliff A, Crabb D, Waites KB, Bharat A. Ureaplasma transmitted from donor lungs is pathogenic after lung transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;103:670–1.
Whitson BA, Hertz MI, Kelly RF, et al. Use of the donor lung after asphyxiation or drowning: effect on lung transplant recipients. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;98:1145–51.
Gammie JS, Cheul Lee J, Pham SM, et al. Cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with early allograft dysfunction but not death after double-lung transplantation. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1998;115:990–7.
Wiesen AR, Byrd JC, Hospenthal DR, et al. Transient abnormalities in serum bilirubin and lactate dehydrogenase levels following red blood cell transfusions in adults. Am J Med. 1998;104:144–7.
O’Dwyer DN, Dickson RP, Moore BB. The lung microbiome, immunity, and the pathogenesis of chronic lung disease. J Immunol. 2016;196:4839–47.
Kiberenge RK, Lam H. Fatal hyperammonemia after repeat renal transplantation. J Clin Anesth. 2015;27:164–7.
MacLellan A, Fam D, Robblee J, Andrade D. A rare cause of a common presentation: hyperammonemic encephalopathy secondary to Mycoplasma hominis pneumonia (P3. 220). In. AAN Enterprises 2016.
Bhatia V, Singh R, Acharya SK. Predictive value of arterial ammonia for complications and outcome in acute liver failure. Gut. 2006;55:98–104.
Batshaw ML. Inherited hyperammonemia: an algorithm for diagnosis. Hepatology. 1987;7:1381–2.
Aguilar C, Gohir W, Tikkanen J, et al. Ureaplasma spp. and Mycoplasma hominis PCR in respiratory samples from lung transplant recipients with hyperammonemia syndrome and cerebral edema. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2018;37:S360.
Gupta S, Fenves AZ, Hootkins R. The role of RRT in hyperammonemic patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11:1872–8.
Madathil RJ, Gilstrap LG, Pelletier MP, Mehra MR. Isolated hyperammonemic encephalopathy in heart transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2018;37:427–9.
Sampath R, Patel R, Cunningham SA, et al. Cardiothoracic transplant recipient Mycoplasma hominis: an uncommon infection with probable donor transmission. EBioMedicine. 2017;19:84–90.
Matson KM, Sonetti DA. Successful treatment of Ureaplasma-induced hyperammonemia syndrome post-lung transplant. Transpl Infect Dis. 2019;21:e13022. https://doi.org/10.1111/tid.13022.
McLaughlin DC, Mallea JM, Ng LK. Hyperammonemia presenting as refractory status epilepticus after lung transplant in a patient positive for Ureaplasma parvum. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2018;22:463–5. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijccm.IJCCM_356_17.
Foschi FG, Morelli MC, Savini S, et al. Urea cycle disorders: a case report of a successful treatment with liver transplant and a literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:4063–8.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Elsevier, the publishers of American Journal of Neuroradiology, for granting us the permission to republish the MRI scan images (Fig. 3) for review purposes.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and informed consent
Ethics approval and informed consent was not required as individual patient data has not been reported in the publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors have nothing to disclose with respect to the present submission.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A., Advani, S., Asim, K. et al. Hyperammonemia in lung transplant patients and its management: a review. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 38 (Suppl 2), 335–346 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-021-01319-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12055-021-01319-6